ChatGPT is free but it consumes a significant amount of water that you might not expect
ChatGPT is the most popular AI chatbot today, because it is free and easy to use. However, ChatGPT is silently consuming liters of water with each question.

You ask. ChatGPT answers. No clicking through multiple tabs. No ads. No clutter. Just pure, concise answers.
But here's what you don't know:
Every time you press 'enter,' something real happens. Real resources are mined. Electricity flows. Cooling fans spin. And water—real water—is pulled from the planet just to keep the system alive.
And what's scary?
It's invisible. You don't hear it. You don't see it. You never feel the moisture evaporating from a remote server farm. But it's there—gallon by gallon—dissipating into the air so your chatbot can spit out answers in two seconds flat. We like to think of AI as a feather-light, clean, frictionless tool powered by the cloud and code.
But maybe that's a lie we tell ourselves. Maybe the truth—the hidden environmental cost of every ChatGPT interaction —is a little more sobering.
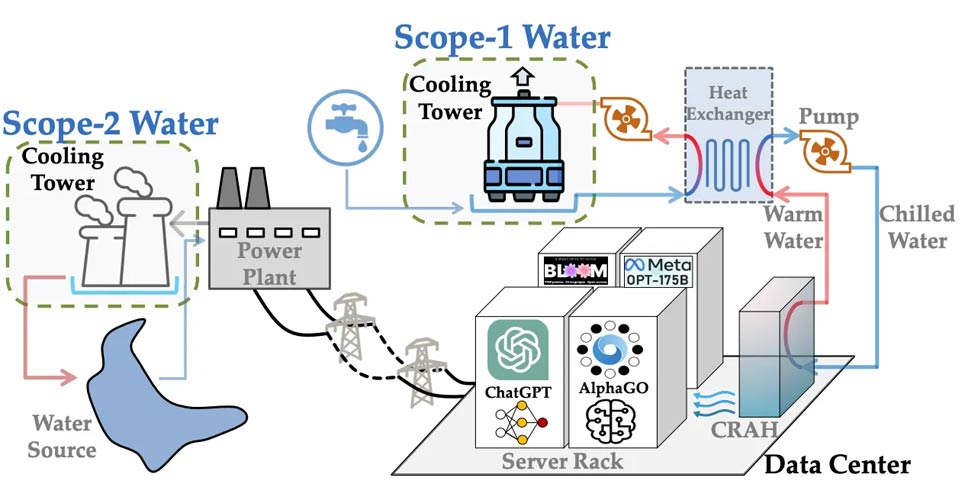
Estimates of ChatGPT's water consumption vary widely depending on the source. According to OpenAI CEO Sam Altman, each ChatGPT query uses about 0.3 milliliters of water—about 1/15th of a teaspoon. However, academic research and independent studies suggest the actual number may be closer to 10 milliliters per query, if you take into account the entire lifecycle of the data center's cooling and power generation systems.
While the amount of water used for each individual interaction may seem small, when multiplied by billions of queries per day, the total water consumption becomes a significant environmental concern. Understanding these numbers is key to assessing the sustainability and hidden costs behind AI tools like ChatGPT.
What does OpenAI say about ChatGPT's water consumption?
So — how much water does ChatGPT actually use?
OpenAI has provided a rare behind-the-scenes look. In the esoteric world of AI infrastructure—where data center cooling, energy consumption, and cloud-based computing power collide—it's not easy to nail down an exact number. But one number stands out, tweeted straight from the source.
Sam Altman's "One Teaspoon" Statement
Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, came up with a striking and memorable statistic: each ChatGPT query consumes about 0.3 milliliters of water — about 1/15th of a teaspoon. Think smaller than a teardrop. Just enough that no one notices — until you measure it.
But here's the catch: Altman's figure only includes the direct water use inside server cooling systems—specifically, the on-site evaporative cooling at OpenAI's data processing facilities. It doesn't account for indirect water use—like the huge amounts needed to generate electricity, maintain AI hardware, or cool power plants that feed the grid.
Let's expand and calculate:
1 billion AI queries per day (conservative estimate)
× 0.3 mL per prompt
= approximately 85,000 gallons of water used daily
Equivalent to the water usage of about 1,000 US households, based on EPA standards (an average of about 82 gallons per household, per day).
In other words, ChatGPT's daily water needs, even by conservative estimates, are equivalent to that of a small town.
Still, Altman's number offers something valuable: a baseline. A minimum threshold for understanding the environmental 'footprint' of AI systems. But it's just the tip of the iceberg.
When taking into account the entire lifecycle of a large language model — including server cluster operations, cloud infrastructure energy needs, and the production of advanced chips and GPUs — the total water consumption increases significantly.
That's why many environmentalists and sustainability advocates are cautious about accepting this teaspoon-sized number.
Behind every interaction with ChatGPT is a network of resource-intensive processes running silently across global cloud networks. And water—the silent workhorse of modern computing—flows through all of them.
Is ChatGPT really harmful to the environment?
It depends on how you define 'harmful.' While each ChatGPT interaction uses only a small amount of water and electricity, the sheer scale of its use makes it a significant environmental concern. The carbon and water footprint of training and deploying large-scale AI models contributes to climate impact — though tech companies are working on solutions like renewable energy, more efficient models, and water stewardship programs.
In short, at first glance, ChatGPT's water usage may seem insignificant—just a few drops per query. But when multiplied by billions of queries per day, that water usage becomes a huge amount, raising real concerns about AI's environmental footprint.
Tin tốt là gì? Đây không phải là một nỗ lực vô ích. AI có thể được xây dựng bền vững hơn, nhưng nó đòi hỏi hành động có chủ đích trên mọi phương diện. Các công ty công nghệ phải thiết kế cơ sở hạ tầng sạch hơn, tối ưu hóa mô hình của họ và công bố các số liệu môi trường một cách minh bạch. Đồng thời, người dùng có thể hình thành những thói quen có chủ đích hơn, coi mỗi truy vấn như một phần của hệ sinh thái rộng lớn hơn.

Cuối cùng, tính bền vững của AI không chỉ nằm ở lượng nước mà một chatbot sử dụng. Nó còn nằm ở những lựa chọn mà chúng ta đưa ra — với tư cách là nhà phát triển, nhà quản lý và người dùng hàng ngày — để đảm bảo tương lai của trí tuệ nhân tạo không bị cạn kiệt.