6 Linux permission commands every admin needs to know
Once you understand how Linux handles files—who can read, write, or execute—you'll be a true Linux administrator. There are a number of Linux terminal permission commands you'll need to master, and here are the top terminal commands you should memorize.
chmod
Control who can read, write, or execute files
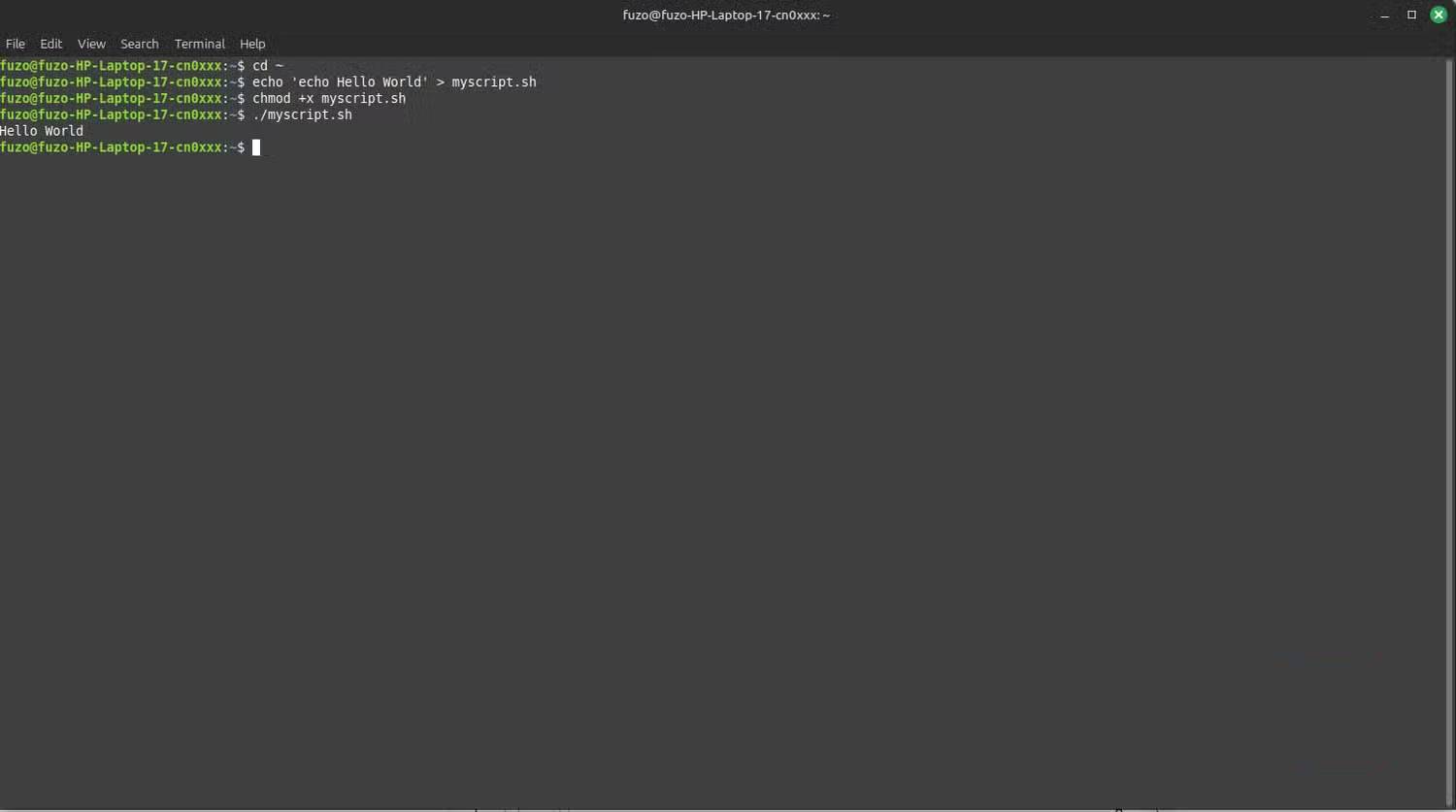
Once you know why a script isn't running, start using the "chmod" command more often. All Linux files have read (r), write (w), and execute (x) permissions. If you run chmod +x followed by the script name, the file will be executed as a program.
