How to fix Winget not recognized error on Windows
Windows users often use WinGet to install and manage applications through PowerShell , Command Prompt, and any other interpreter. Sometimes, when running the WinGet command, you may encounter an error stating that the command is not recognized as a valid cmdlet, function, or script file. Today's tutorial shows you how to fix this annoying error and get WinGet working again.
1. Re-register or repair WinGet
One of the biggest causes of this WinGet error is a corrupted or misconfigured Windows Package Manager installation. If this is the case, you can easily fix it by re-registering WinGet, which will reset the installation and potentially fix any issues that may be occurring.
Type PowerShell in the search box and click Run as Administrator . When the command prompt opens, copy and paste the following command into PowerShell:
Add-AppxPackage -RegisterByFamilyName -MainPackage Microsoft.DesktopAppInstaller_8wekyb3d8bbwe 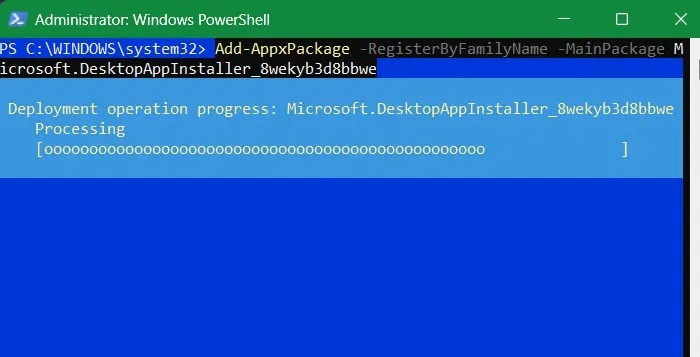
The above command tells Windows to re-register the App Installer from its official Microsoft source, which will then restore WinGet functionality.
Instead of completely reinstalling, you can repair the existing WinGet package with the following command.
Add-AppxPackage -RegisterByFamilyName -MainPackage Microsoft.DesktopAppInstaller_8wekyb3d8bbwe 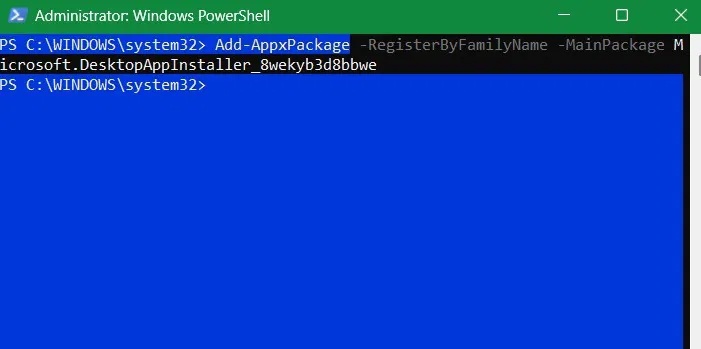
When executed correctly, Windows will quickly re-register the WinGet application and fix Windows Package Installer issues like broken shortcuts, missing dependencies or any corrupted registry entries.
2. Enable App execution aliases for Windows Package Manager
In a command-line context, the name WinGet is the application executable alias name for Windows Package Manager.
Application execution aliases are essentially shorthand or abbreviated CLI commands. If you disable this feature for Windows Package Manager, the CLI may not recognize WinGet. This can also happen due to third-party cleanup tools or system optimizers.
To enable app execution aliases for Windows Package Manager, press Win + I to open the Settings app , go to Apps -> Advanced app settings and click App execution aliases .
If the toggle for Windows Package Manager Client is Off , switch it back to On .
