Guide to speeding up the context menu on Windows
Windows context menus often become sluggish over time, causing frustration and reducing productivity. With just a few system settings, you can improve the speed of the context menu. Below are some settings to speed up the Windows context menu.
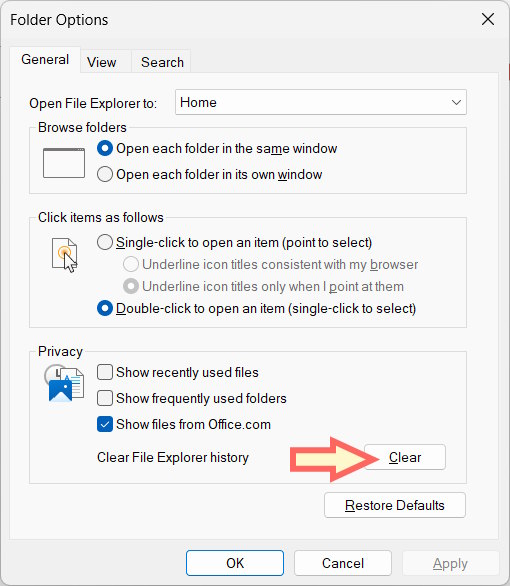
Delete File Explorer history
If your File Explorer history is too large, it can cause the context menu to slow down. In the File Explorer interface, click the three-dot icon, then select General, and then click the Clear button under Clear File Explorer history .
Remove unnecessary context menu items.
Many third-party applications add their functional items to the context menu for quick access. If you have many such items or an application malfunctions, it can slow down the context menu.
Turn off visual effects for the context menu.
If you don't like the slow opening/closing effect of the context menu in Windows 11, you should turn it off.
Type "adjust performance" into the search bar and then click on "Adjust the appearance and performance of Windows" to access it.
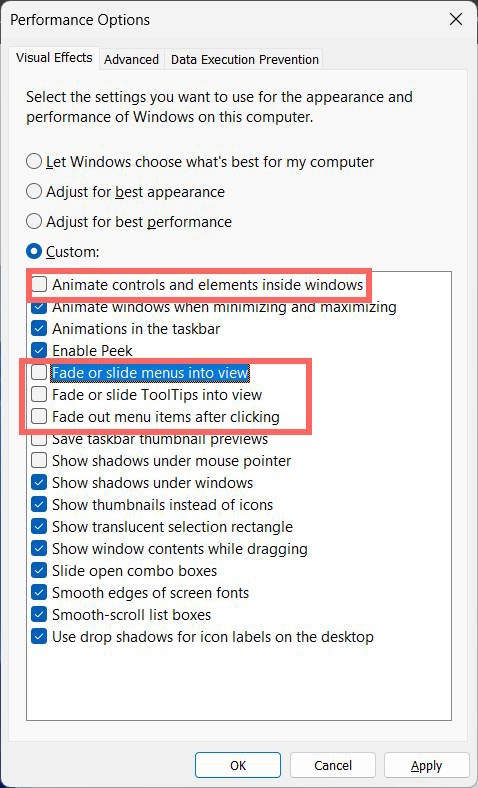
In the new interface, uncheck the settings below .
- Fade or slide menus into view
- Fade or slide ToolTips into view
- Fade out menu items after clicking
- Animate controls and elements inside windows
Use the classic context menu.
The new context menu in Windows 11 looks more visually appealing than the context menu in Windows 10. However, it is also slower than the classic context menu.
- How to restore the old context menu in Windows 11
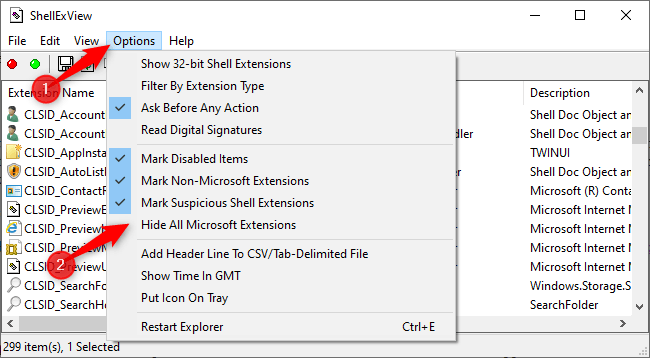
Use ShellExView to remove other application options.
