How to setup GUFW (Graphical Uncomplicated Firewall) on Ubuntu
Firewalls play an important role in improving the security of computer networks and preventing unauthorized access. In Linux, a tool called Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) is used to manage these rules effectively. This tool also has a graphical interface, called Graphical Uncomplicated Firewall (GUFW). This guide will explain how to install and use GUFW on Ubuntu.
Note : Although the instructions below are shown for Ubuntu , it will also work with most Linux distributions.
Install GUFW on Ubuntu via Terminal
GUFW can be easily installed on Ubuntu using the apt package manager. Before proceeding with the GUFW installation, make sure the Universe Repository is enabled on your system as GUFW is available in this repository:
sudo add-apt-repository universe 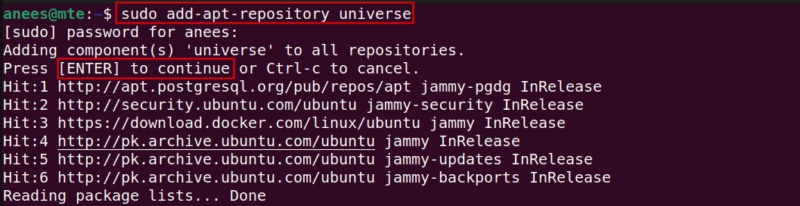
Now that the Universe Repository has been added, update the package repository:
sudo apt updateOnce your system is updated, run the command below to install GUFW on your Ubuntu machine:
sudo apt install gufw -y 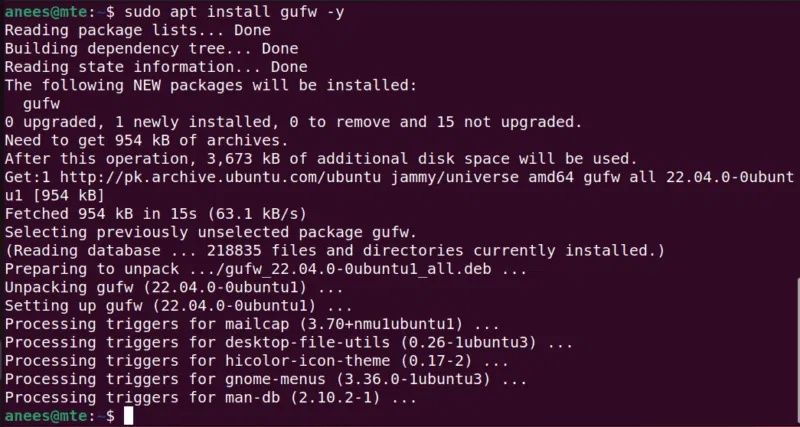
Install GUFW on Ubuntu via Software Center
GUFW can also be installed from the Ubuntu Software Center. First, open the Ubuntu Software Center, type GUFW in the search bar, and select the application to install:
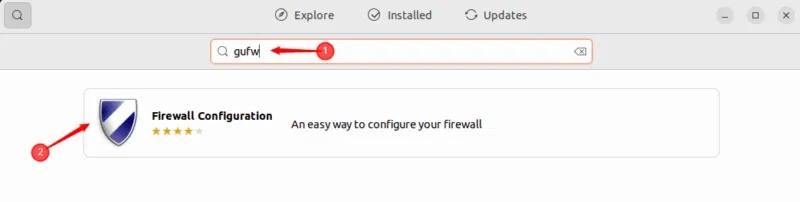
Click the Install button to start the GUFW installation process:
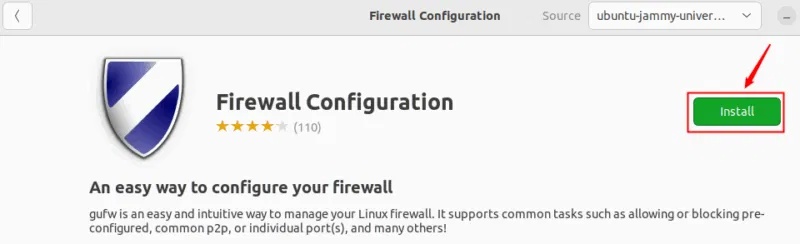
It will be installed on the system in just a few minutes.
Note : If you are not using Ubuntu, you should be able to find GUFW in your distribution's package manager.
