Basic Linux commands everyone needs to know
Just like the Windows operating system, when using Linux, you should also learn basic Linux commands to make operations quicker and easier. Here are some basic commands on Linux you should know.
With some of the commands below, you will see commands with simple explanations, specific examples to help you or the Linux users you are supporting using this operating system in general and the command line above. Linux in particular is more effective.
Basic Linux commands
- 1. Some important notes about Linux Terminal
- 2. Get familiar with the account
- 3. Create a new folder
- 4. Search for the current directory
- 5. Create and edit files
- 6. Read some files
- 7. Copy or move the file
- 8. Delete files and folders
- 9. Find the file
- 10. List of directory contents
- 11. Search for previous Linux commands
- 12. Invisible password
- 13. Copy and paste the Linux command
- 14. Display progress in Linux system
- 15. Check Socket information and TCP / UDP network information
- 16. Track Average CPU Load and Disk Activity
- 17. Check the Memory Map of processes in Linux
- 18. Check the operating time of the system
- 19. Check user login
- 20. Control system behavior, hardware and system information in Linux
- 21. Check hardware information of Linux system
- 22. The commands to process files on Linux
- 23. Network commands on Linux
- 24. Start, stop and list services
- 25. Determine the operating system version
- 26. Measure system performance
- 27. Manage users and groups
- 28. Set up and run scheduled processes
- 29. Update, install and list applications
- 30. Turn off and restart
- 31. Linux security command
- sudo
- visudo
- who and w
- last
- t?m
- file
- which
- ss
- ufw
- iptables
- ip
- ip route
- kill, pkill and killall
- passwd
- pwck
- setfacl and getfacl
- sestatus & apparmor
1. Some important notes about Linux Terminal
To quickly open the Terminal from the GUI, press Ctrl + Alt + T.
Split most Linux commands:
[sudo] command [optional switch] [t?p tin hay th? m?c]
Using sudo will run any command under Admin. Most Linux commands used to install / remove system files are a program, used to request sudo.
2. Get familiar with the account
These commands will help Linux users get used to their Linux accounts.
Command FunctionExample shows the current location in the file system. pwd whoami Display usernames - most useful if users switch with su command and need to be reminded about which account is using whoami ls Provide a file list. With the -a parameter , the command displays the files whose name starts with a dot (eg .bashrc). With the -l parameter , the command displays the right, the file size and the latest update date / time. lsls -a
ls -l env Displays user environment settings (eg search path, saved history size, main directory, etc.) env echo Repeat the text that the user provides or display the value of some variables. echo hello
echo $ PATH history Lists the commands given earlier. history
history | tail -5 passwd Change password. Note that complex requirements can be enforced. passwd
history | tail -5
3. Create a new folder
mkdir is the basic directory manipulation command on Linux, which helps you create a new directory quickly. Syntax syntax:
mkdir folder
Note:
Folder is the name of the folder you want to create. For example, if you want to create a folder called backup, the syntax is:
mkdir / home / marin / backup
In case if you want to create a folder containing many subdirectories, you can use the "-p" option . Suppose, you have the foo folder and have access to it:
mkdir -p / foo / bar / baz
The above command will create a bar, baz folder located in the bar; bar and baz located in / foo already.
4. Search for the current directory
If you want to search your current directory, you can use the pwd command .
Eg:
marin @ [LinuxVeda]: [~ / work] $ pwd
/ home / marin / work
5. Create and edit files
Linux systems provide commands to create files. Users can select the desired text editor. Some commands require users to be proficient before using, while others are quite simple.
Command Function An example editor An easy-to-use text editor that requires users to navigate through the file with the arrow keys and provide control sequences to locate text, save changes, etc. micro myfile micro more sophisticated editing, allowing users to enter commands to find and change text, make overall changes, etc. vi myfile ex A text editor designed for programmers and both visual mode and command line. ex myfile touch Create a file if it does not already exist or update the timestamp if it has been created. touch newfiletouch updatedfile> Create file by directing the output to them. > create a file while >> binds an existing file. cal> calendar
ps> myprocs
date >> date.log
6. Read some files
Usually you have to consider the content of many different files. Regularly reviewing different files is often quite complicated and time-consuming. So the simplest way to read their contents is to use the cat command. Command syntax is quite simple:
Cat FILE
Just change FILE with the file name you want to read. As a result, you will see the contents of the file appear at the end of the Terminal.
Eg:
cat script.sh

