The Moon is Getting Farther From Earth: What Will Happen in the Future?
Every year, the Moon moves 3.8 cm (1.5 inches) farther from Earth. Scientists measure the distance to the Moon by reflecting lasers from mirrors placed on it by space probes and astronauts.

By measuring the time it takes light to travel from Earth to the Moon and back, scientists can accurately measure the distance to the Moon and how that distance changes.
The distance to the Moon actually changes over the course of a month as it orbits Earth. The Moon is typically 239,000 miles (385,000 km) from Earth, but its orbit is not a perfect circle and varies by about 12,400 miles (20,000 km) as it orbits Earth. This variation is why some full moons appear slightly larger than others—they are called supermoons .
The motions of the Earth and Moon have many interesting consequences, and studying how they move over time can help us better understand how each object has changed over the 4.5 billion years since the Earth and Moon formed.
Tidal force
So, why is the Moon moving further away from Earth? It's all because of tides.
Tides result from the difference in gravitational pull between two objects. The gravitational pull exerted by the Moon is about 4% stronger on the side of the Earth facing the Moon than on the opposite side of the Earth facing away, because gravity weakens with distance.
This tidal force causes the oceans to ripple in two masses toward and away from the Moon. This is because the gravitational force that the Moon exerts on Earth is not just an average force that is the same everywhere.
The Moon's gravity is strongest on the side closer to Earth, causing a mass of water to gravitate toward the Moon. Gravity is weaker on the opposite side of Earth, causing another mass of water to gravitate more slowly toward the rest of Earth.
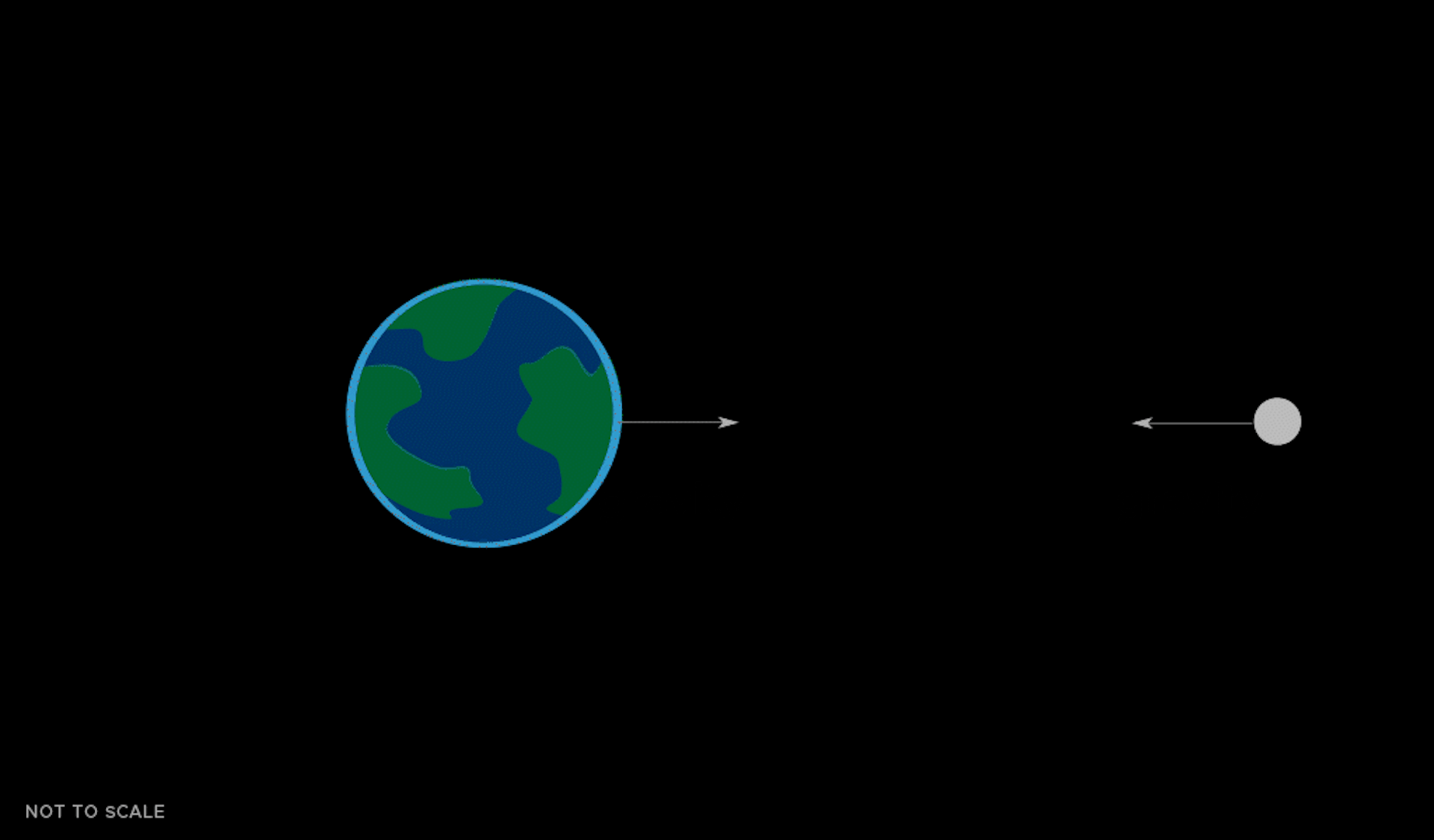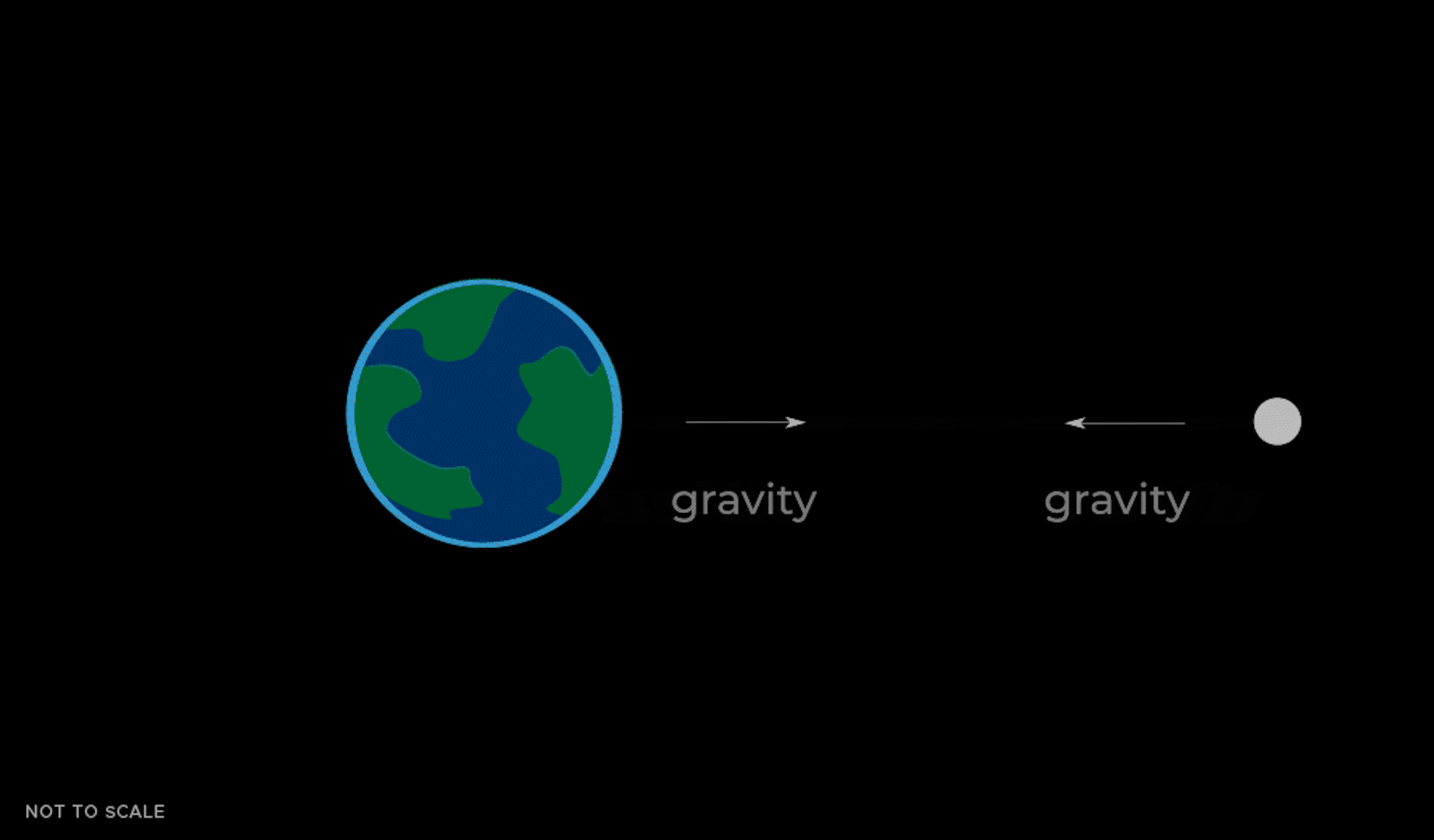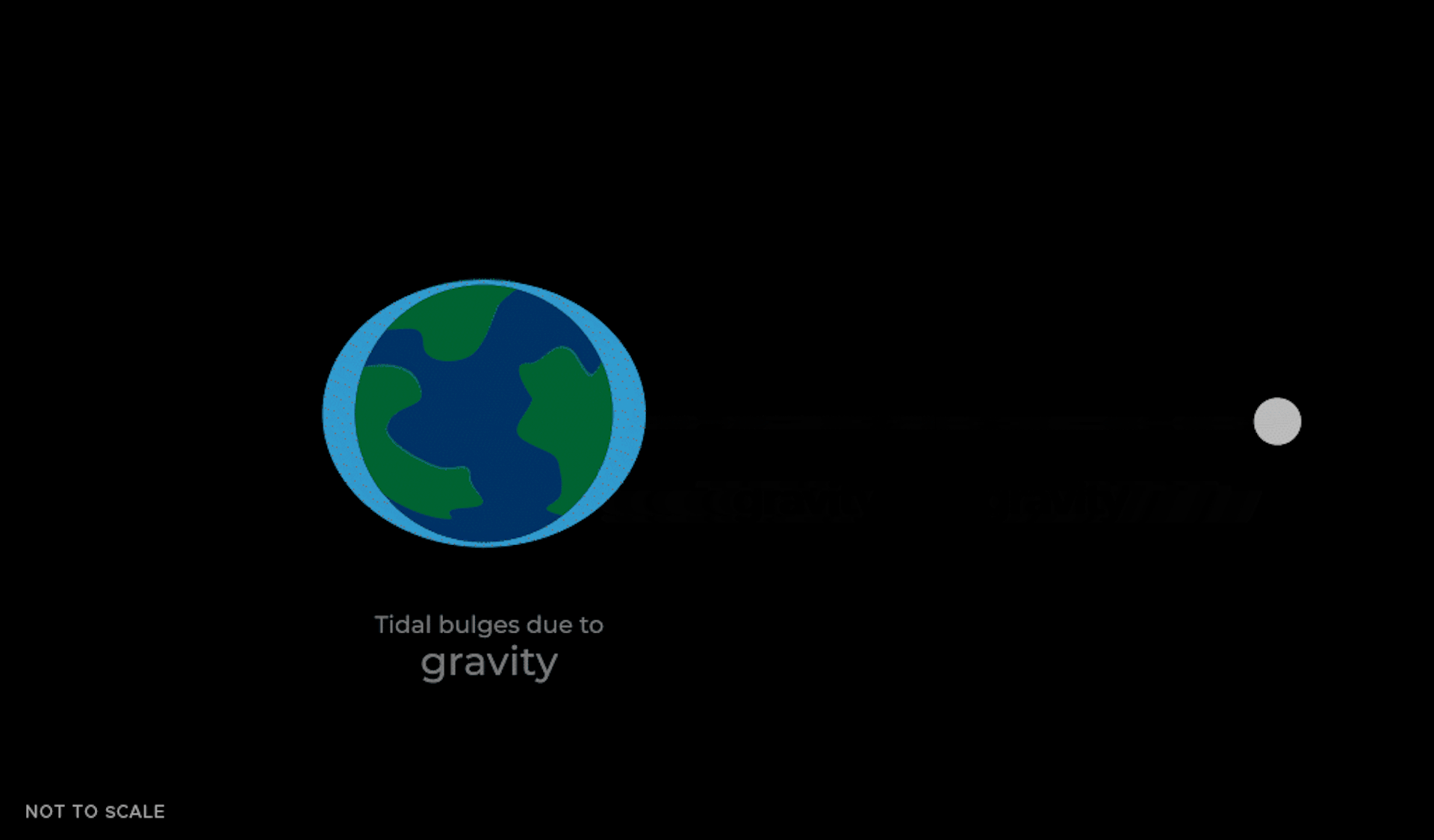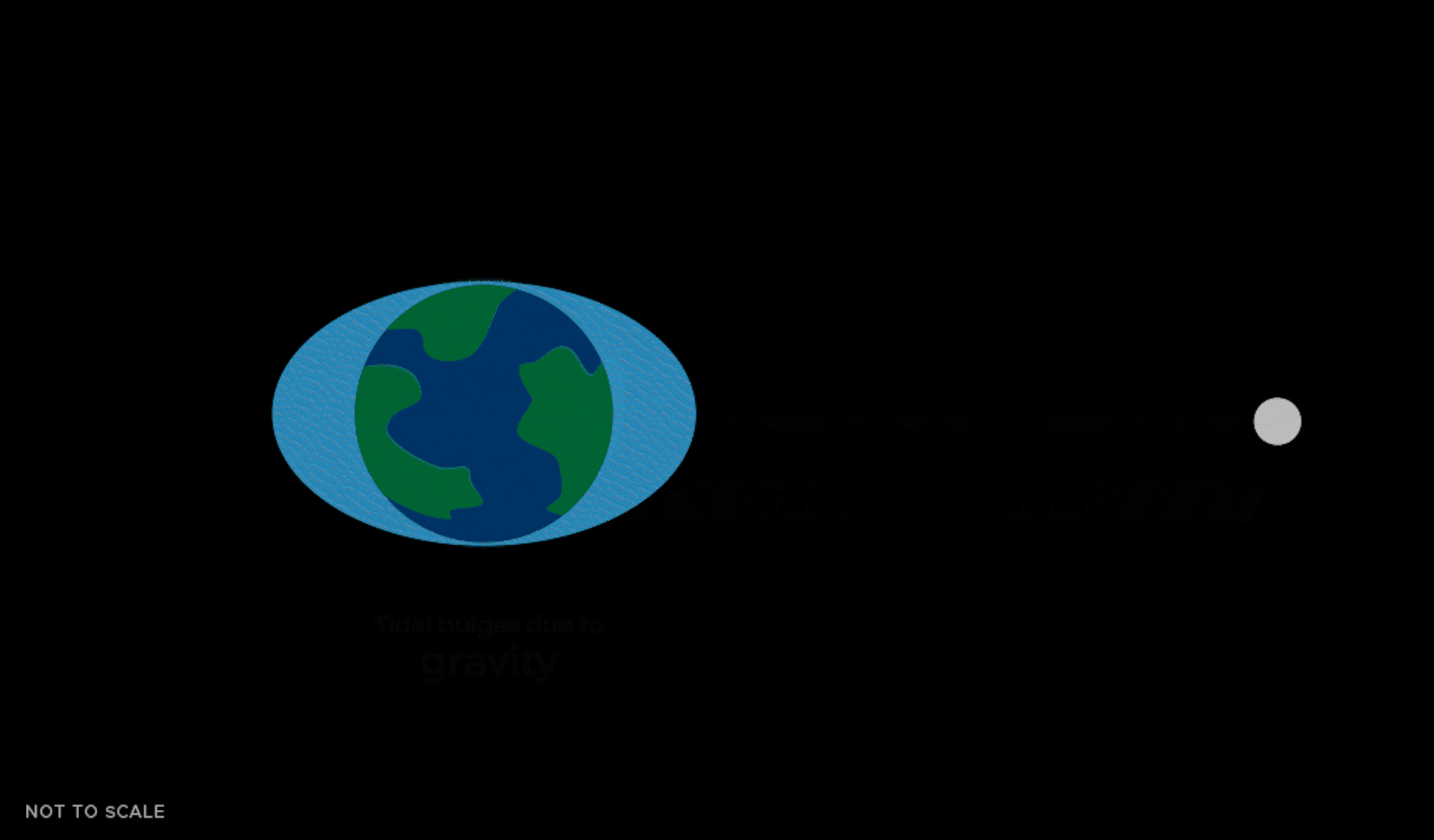
As the Earth rotates, these bulges move and continue to move toward the Moon due to its gravity. In New York City or Los Angeles, the water level can change by about 1.5 meters due to these tidal bulges.
The tidal bulges aren't perfectly aligned with the Moon – they 'lead' the Moon a little bit as the Earth spins and pulls them forward. These bulges also exert a gravitational pull on the Moon. The bulge closer to the Moon not only pulls the Moon toward the center of the Earth, but also moves it forward a little bit in its orbit – like the thrust of a sports car going around a corner.