chmod also allows you to change permissions numerically. The command chmod 755 filename gives the owner full access (rwx) and everyone else read and execute (rx). After you encounter your first "Permission denied" message, running this command can become a habit.
chown
Take ownership of files as administrator
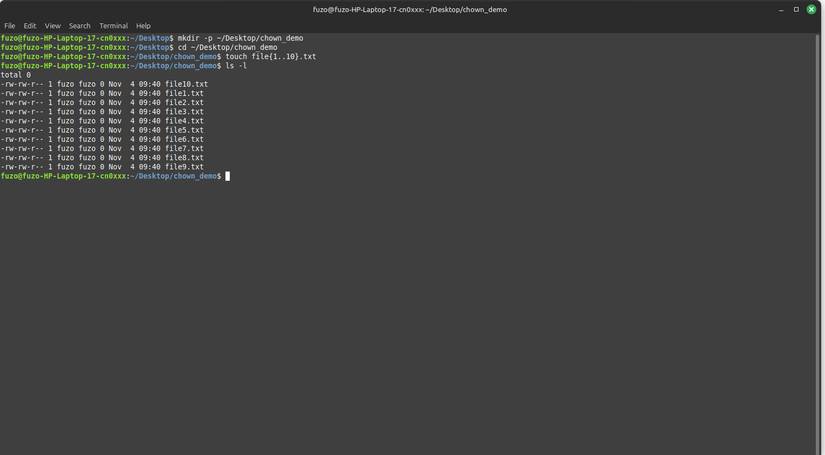
"chown" is a lifesaver when you're copying files between drives and can't access them afterwards. It directly affects permissions by changing the ownership of a file or directory. The basic format is: sudo chown user:group filename .
You will need this command after moving important system data or restoring a backup. For example, if you need the web server (Apache) to read a directory, use the command sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /path/to/project , where www-data is the username and group specific to the Apache web server.
umask
Set default permissions for new files
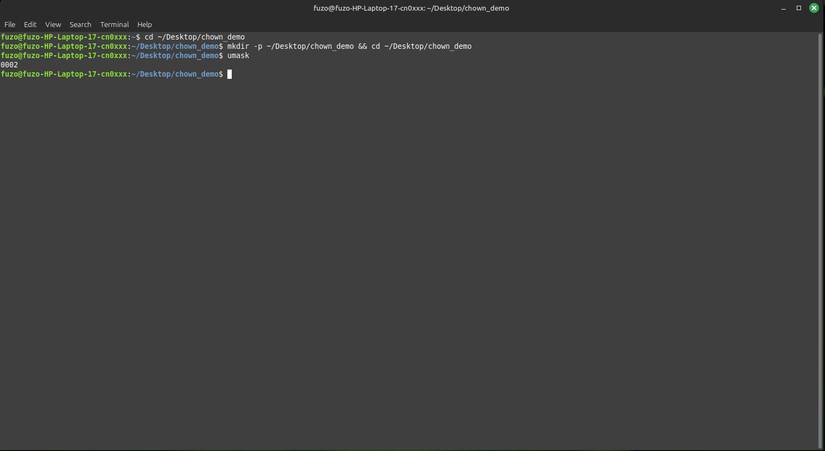
On Linux, umask determines how new files and directories inherit permissions. Linux uses your current umask value to determine which permissions to mask (remove) from the base permissions. The umask command allows you to view or change this setting for the current session.
The common default value of umask is 0022 , and it removes write permissions from "group" and "other users". You can type umask to see your current value, and a command like umask 0027 will change it for the current session. This setting makes new files more secure, often blocking access from other users or anyone outside your group.
