New research reveals a simple solution to reduce motion sickness
Motion sickness can be a nightmare for many people, causing dizziness, nausea, and discomfort that can last for hours or even days. However, a new study from Nagoya University in Japan has found that just one minute of exposure to low-frequency bass can significantly reduce these symptoms.
Sound stimulates the inner ear to help reduce motion sickness
A team of researchers at Nagoya University School of Medicine, led by Takumi Kagawa and Masashi Kato, found that exposing the inner ear to sound waves at a certain frequency for just one minute can reduce discomfort such as dizziness and nausea in people reading in a moving vehicle. The findings, published in the journal Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine, open up a potential new approach to controlling motion sickness.
' Our study demonstrates that short-term stimulation with a unique sound called 'sound spice®' reduces symptoms of motion sickness such as nausea and dizziness,' said Kagawa. 'The effective sound levels are within the range of everyday environmental noise exposure, suggesting that this sound technology is both effective and safe .'
The study builds on recent scientific evidence that stimulating the inner ear with sound can improve balance. The research team determined that a test tone frequency of 100 Hz (a mid-bass tone) was optimal for activating the vestibular system, the part of the inner ear responsible for balance and spatial orientation.
Kato explains how the device works: " The vibrations from this unique sound stimulate the otolith organs in the inner ear, which are responsible for detecting linear acceleration and gravity. This suggests that a unique sound stimulus can broadly activate the vestibular system, which is responsible for maintaining balance and spatial orientation ."
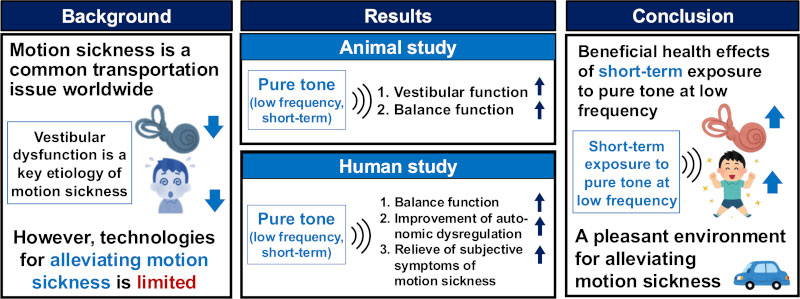
Researchers tested the device by exposing participants to sounds before inducing motion sickness through a Ferris wheel, a driving simulator, and an actual car ride. Symptoms were measured using a postural control test, an electrocardiogram (ECG), and the Motion Sickness Assessment Questionnaire. Pre-test sound exposure was found to increase sympathetic nerve activation, which is often disrupted in cases of motion sickness. Participants reported a reduction in symptoms, including lightheadedness and nausea.
" These results suggest that sympathetic nerve activation, which is often disturbed during motion sickness, was objectively improved by exposure to the unique sound ," Kato added.
The research team also emphasized the safety of this technology. The health risks from short-term exposure to sound spice® are virtually non-existent, with irritation levels well below workplace noise safety standards.
New research by Japanese scientists has opened up a safe and effective way to deal with motion sickness while traveling, potentially benefiting millions of people around the world. The researchers aim to continue improving the technology and expanding its applicability to a variety of travel situations, including air and sea travel.
You should read it
- ★ How to effectively prevent car sickness without taking medicine
- ★ Apple reveals 'Vehicle Motion Cues' feature to help prevent motion sickness
- ★ Apple is about to launch a feature to help users reduce motion sickness
- ★ Learn About Motion: The AI-Powered Task Manager
- ★ How to make Stop Motion videos on Android phones