You download and launch ShellExView to get started.
You'll see a long list of Windows shell extensions. However, many of them are created by Microsoft and come with Windows. Those won't slow down your system. To hide all Microsoft extensions, click Options > Hide All Microsoft Extensions .
First, select the extensions you want to disable. You can click on each one individually to select them, press Ctrl+ A, or click Edit > Select All to select all, press and hold the key Shiftwhile clicking to select a range, or press and hold the key Ctrlwhile clicking to select multiple extensions.
To disable one or more selected shell extensions, right-click them and select Disable Selected Items , or click File > Disable Selected Items . (To re-enable them, select Enable Selected Items here.)
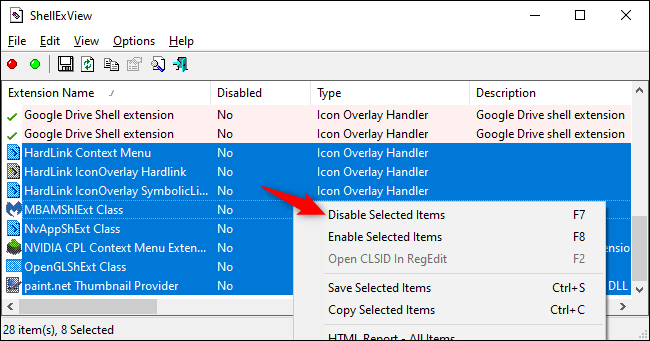
A disabled shell extension will display "Yes" in the Disabled column.
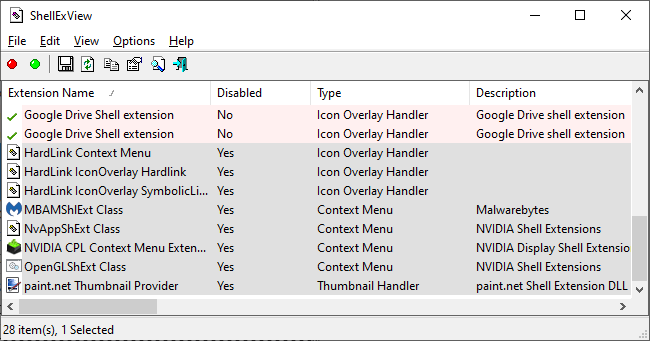
The changes won't take effect until you restart Windows Explorer. You'll see an option for this in the ShellExView Options menu , but you shouldn't do it. It causes Explorer and the Windows taskbar to keep loading until you log out.
Instead, you should use Task Manager . To open Task Manager , press Ctrl+ Shiftor Escright-click on the taskbar and select Task Manager.
Click on Windows Explorer in Apps on the Processes tab . (If you don't see this tab, click on More Details .) Then, click the Restart button in the lower right corner of the Task Manager window .
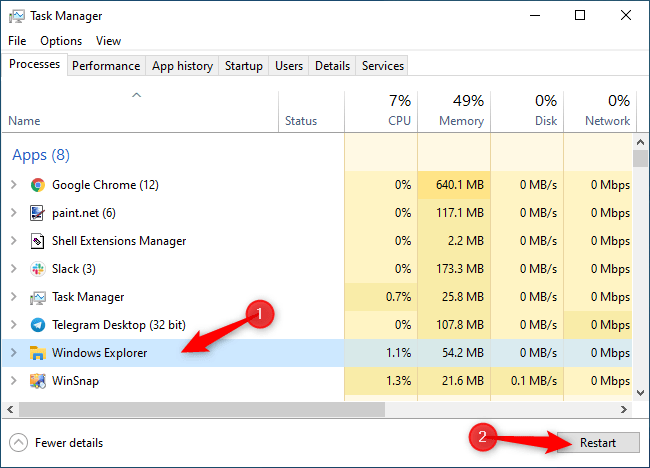
Explorer will restart. Now, try right-clicking on your folder, file, or desktop—anything that was slow before. If it's still slow, you need to try disabling other shell extensions. If it's faster than before, it means you've disabled a shell extension that was slowing it down.
You should read it
- ★ Microsoft is committed to improving the context menu experience on Windows 11
- ★ How to add items to the 'Create New' context menu in Windows 10
- ★ How to delete options in the Windows context menu
- ★ How to restore the old context menu in Windows 11
- ★ How to bring Windows 10's right-click menu to Windows 11