sudoers
Grant or restrict security admin rights
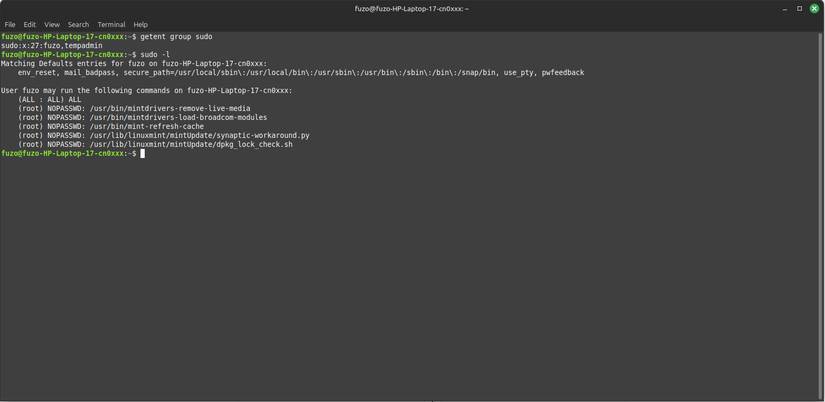
Many people might think that you only become a real Linux administrator after successfully editing the sudoers file. The /etc/sudoers file determines who has sudo privileges and what commands they can run. As a rule, always edit this file with sudo visudo to avoid syntax errors that can get you locked out.
On Linux Mint , if you need to give admin privileges to another user, use the command sudo usermod -aG sudo username . This is much cleaner and safer than editing the file manually, although you may need specific command permissions for advanced settings.
groups
See which access group you belong to
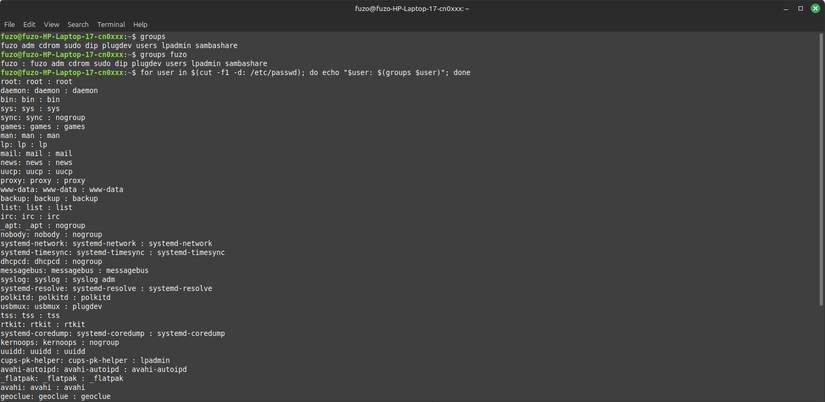
Groups on Linux determine what you can access and tell you which group you belong to in the hierarchy. For example, if you run the command groups afam , it might return afam sudo adm lp , showing you are an admin user with access to the printer.
Running sudo usermod -aG project afam can make a big difference if you're new to a project. It allows you to run scripts and edit files with teammates without having to sudo for every command.
id
Identify yourself with the system
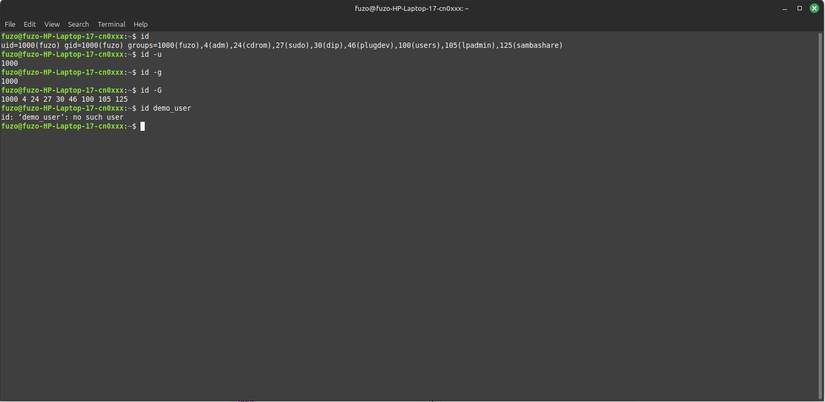
The id command tells you who you are to the system, which is necessary before you can fix permissions. Simply running the id command will show you your user ID (UID), group ID (GID), and a list of all the groups you belong to. While this command doesn't directly label your user type, the UID can infer which of the four main Linux user types you are.
Rely on this command when debugging access issues. So if a certain share fails to open, you can use the id to see if your user matches the owner or group, confirming whether the "permission denied" issue is due to identity or permissions.