What happens to the body when you fall in love?
When you look at someone you love, chemicals are released in your body that cause your heart to beat faster and your pupils to dilate. If you've ever been in love, you'll be familiar with these signs. Feelings of excitement, a pounding chest, and butterflies in your stomach all indicate that you're in love.

Love is generally considered a matter of the heart. But the truth is that it can affect many other parts of the body. This article will decode the body's response to love, explaining how love matures over time.
The Science Behind Love and Attraction
It may sound surprising, but the truth is that love begins in the brain. Tiny chemical messengers released by neurons are responsible for the feeling of love.
There are different hormones that correspond to different stages of love. According to scientists, love can be divided into three levels: desire, attraction and attachment.
Lust comes first. It is the initial superficial stage, triggered by the hormones involved in reproduction, testosterone in men and estrogen in women. It is just the basic natural human desire to mate and procreate.
The next stage is attraction, when things start to get more serious. You are captivated and don't want to let go. This stage goes beyond primal instincts; two hormones are usually responsible.
First is adrenaline, the hormone responsible for alertness. That's why your heart races and your palms sweat when you see someone you like. Dopamine is also involved in this process, to keep you coming back for more.
The final stage is attachment, when you move on to planning your life together. The main hormone for this stage is oxytocin, the cuddle hormone.
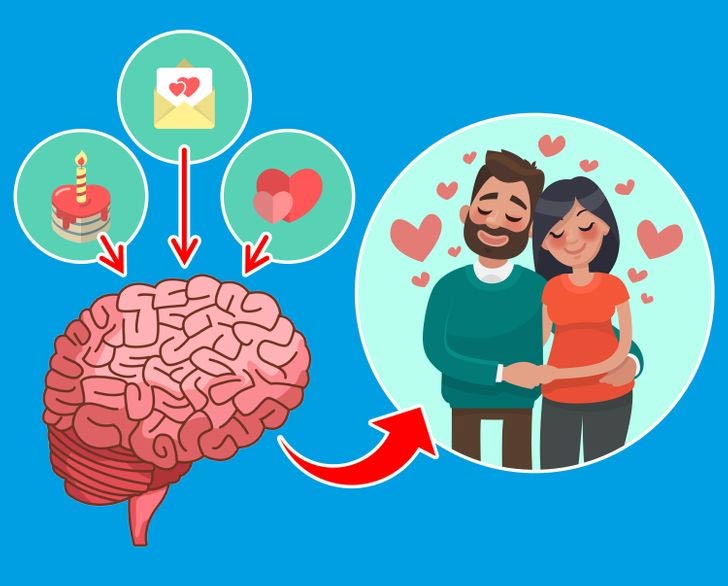
How does the body change when in love?
We now know that the brain and brain chemicals are responsible for the feeling of love, but it doesn't stop there. These hormones are released into the bloodstream, triggering changes in other organs.
A clear example is the way your heart beats fast and your palms sweat in response to the fight-or-flight hormone, adrenaline.
These changes will come to your eyes as your pupils dilate looking at your loved one. Additionally, seeing their face will make you feel good by stimulating the pleasure centers of your brain.
When talking to your significant other, your voice may also change and often become higher in pitch.
However, not all changes in your body when you are in love are pleasant. The feeling of unease in your stomach when you are away from your lover is the most obvious example, as this is due to an increased stress response.
Happy love is good for your long-term health. Scientists have found that love can help reduce chronic pain, promote strong bones and support a healthier lifestyle.
On the other hand, if love goes bad, it can literally cause a broken heart. This is a legitimate medical condition called stress cardiomyopathy with symptoms similar to a heart attack. And while it can resolve on its own, the condition can easily get worse with serious complications.
How does romantic love change over time?
The days of intense, heart-pounding love won't last forever. Things will change over time, but that doesn't mean you'll ever love any less.
Think of it like the evolution of true love, like fine wine, only gets better with age.
The first stage is when passion is at its most intense. Emotions seem to reach a peak, known as the honeymoon phase. Stress hormones and a cocktail of other messengers, from adrenaline to dopamine, drive these fiery emotions.
Over time, the flame of love will mature and progress into the slow burn stage. This stage occurs after facing many obstacles, challenges in life and weathering the storm.
Slow love is loving love. Here, you get to know your partner better and gain a better understanding of their personality. And while it feels a little different than the passionate honeymoon phase, it's no less real.
The "love chemical," just another one, still regulates mature emotions. By this time, stress hormones have generally returned to normal levels, but the pleasure center in the brain is still active.

How is platonic love different from romantic love?
Platonic love is the love we have for our family and close friends. Of course, the love you have for your friends, family, and even your pets is significantly different from the love you have between people. But it is not necessarily a bland form of romantic love, but a separate but deep and meaningful emotion.
The truth is that there are some similarities between romantic love and platonic love. Both involve caring deeply about someone. The cuddle hormone, oxytocin, comes into play in both cases, and you also have better mental and physical health.
Love can come in many different forms, romantic or platonic, but in the end it is still love.
Either way, love changes the way your body functions, starting with the release of special "messengers" in the brain.
Most importantly, however, you can't reduce everything about love to a series of chemical reactions.
After all, love is a deep, complex emotion influenced by personal experiences and everyone experiences it differently!