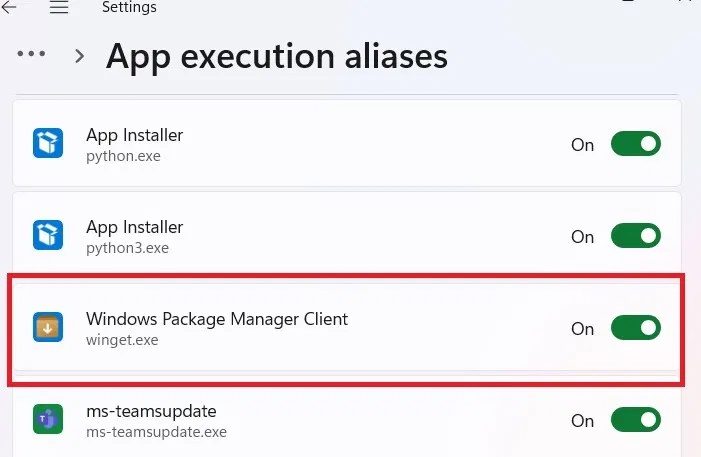
Windows 10 users can find the toggle for Windows Package Manager Client by going to Settings -> Apps -> Apps & Features and clicking the App execution aliases link .
3. Verify that you have the latest version of App Installer
WinGet is part of App Installer, a pre-installed Windows package that allows users to easily install and manage programs. If App Installer is malfunctioning, it can lead to WinGet errors. To fix App Installer, update from the Microsoft Store.
Go to the official App Installer download link and click the big blue Download button. It will search your PC location to download the MSIXBUNDLE file.
Now you will see a message that App Installer has been installed. You can click Reinstall , this will fix any missing dependencies.
Otherwise, you'll see the option to update through the Microsoft Store.
4. Reinstall App Installer from GitHub
If updating the App Installer doesn't work, perhaps a reinstallation can help fix whatever is causing Winget to malfunction. To do so, follow the steps below:
Visit the Windows Package Manager GitHub page .
Scroll down to the Assets section and click on the Desktop App Installer MSIXBundle file to download.
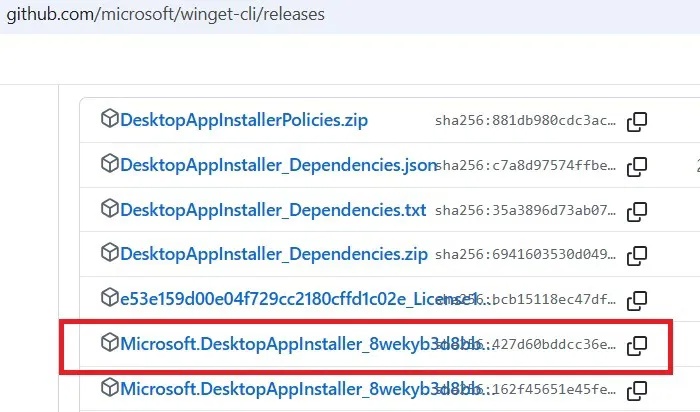
Double-click on the file you just downloaded and click Reinstall in the pop-up window.
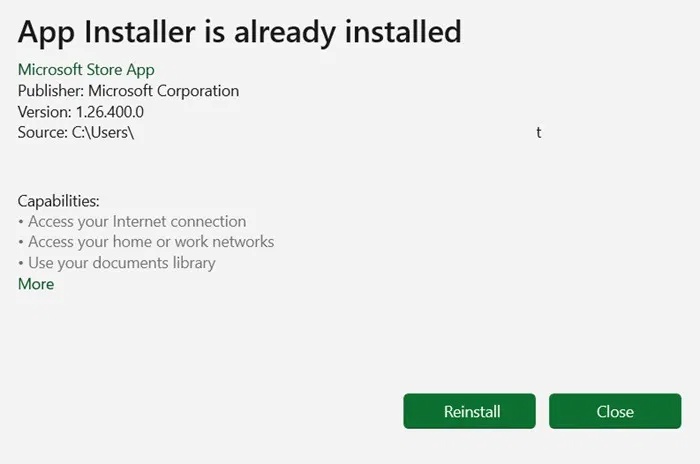
Follow the remaining instructions to complete reinstalling the App Installer.