Enable or disable GUFW on Ubuntu
After successfully installing GUFW, you can access GUFW on your system by executing the following command:
sudo gufwAlternatively, you can access it via your menu. Navigate to the system menu, search for GUFW and select the Firewall Configuration application to open it:
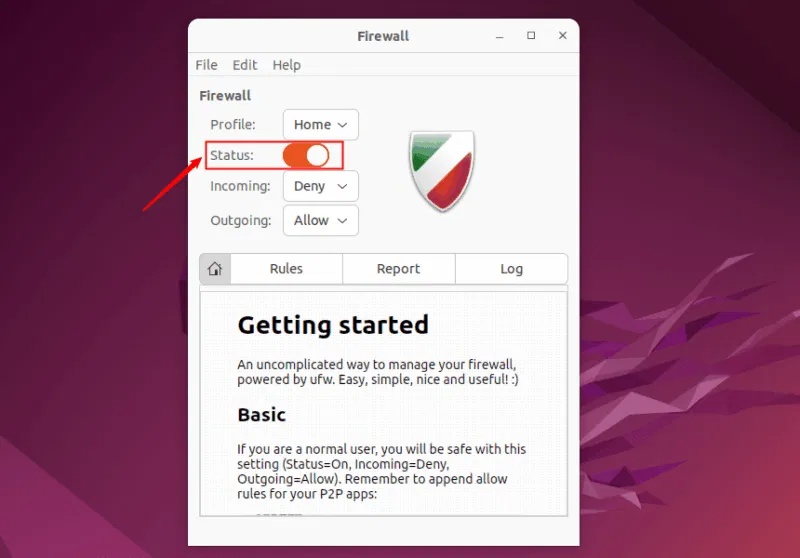
The GUFW main screen displays various details, such as profile, status, and information about incoming and outgoing traffic rules. The status switch shows whether the firewall is running or not.
To enable or disable GUFW, you can toggle the status switch on or off:
Edit GUFW profile
GUFW comes with different pre-configured firewall settings. You can click on the drop-down menu next to the profile to view the pre-configured profiles. These profiles represent different security levels and based on the selected profile, the firewall will apply corresponding rules to manage network traffic:
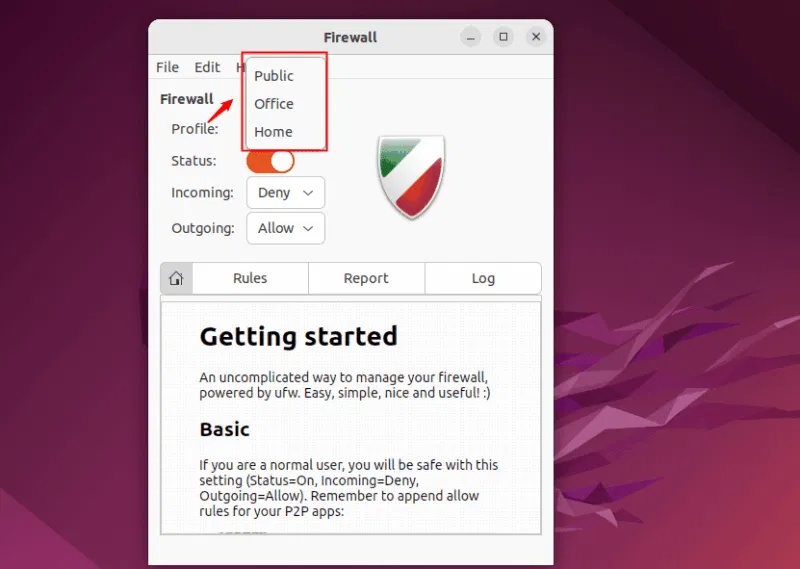
There are 3 pre-configured profiles, their details are listed below:
1. Public Profile
Public Profile in GUFW is designed for untrusted networks like public Wi-Fi. It blocks all incoming connections to reduce the attack surface and allows outgoing connections, so you can still browse the Internet and access external services. Using Public Profile on public networks helps protect your system from threats or unauthorized access.
2. Office Profile
It allows outgoing connections and can be configured to restrict incoming connections based on your organization's needs. It is suitable for use in corporate or office environments.
3. Home Profile
Home Profile allows all outgoing connections and allows certain incoming connections for trusted services like SSH or web access. Suitable for use on home networks where devices are generally trusted.
In addition to the pre-configured profiles, we can also create custom profiles and delete any unnecessary profiles.