Alternatively, you can use the cat command for multiple files at once:
cat FILE-1 FILE-2
The output of the command will display the contents of the files in the order of the contents of FILE - 1 and the content of FILE -2.
In addition, Linux provides several commands to review the content and nature of files. Here are some of the most useful commands.
Function FunctionExperts Displays the entire contents of a text file. cat .bashrc more Displays the contents of a text file. Press the spacebar to move to each additional segment. more .bash_history less Displays the contents of the text file, but allows you to go back using the up arrow key. less .bash_history file Specifies files by type (eg ASCII text, executable file, image, directory) myfile file~ / .bashrc file
file / bin / echo
7. Copy or move the file
Copying or moving files in Linux terminal is quite simple and easy.
- To copy a file, you can use the: cp command .
- To move a file you use the command: mvoflder.
Both use commands are quite simple. With cp command. To copy a file, enter the file name and enter a new copy file name. For example:
cp file1 file2
On the above command copy file1 and create file2 containing file1 contents. You can use cp to copy the directory. It is important to note that when you want to copy a directory you should use the -r option.
In other words, cp -r will copy the contents of a certain directory (and subdirectories) to the directory of your choice. Alternatively you can use cp with the full path:
cp -r / home / marin / work / / home / marin / backup
The above command will copy the content of the "work" folder to the new folder named "backup".
If you want to copy all the files and folders of a folder to another folder, you can use the "*" character . Characters are used to find appropriate ports (in this case files and folders). For example:
cp / home / marin / work / * / home / marin / backup /
Next is the mv command . Syntax syntax:
mv file1 file2
The above command changes first file1 to file2. The same goes for directories. However, if you specify a file and a folder, the file will be moved into the directory. Such as:
mv / home / marin / file1 / home / marin / work /
In the above command will move file1 from '/ home / marin /' to '/ home / marin / work /'. If you want to move all the files in one folder to another folder, you can use the "*" character :
mv / home / marin / work / * / home / marin / backup /
8. Delete files and folders
If you want to delete a folder or a file you can use the rm command. It is important to note that when using this command to delete a file or directory, these files cannot be restored. To delete a file you do:
rm /home/marin/useless-file.txt
You can use rm with many different options. Some important options like:
- -f: force to delete files with reminder notifications
- -i: prompt before deleting
- -r: delete recursive directories
- -d: delete empty directories
- -v: explain what the mission is doing
9. Find the file
There are two commands that can help users find files on Linux, but they work very differently. A command searches the file system, while the other considers the database that was built earlier.
OrderFunction
Example set Locate files based on the criteria provided (name, type, owner, permissions, file size, etc.). Unless provided a location to start the search, otherwise this command will only search in the current directory. t?m. -name myfilefind / tmp -type d locate Locate files using the contents of /var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db updated with the updateb command running through cron. No start position required. locate somefile
locate "* .html" -n 20
Note: The find command details are in the section below.
10. List directory contents
To list the directories, you can use the ls command:

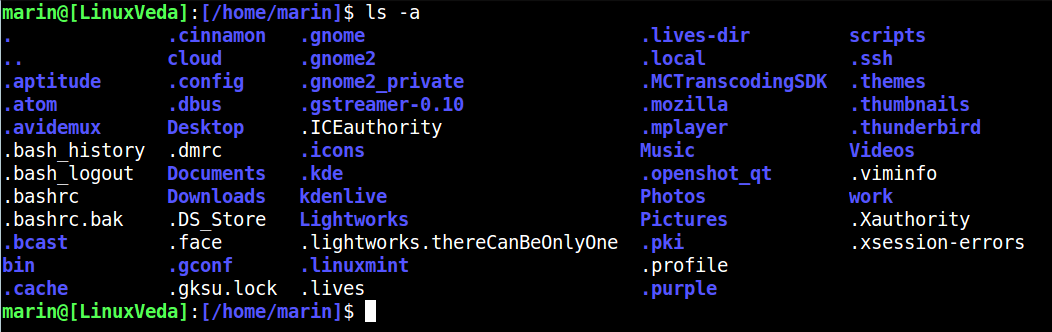
The "ls" command can take different parameters to help you change the output of the statement. For example, the "-a" parameter will display all files and folders, including hidden folders containing "-a".
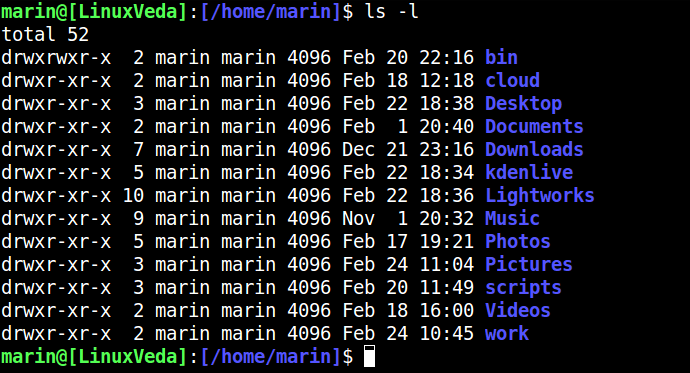
If you want the command output to display a list of detailed information for each file and folder, you can use the '-l' (L) option :
ls -l You can try different
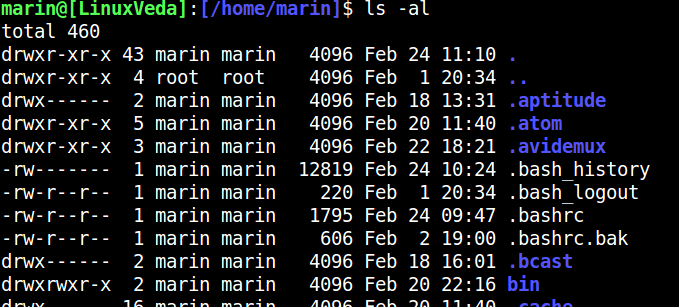
In addition, you can combine parameters to display details of all files:
ls ?al
11. Search for previous Linux commands
Clicking Up will display the final Linux command you successfully used. No error statements are displayed here.
Alternatively, you can use the history command to see all the Linux commands you have used on Terminal.
12. Invisible password

When asked to enter a password, suppose in the case of using sudo , when you type in the password on the screen nothing will be displayed, no star or dot . After you enter the password, you Press Enter to finish.
13. Copy and paste the Linux command

To copy or paste the Terminal command, you cannot use the familiar key combination Ctrl + C and Ctrl + V.
Instead you can use Ctrl + Shift + C and Ctrl + Shift + V or right-click and select Copy or Paste from the Context Menu.
14. Display progress in Linux system
One of the tasks needed to administer Linux systems is to control the currently running processes. Once you know which processes are running, you can turn off processes that slow down the system. In addition, information about system processes tells us to turn off but the process makes the system unstable. Therefore it is important to know which processes are running on the system. Linux supports a variety of process testing methods, one of which is using the ps command. When using this command all information about running processes will be displayed. You just need to enter the following command syntax into the terminal window:
# ps aux | less

Figure 1: Process information running in the system.
In addition, this command can be used in combination with some other parameters such as:
# ps -A : Check every process in the system.
# ps -U root -u root -N : Checks all processes except system processes.
# ps -u username : Check the processes performed by a certain user.
Or you can use the # top command to see the processes running on the system in real time.
15. Check Socket information and TCP / UDP network information
After configuring the network services of the Linux system, you need to keep the tabs of the ports that are actually receiving the signal on the network interface of the system. This is very important because the system can be compromised through open ports. There are a number of Linux management tools that tell you information about open ports and access open ports on the network. One of the simplest and most reliable methods is to use the ss command to check the Socket information, in addition to displaying more TCP information and status information than other tools. This ss command provides information about:
- All TCP Socket.
- All UDP Socket.
- All connections ssh / ftp / http / https.
- All local processes are connected to the X server.
- All TCP Socket in FIN-WAIT-1 state.
Here are some ss commands:
- # ss ?s : Displays the total number of Socket.
 Figure 2: Output information when running # ss ?s command.
Figure 2: Output information when running # ss ?s command.
- # ss -1 : Shows all open ports.