5. Create Path environment variable for Winget
When you run a WinGet command in Command Prompt or PowerShell, Windows searches the PATH variable to find the executable file. In short, this variable maintains a list of directories that contain executable files for various Windows commands. If PATH doesn't list a directory that contains WinGet executable files, you'll get an error.
To fix this error, you will have to manually add the missing directory to the PATH variable:
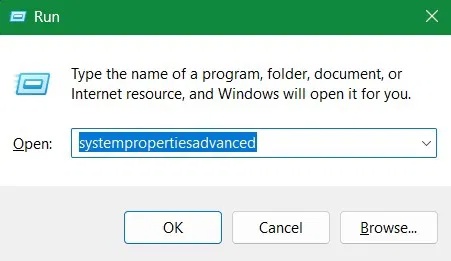
Press Win + R to open Windows Run , type systempropertiesadvanced into the text box and click OK . This will launch the System Properties window .
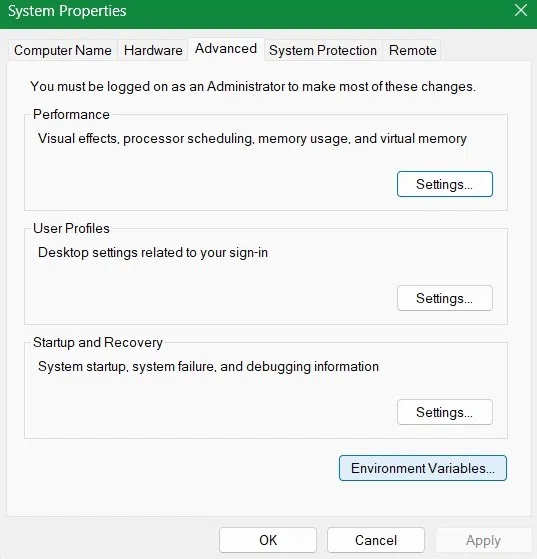
Select the Advanced tab , then click Environment Variables.
Select the Path variable , then click Edit to open the Edit environment variable window .
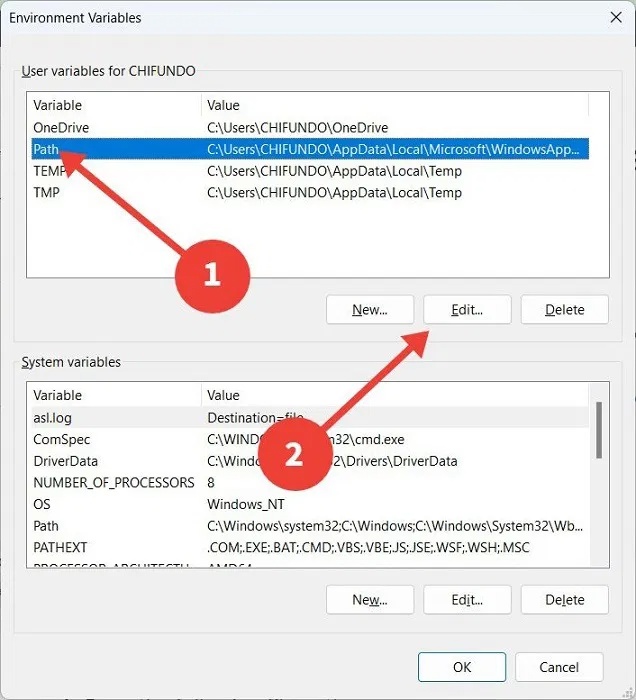
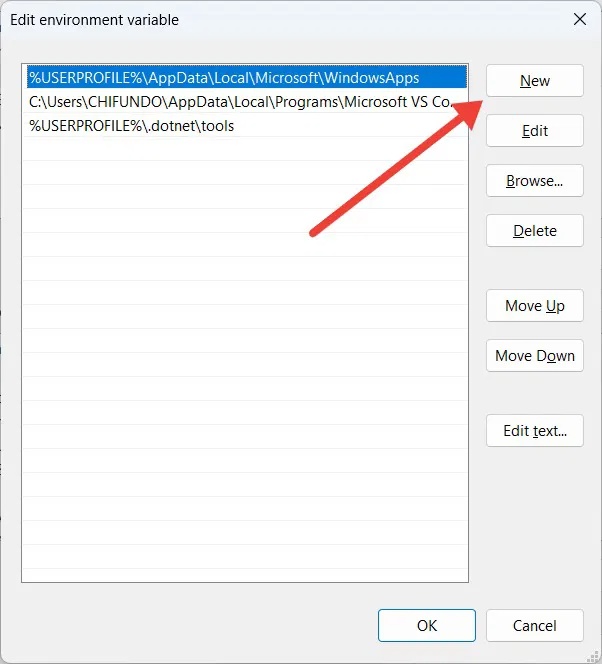
Copy the following file path: %UserProfileAppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsApps.