To edit the configuration, go to the Edit tab and select Preferences :
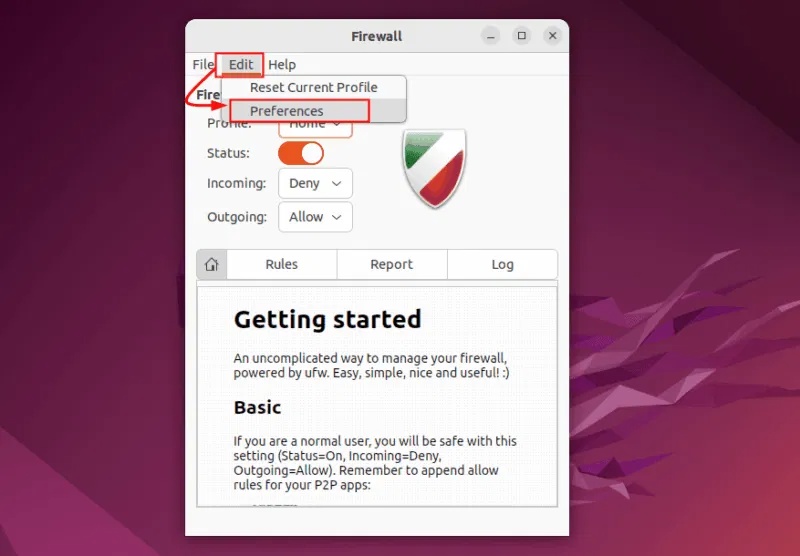
To add a new profile, click the + icon at the bottom of the Firewall Preferences window:
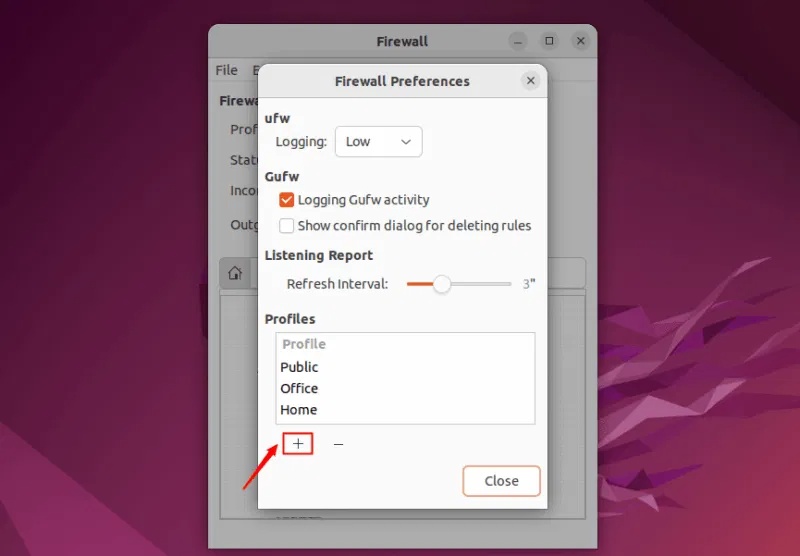
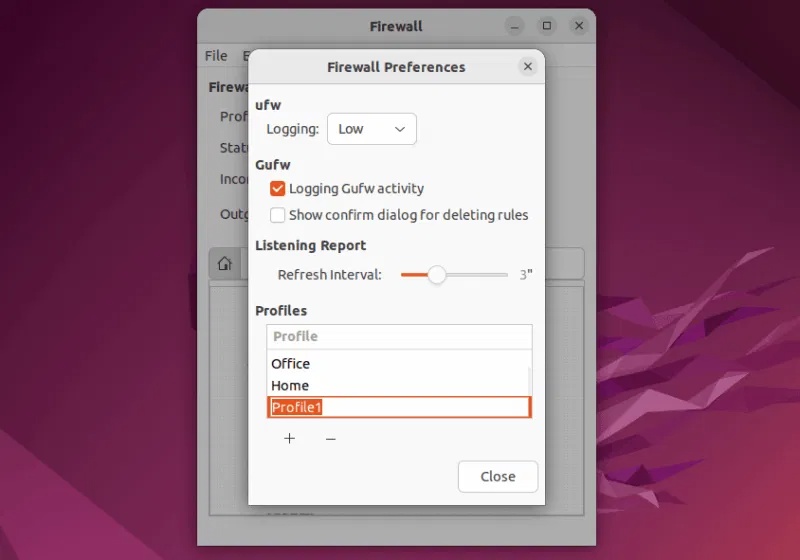
By default, the new profile will be named Profile1, Profile2, etc. Double-click on the profile to rename it:
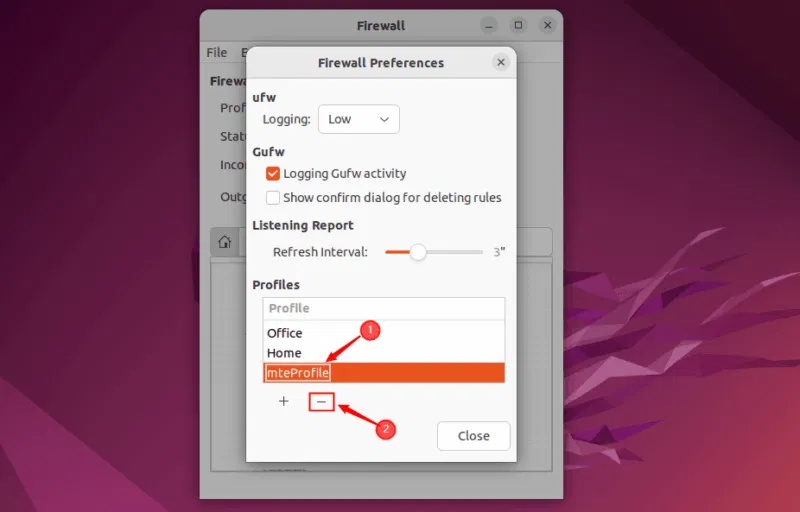
To delete a profile, select the profile you want to delete and click the – button :
Now click on the close button to exit Firewall preferences and continue with other rules.