Figure 3: Output information when running # ss -1.
- # ss ?pl : Check the open socket process name using the following command:
- # ss -lp | grep : Check that the user is working with the Socket open.
- # ss -t ?a : Displaying all TCP Socket.
- # ss -u -a : Displays all UDP Socket.
16. Track Average CPU Load and Disk Activity
If you are a Linux system administrator, you need to know how to maintain a reasonable balance in the process of loading input and output between physical drives. You can change the system configuration to perform this task. However, a much simpler method is to use the isostat command to manage the input and output loading system in Linux by monitoring the uptime and average transfer rates of devices. this. This command will inform CPU information (Central Processing Unit), input and output information for devices, partitions and network file system (NFS).
When running the isostat command the output information is of the form:
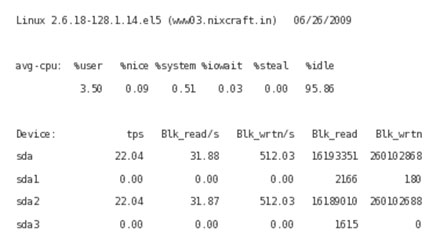 Figure 4: Information displayed when running the isostat command.
Figure 4: Information displayed when running the isostat command.
To get NFS directory information, use the following command:
# iostat ?n
17. Check the Memory Map of processes in Linux
When working in a Linux system you may need to check the amount of memory used in the system. Linux integrates many commands to check the amount of memory occupied. There is a simple command that displays the total information of the occupied and unused space of the physical memory and the total memory capacity is the free command.
After running this command, you will see the total occupied and unused space of the physical memory and the total amount of memory in the system. In addition, it displays caching information that individuals use.

Figure 5: Information displayed after running the free command
18. Check the operating time of the system
Do you want to know how long the server has been running? If you want, you just need to use the uptime command to check the time that the system is running. This simple command not only tells you how long the system is running but also indicates how many users have logged into the system in the previous period.
 Figure 6: Uptime command result.
Figure 6: Uptime command result.
19. Check user login
In addition to Linux management tools, you can use a command to check which users have logged into the system and what they have done. This command will show the current time, the time the system has run, the number of users logged in.
This command also displays the average load in every 1, 5 and 15 minutes. This command is useful for system administrators who want to use average load information to plan capacity.
To check who logged in to the system and what tasks they have performed, just run the following command:
# w username

Figure 7: Information displayed after running the # w username command.
20. Control system behavior, hardware and system information in Linux
For many Linux users, system control is a complex task. Most Linux distributions integrate a lot of control tools. These control tools provide methods that can be applied to check system behavior information. Controlling the system allows users to monitor the cause of the system's performance being hindered. One of the essential tasks of the system control process is to look up information about system behavior, hardware and memory information. There is a simple command that displays information about the progress, memory, record page, IO group, error and CPU behavior that is the vmstat command.
You only need to enter the following command in the terminal window:
# vmstat 3

Figure 8: Output information of # vmstat 3 command.
Alternatively, you can use the # vmstat -m command to check memory information, and the # vmstat -a command to display the active and inactive memory page information.