In the Edit environment variable window , click New. There, you should paste the file path you copied above, then click OK to save the changes.
6. Enable App Package Deployment setting in Local Group Policy Editor
On Windows Pro/Enterprise devices, open Group Policy by typing gpedit.msc into Run.
Navigate to the following path: Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> App Package Deployment .
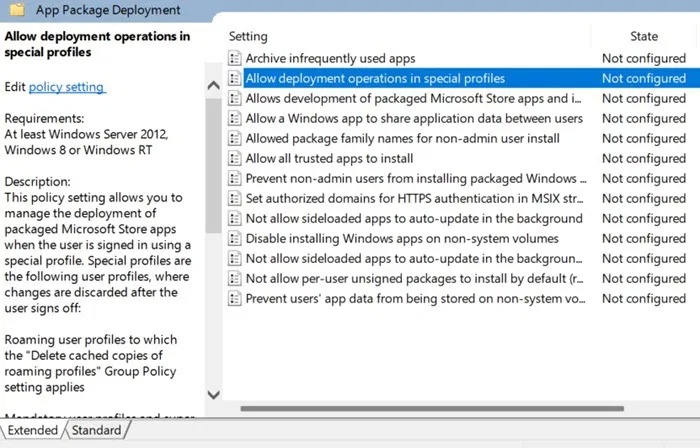
Here you will see a Not configured status for most of the components. The ones we need to focus on in particular are "Allow deployment operations in special profiles" and "Allow all Trusted apps to install" . Double click on these entities and in the next pop-up screen, just click Enabled , followed by OK .
7. Fix App Installer cache using various methods
You can fix the cache of many different services. Open Control Panel and go to Programs -> Programs and Features . Find App Installer in the list.
If you find the program listed, right-click and select Repair (or Uninstall , then reinstall from GitHub as described earlier.
Alternatively, you can open Run and type wsreset.exe . This will clear the Microsoft Store cache, allowing you to run WinGet commands smoothly.
8. Reset Windows PC to factory settings
If all else fails, there may be a more serious bug or misconfiguration with your operating system. If you're not sure what to do, resetting Windows to factory settings will help you start over with settings and configurations that may be affecting Winget. But before resetting your PC , make sure you have backed up your important data, as it will be lost in the process.
Make Winget work again on PC
If you like to set things up in Command Prompt or PowerShell, Winget is an essential utility. When command line tools on your PC fail to recognize it, it can slow down Windows performance. By following the troubleshooting steps above, you can get it working again.
If you are looking for an alternative to Winget, try using Chocolatey to install various applications on your Windows PC.
You should read it
- ★ Summary of some ways to fix USB Device Not Recognized on Windows 7, 8 and 10
- ★ 6 ways to fix the error of not recognizing SSD drive in Windows 10
- ★ 10 common ways to fix USB Device Not Recognized errors
- ★ How to fix USB device not recognized error on Windows
- ★ Details on how to effectively fix USB Device Not Recognized Windows 11 error