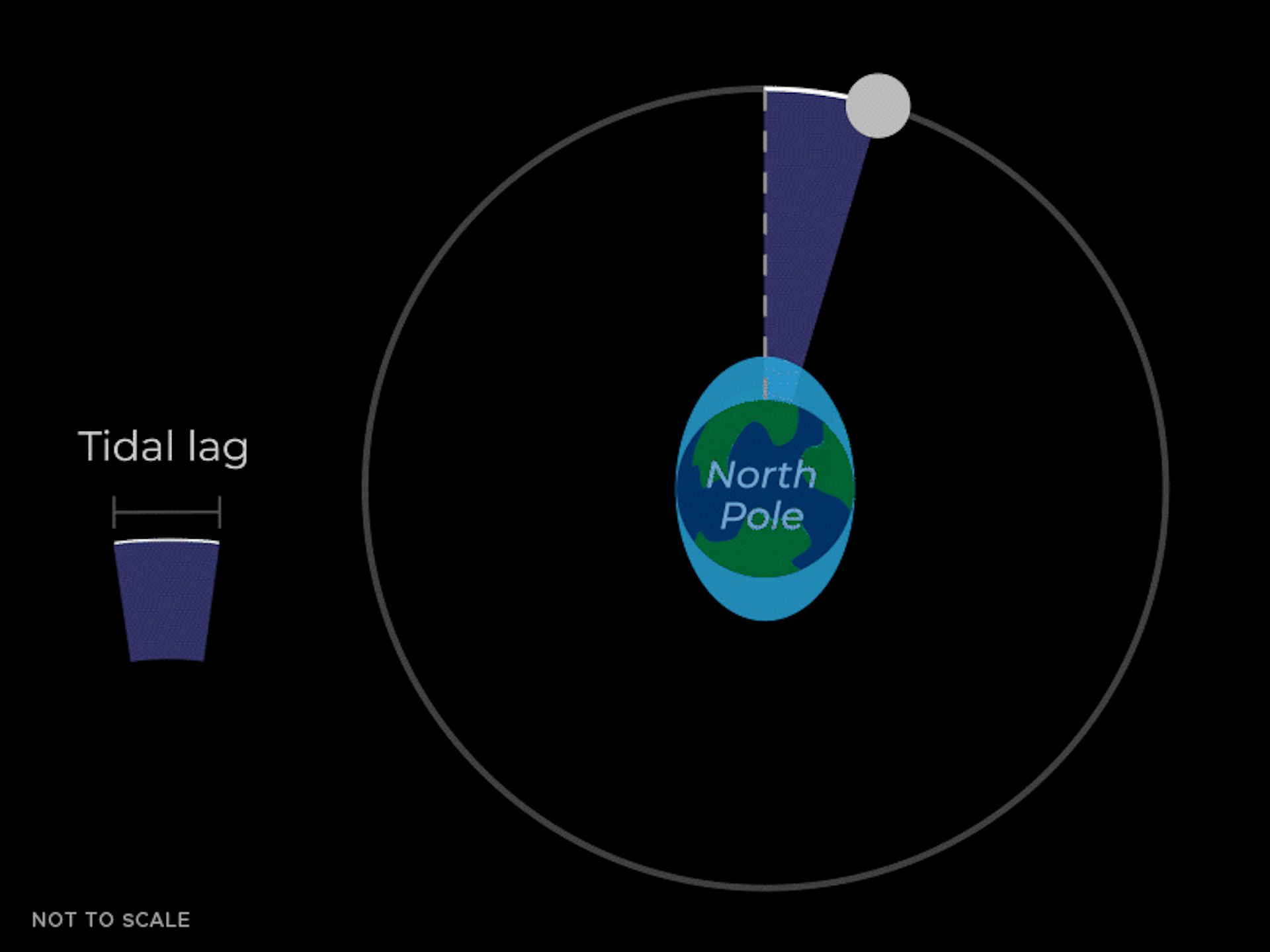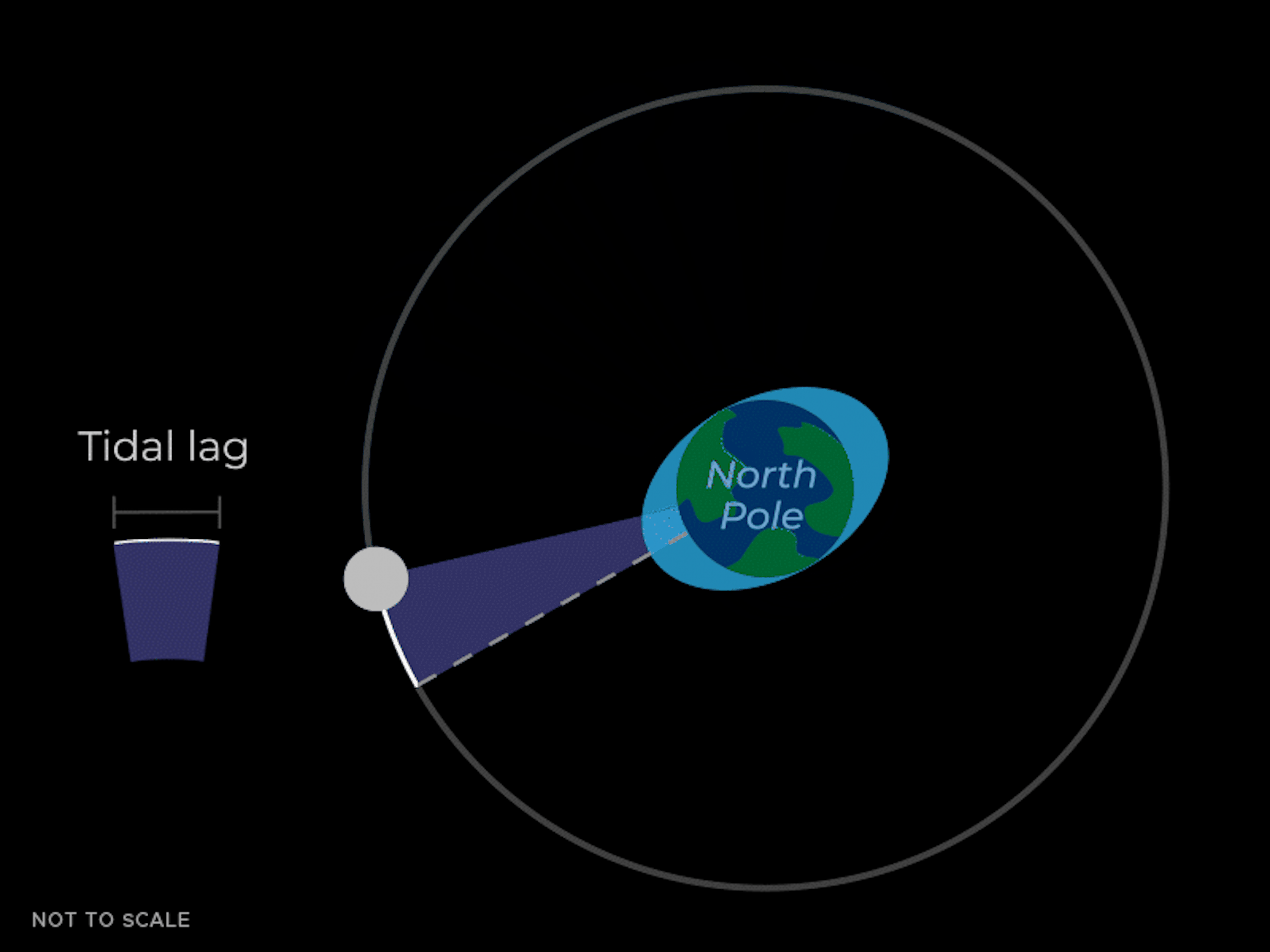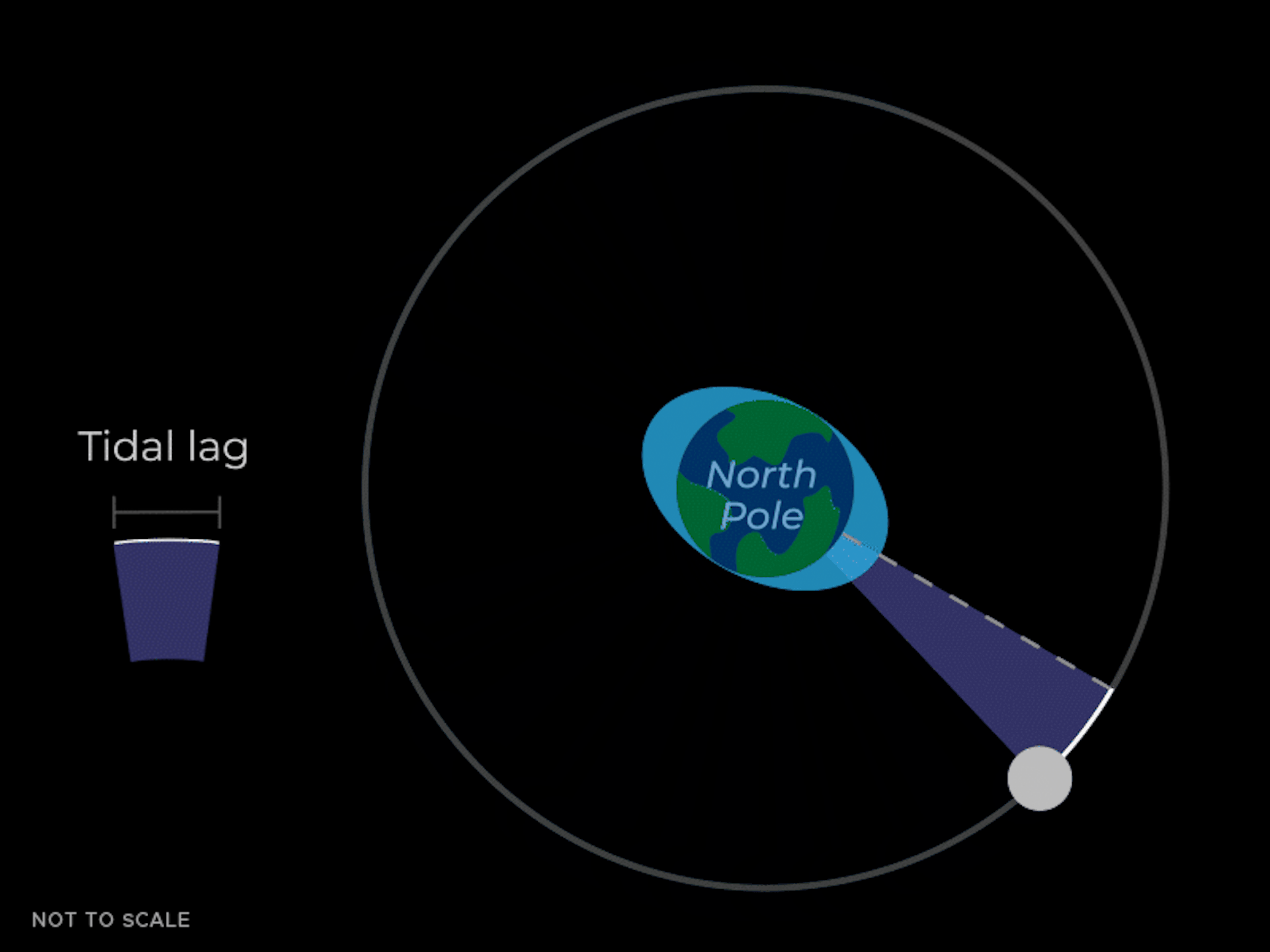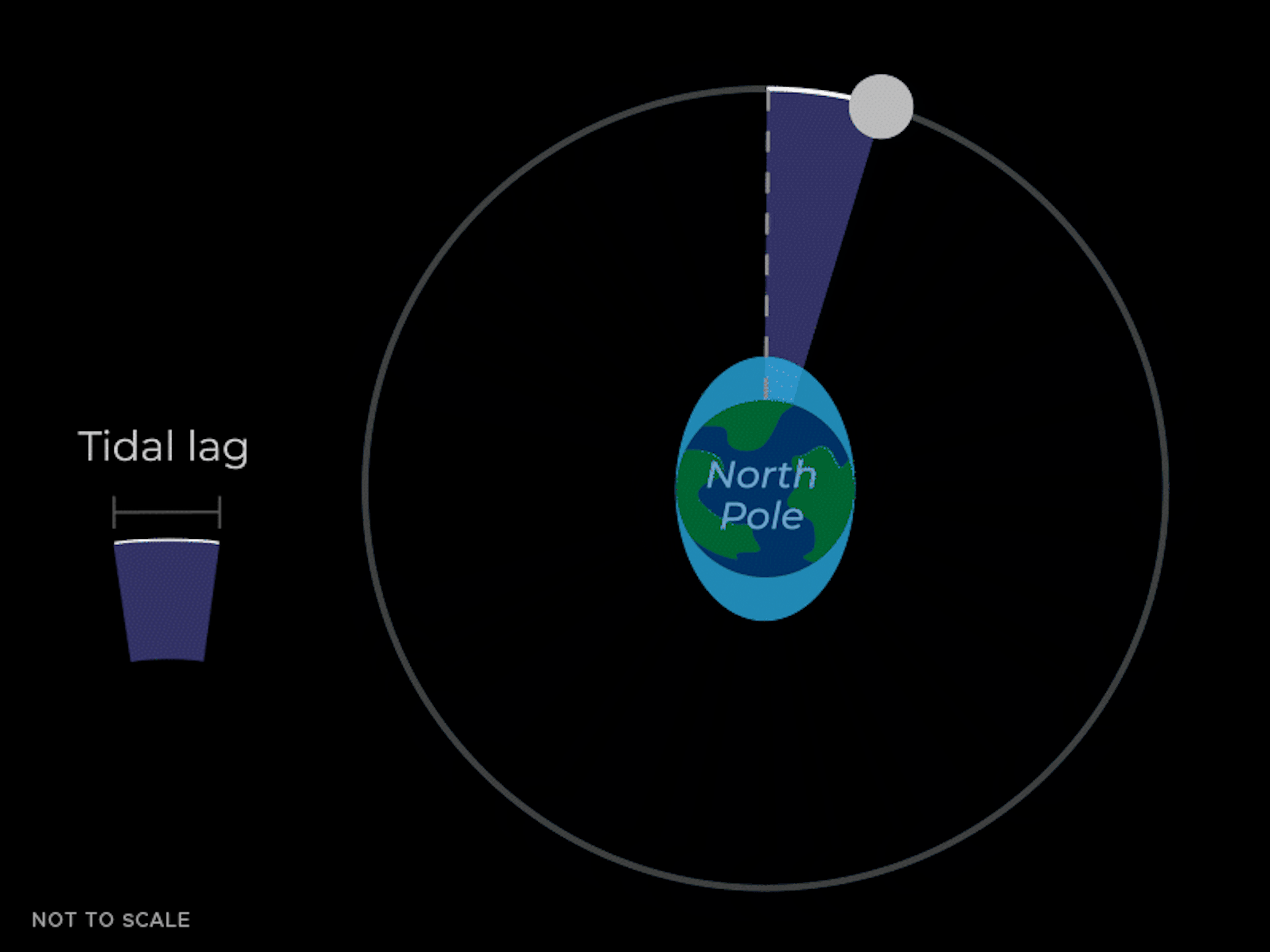
The forward pull from the closer tidal mass causes the Moon to speed up, causing its orbit to increase. Imagine a baseball player hitting a home run. If the player hits the ball faster at home plate, the ball will soar higher in the sky.
So the bottom line is that the gravitational pull of the tidal mass closer to Earth is pulling the Moon forward, increasing the size of the Moon's orbit. This means the Moon is moving further away from Earth. This effect is very slow and can only be seen on average over many years.
