How to Get Full Root Privileges in Linux
Get root access with terminal
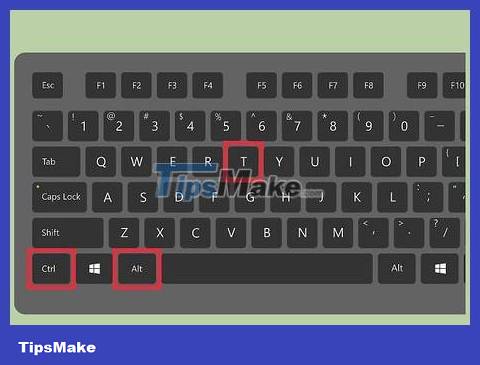
Open the terminal command line interface program. If the terminal is not already on, open it. Many Linux versions allow opening the terminal by pressing the key combination Ctrl+ Alt+ T.
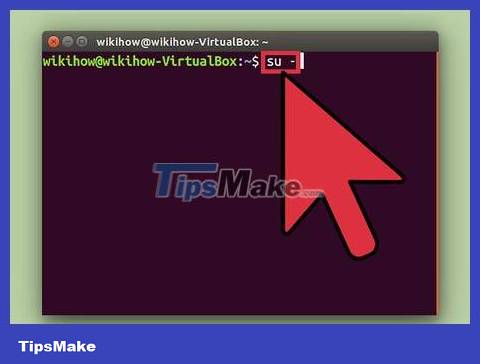
Type . su - and press ↵ Enter. You will be logged in as a "super user". Actually, you can use this command to log in to the computer like a normal user. However, when left blank, it will let you log in with priority.
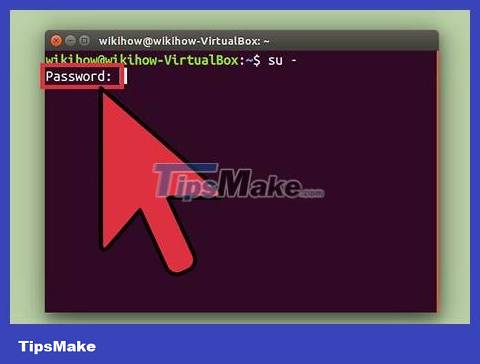
Enter your preferred account password when prompted. After typing su -and pressing ↵ Enter, you will be asked to enter your priority access account password.
If you receive an "authentication error" message, it's likely that your root account has been locked. Read the next section to learn how to unlock it.

Test the command line interpreter. When logging in with privileged privileges, the command line interpreter will end #with $.

Enter commands that require priority access. Once used su -to log in with privileged access, you can run any command that requires privileged access. The command suis maintained until the session ends, so you don't need to re-enter the privilege password every time you need to run the command.
Consider using . sudo instead of su -. sudo("super user do" - super user do) is a command that allows you to run other commands with temporary priority. This is the best way to run commands that require root access for most users, because at this point, you do not need a privileged access environment and the user does not need to know the password for that account. Users will enter their regular login password to gain temporary root access.
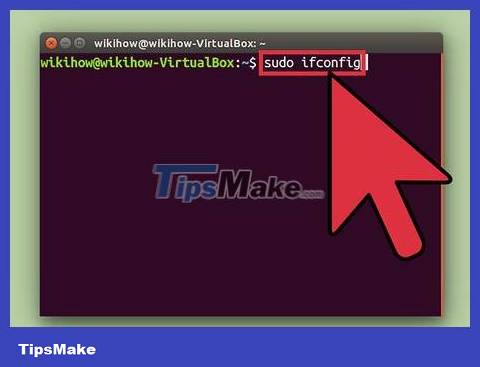
Type and tap (such as ). When prompted, type your user password , not your preferred account password.sudo command↵ Entersudo ifconfig
sudois the preferred method for versions like Ubuntu: it works even when the root account is locked.
This command is only for users with administrative rights. Users can be added or removed/etc/sudoers.
Unlock root account (Ubuntu)
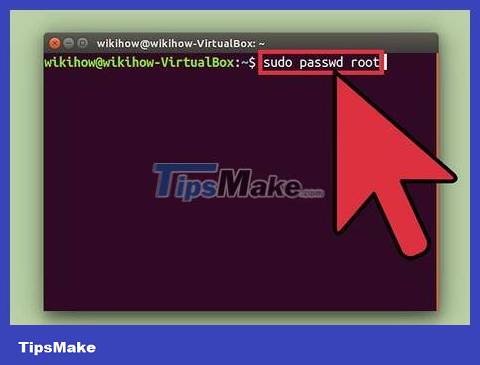
Unlock root account (Ubuntu). Ubuntu (and some other versions) locks the root account to prevent normal users from accessing it. This is because when using commands sudo(see above), we rarely need privileged access. Unlocking the root account will allow you to log in with full privileges.

Open terminal. If you are working in a desktop environment, you can press Ctrl+ Alt+ Tto run the terminal.