Figure 9: Information displayed after running # vmstat -a.
21. Check hardware information of Linux system
For some Linux users, checking hardware information is not easy. Linux is a complex system, but it includes a number of tools to get detailed information about the hardware, for example we can use a fairly simple command to check the hard disk information on that system. is the hdparm command. This command provides a command-line interface for managing multiple types of hard disks supported by the ATA / IDE device driver subsystem. It provides a command to display verification information such as capacity, details, etc. directly from the drive. This information is saved in a new extension format. You only need to log in as root user and use the following command:
# hdparm -I / dev / sda
Or use the command:
$ sudo hdparm -I / dev / sda
Then the system hard disk information will immediately display.
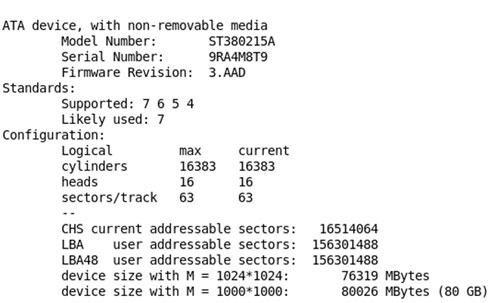
Figure 10: Details of the hard disk.
22. The commands to process files on Linux
The command to navigate around the Linux file system is ls, but there are many variations.
Linux command Command task will do ls List current directory contents ls -al List directory contents including hidden files cd dir Move from current directory to dir cd directory Transfer from current directory Go to the private directory (usually [User Name] at Home) cd . Move up (to /) a folder from the current location. CDTake the user to the specified location. If the position starts with /, it is considered relative to the root and current location. ~ Character represents the Home directory. For example:
cd / tmp
cd Documents
cd ~ / Documents
23. Network commands on Linux
TipsMake.com has a pretty detailed tutorial about the commands that work with the network on Linux, you are interested to consult.
24. Start, stop and list services
These commands allow users to display services as well as start and stop them.
Command Function Systemctl command Systemctl command can start, stop, restart and reload the service, admin permission is required. sudo systemctl stop apache2.servicesudo systemctl restart apache2.service
sudo systemctl reload apache2.service service List services and indicate whether they are running. service --status-all
25. Determine the operating system version
The table below lists the commands that will show details about the Linux operating system running on the system.
Command FunctionExample shows the operating system version information in a text line. uname -auname -r lsb_release On Debian-based systems, this command displays information about the operating system including codename and distributor ID. lsb_release -a hostnamectl Displays information on the system including server name, chassis type (operating system), operating system, kernel and structure. hostnamectl
26. Measure system performance
The following are some useful tools for checking system performance.
Command FunctionExample Displays running processes along with resource usage and system performance data. Processes can be displayed for a selected user or all users. Processes can be organized according to different criteria (by default, CPU usage). toptop jdoe atop Similar to the above command, but more towards system performance than individual processes. Free atop Displays memory and exchanges total memory, used and free space. free df Displays the use of the system disk space of the file. DF
df -h
27. Manage users and groups
Commands to create and delete user accounts and groups are quite simple.
Command FunctionExampleadd Add a new user account to the system. Username is required. Other fields (user descriptions, shells, initial passwords, etc.) may be specified. The main directory will default to / home / username. useradd -c "John Doe" jdoeuseradd -c "Jane Doe" -g admin -s / bin / bash jbdoe userdel Delete user accounts from the system. The -f option is stronger, deleting main files and other user files even if the user is still logged in. userdel jbdoe
userdel -f jbdoe groupadd Add a new user group to the system, update / etc / group . groupadd developers groupdel Delete user groups from the system. groupdel developers
28. Set up and run scheduled processes
Tasks can be scheduled to run periodically using the commands listed below.
Command FunctionArtrontab Set up and manage scheduled processes. With the -l option , recurring jobs are listed. With -e option , recurring jobs can be set to run at selected time intervals. crontab -lcrontab -l -u username
crontab -e anacron Allows users to run only scheduled tasks. If the system is turned off when a job is scheduled to run, it will run when the system starts. sudo vi / etc / anacrontab
29. Update, install and list applications
The commands to install and update applications depend on the version of Linux in use, specifically based on Debian or RPM.
Commands Function Example apt update On Debian-based systems, this command updates the list of available packages and their versions, but does not install or upgrade any sudo apt packages to update apt upgrade. on Debian, this command installs newer versions of existing packages. sudo apt upgrade apt list List all packages installed on Debian-based systems. With the --upgradable option , it only displays packages with an upgrade. apt listapt list --installed
apt list --upgradable apt install On Debian-based systems, this command installs the required package. sudo apt install apache2 yum update On RPM-based systems, this command updates all or specified packages. sudo yum update
yum update mysql yum list On RPM-based systems, this command lists the packages. sudo yum update mysql yum install On RPM-based systems, this command installs the required package. sudo yum -y install firefox yum list On RPM-based systems, this command lists known and installed packages. sudo yum list
sudo yum list --installed
30. Turn off and restart
The commands to shut down and restart the Linux system require admin rights. Options like +15 are the number of minutes that the command will wait before the shutdown request is made.
Command Function Exampleshutdown Turns off the system at the time of the request. -H option pauses the system, and the -P option turns off the power. sudo shutdown -H nowshutdown -H +15
shutdown -P +5 halt Turn off the system at the time of the request. sudo halt
sudo halt -p
sudo halt --reboot poweroff Disconnect power from the system at the time of request. sudo shutdown -H now
sudo shutdown -H +15
sudo shutdown -P +5
31. Linux security command
I have synthesized 20+ essential Linux security commands, essential for security issues on Linux, you need to consult.
Refer to some of the following articles:
- Ubuntu Bash tutorial on Windows 10
- Certain deadly commands never run on Linux
- How to access Linux partitions on Windows?
Good luck!