Does the Moon's increasing distance affect the Earth?
The Moon gains momentum as its orbit gets larger. Imagine spinning a heavy object attached to a string. The longer the string, the more momentum the object has and the harder it is to stop.
Because the Earth is doing the work of increasing the Moon's momentum, the Earth's rotation also slows down, as its momentum is transferred to the Moon. In other words, as the Moon's orbital momentum increases, the Earth's rotational momentum decreases to compensate. This compensation makes a day slightly longer.
But don't worry, these effects are tiny: 1.5 inches a year over a distance of 239,000 miles (384,000 km) is just 0.00000001% a year. We'll continue to have eclipses, tides, and 24-hour days for millions of years to come.
What will happen in the future?
So, will the Moon eventually escape Earth's gravity as it moves away?
If we fast forward tens of billions of years into the future, the Earth's rotation may eventually slow down until it is tidally locked to the Moon. That means it will take the Earth the same amount of time to rotate as it takes the Moon to orbit. At that point, the Moon will no longer be far away, and you will only see it from one side of the Earth.
But two things will prevent that from happening. First, in about a billion years, the Sun will become brighter and boil off the oceans. Then there will no longer be the great tides that push the Moon away. A few billion years after that, the Sun will expand into a red giant star, possibly destroying the Earth and the Moon.
But these events are so far in the future that you don't need to worry about them yet. Just enjoy the tides on the beach, the eclipse, and the beautiful moon right now.