Understanding the GUFW Rules
GUFW allows you to create custom rules for each of your profiles. These rules help manage how data enters and leaves your computer network. To set up the right rules, it is important to understand your network setup and the level of security you need. Furthermore, updating your firewall rules, reviewing them regularly, and adjusting them will help you better control network traffic and block any unwanted access.
GUFW provides several types of rules you can apply to manage network connections:
- Allow: Allows all data to pass through a specific port without any restrictions.
- Deny: Block all incoming data through the selected port.
- Reject: Similar to Deny, but it also sends a message back to the sender to let them know the connection was rejected.
- Limit: Block access if someone tries to connect too many times in a short period of time (e.g. more than 6 attempts within 30 seconds). It reduces the possibility of potential attacks like Brute Force .
Add GUFW rules
To add a GUFW rule, you first need to select the profile you want to add the rule to, then click the plus + button :
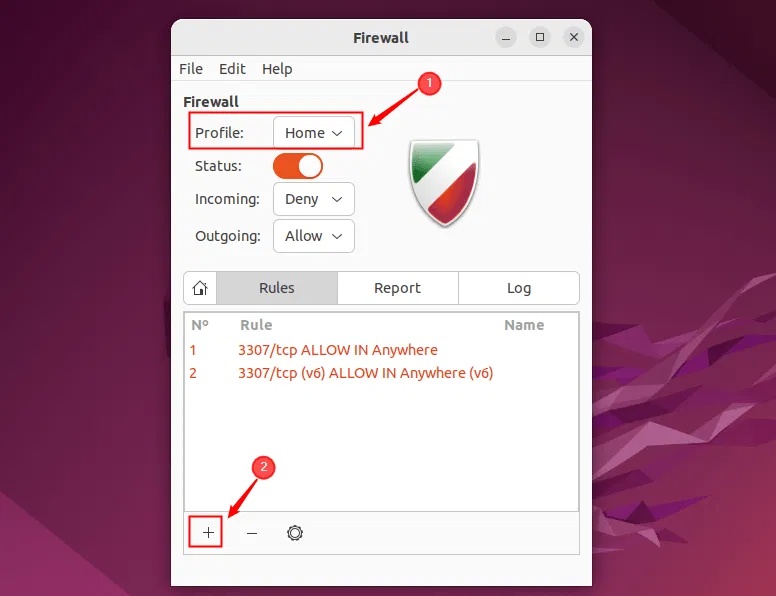
A new window opens where you can add firewall rules. This window is divided into 3 tabs: Preconfigured, Simple and Advanced.
- Preconfigured is the easiest option. This option lets you quickly allow or block common services like HTTP or SSH with just a few clicks.
- Simple is also beginner-friendly but gives you more control, such as selecting specific ports and setting rule directions.