Type . sudo passwd root and press ↵ Enter. When asked, enter your user password.
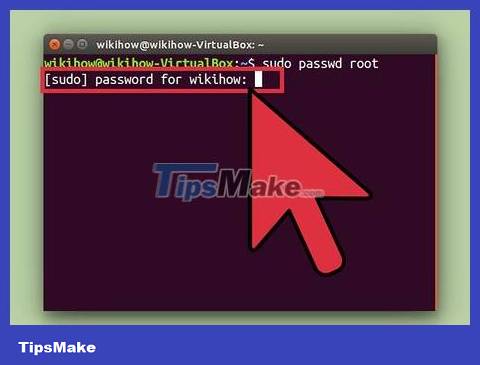
Set a new password. You will be asked to create and enter a new password twice. Once set, the root account will be active.

Lock the root account again. If you want to lock the root account, enter the following command to remove the password and lock the account:
sudo passwd -dl root
Log in with full control

Consider using other methods to gain temporary root access. Logging in with full control should be limited to normal use because doing so makes it easy to execute commands that could cause the system to become inoperable. At the same time, it also contains security risks, especially when the SSH server is running on the computer. Only log in with full access when urgent repairs are needed, such as troubleshooting drive errors or recovering a locked account.
Using sudoor suinstead of logging in with full access will help prevent unwanted compromises during login. These commands give the user the opportunity to consider the command before serious harm occurs.
Some versions, such as Ubuntu, lock the root account until you manually open it. This not only prevents users from accidentally causing too much damage using the root account, but also protects the system from hackers: the root account is often their first target. Once locked, hackers will not be able to gain access with the root account. You can refer to the instructions for unlocking the root account on Ubuntu in the previous section.

Import . root in the user field when logging into Linux. If the root account is not locked and if you know the password, you can log in with root access when asked to log in normally. Enter rootin the user field when asked to log in.
If you need root access to operate a command, use the method above.
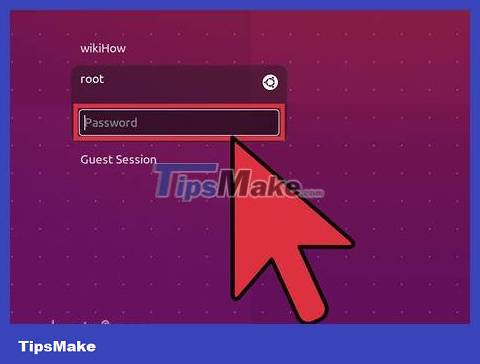
Enter the root password in the user password field. After entering rootthe username field, enter the root password when prompted.
In many cases, the root password can be just "password".
If you don't know or forget the root password, see the password reset instructions below.
In Ubuntu, the root account is locked and cannot be used until it is unlocked.

Avoid running complex programs while logged in as root. It is possible that by gaining root access, the program you intend to run will have a negative impact on the system. Instead of logging in with the root account, sudoit suis recommended to run the program.
Reset root password and admin password

Reset root account password when forgotten. If you forget your root account password and user password, you'll need to boot your computer into recovery mode to change these passwords. If you know the user password and need to change the root account password, just type sudo passwd root, enter the user password and create a new root password.
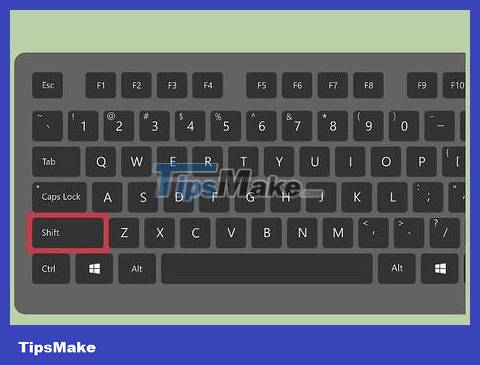
Restart the computer and hold down the - key. ⇧ Shift left when the BIOS screen appears. The GRUB menu will open.
Pressing and holding the key at the right time is quite difficult, so you may have to try many times.

Select item.(recovery mode) - recovery mode - first in the list. Recovery mode for your current operating system version will be downloaded.

Select options.root. root from the menu that appears. The command line interface, in which you are logged in as root, will be launched.
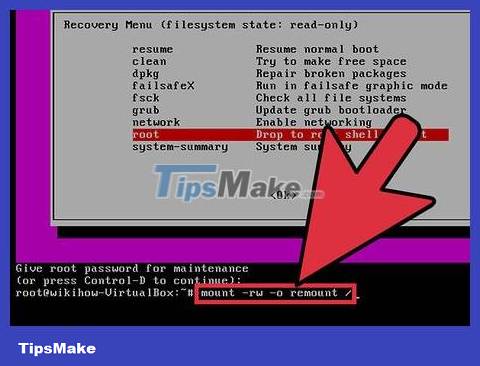
Connect the drive with write access. When booting in recovery mode, you usually only have read permissions. Enter the following command to enable write access:
mount -rw -o remount /

Create new passwords for any locked accounts. When you log in as root and change access permissions, you can create new passwords for every account:
Type and press . If you want to change the root account password, type .passwd accountName↵ Enterpasswd root
Enter the new password twice when requested.

Restart the computer after resetting the password. Once you've reset your password, you can restart your computer as usual. The new password will take effect immediately.