- Advanced is for users who need granular control. This option allows you to create rules based on IP address , subnet, protocol, and network interface:
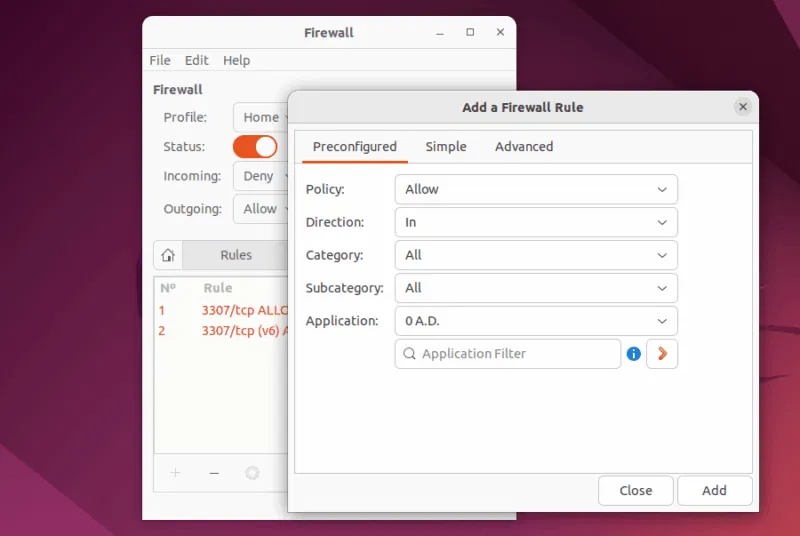
Select the policy, direction, category, subcategory, and application as needed, then click the Add button to apply the rule.
Edit GUFW rules
GUFW allows you to edit an existing rule. To do so, select the rule you want to edit and click on the gear icon:
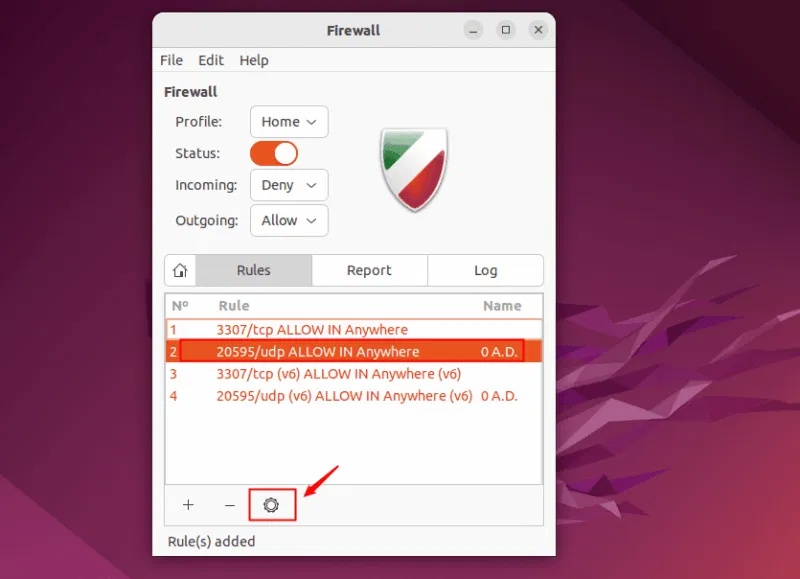
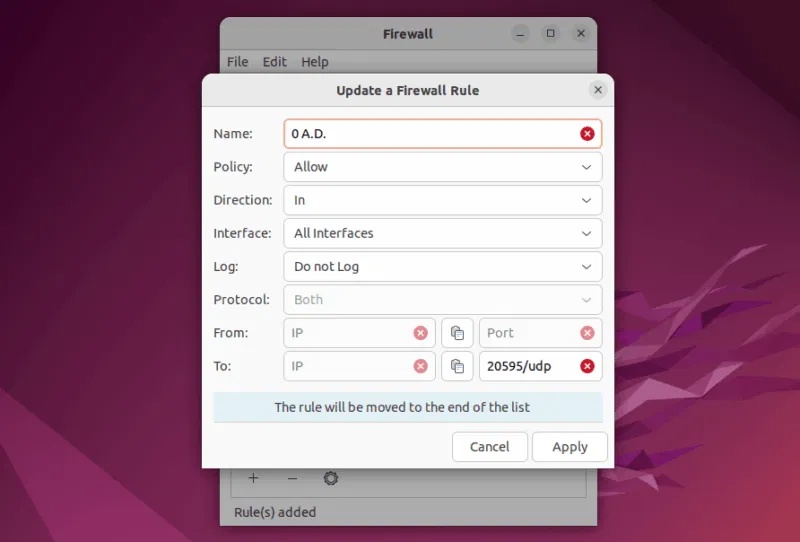
Now, on the pop-up window, you can update the firewall rules and click Apply to save the changes:
Here is how you can set up and use Graphical Uncomplicated Firewall on Ubuntu. Keeping the firewall enabled and configuring the appropriate rules using GUFW is a good practice. It helps you protect your system from unauthorized access while still allowing secure connections. For added security, you can install an antivirus to protect your system from potential threats and malware.