Difference between Laptop CPU and PC CPU
Do you know what is the difference between Laptop CPU (chip) and PC CPU?
In terms of specifications, they are almost similar without too much difference, but those who have used both of them before agree that they do not have the same performance. So what difference caused this?
Specifically, the CPU on a Laptop is usually weaker than on the CPU of a PC if the same specifications. Okay, now let's try to analyze:
#first. Electric used

As you know, with a mobile device, the usage time factor is paramount, it is always one of the important criteria to evaluate whether to buy that device or not.
And laptops are similar, to optimize battery life for laptops, laptop CPUs will consume less power than chips of PCs (desktop computers), considering the same configuration.
So the same configuration parameters, but the CPU power of the Laptop cannot be equal to the CPU of the PC.
Maybe many of you will think that with the modern chip manufacturing process (1nm, 2nm, 5nm…) and new technology, the CPU will be very powerful but does not consume too much energy.
However, that is only on a theoretical basis, used under ideal conditions and they are often compared with previous generations. A law that can be said to be immutable (at least in the near future) is that the more powerful any electrical (electronic) device, the more energy it will consume (electricity).
=> So, in order to balance between performance and battery life, chip manufacturers for mobile electrical devices will have to balance it in the most reasonable way. So about this part of power consumption, the PC computer wins absolutely.
#2. Limited heat dissipation

An electrical (or electronic) device will need a source of energy to function, and it will require more energy when operating at full capacity or operating at high intensity.
The more power is used, the more heat will be generated and it will obviously cause the CPU to heat up quickly. At that time, the problem of heat dissipation was again raised for chip manufacturers.
Anyone who has ever 'dissected' looking at the cooling system on a laptop will probably find it has many inadequacies.
However, limitations in terms of physical size, installation space, or even weight and production costs, so everything cannot be resolved in the best way.
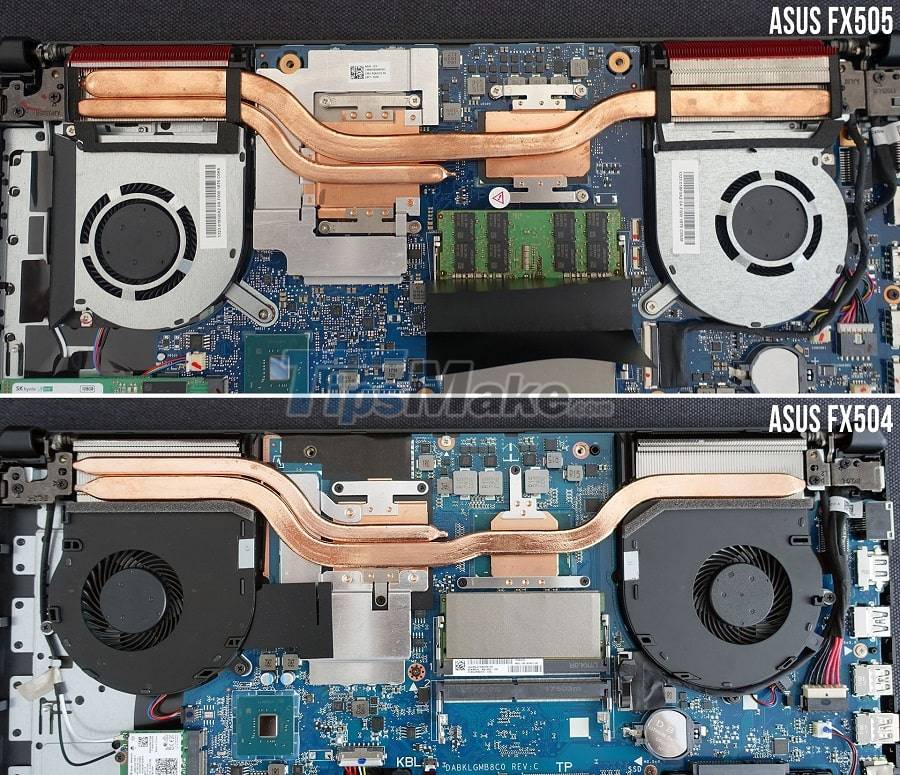
Laptop cooling system consists of only a temporary system called thick copper bar to conduct heat and usually at the end of the road will be a squirrel cage with very limited grilles and fans for cooling.
So obviously they can't be enough, especially when the laptop has very little free space => making the internal temperature unable to escape in the usual way.
On a PC, it's different, the PC case is very large, so the hot air emitted will be easier to push outside. Moreover, it is much easier to install more heat sinks on the PC, there is a lot of area for us to install.
#3. Size restrictions
Obviously, the laptop only has a small space to install the CPU. So the chips will also have to be designed smaller.
#4. Limited upgrade
The current popular laptop lines are almost 90% soldered to the CPU on the motherboard, that is, they are fixed by solder on the Mainboard.
Despite the fact that we can still remove it with specialized equipment and replace it with a more powerful CPU (as long as it is supported), in general, upgrading the CPU is relatively difficult.
Of course, these things should only be done in large centers that have full specialized equipment to do them.
Moreover, removing the old CPU from the mainboard is quite dangerous, because according to many experts, to remove the CPU from the solder joint will require a large amount of heat.
Then, when installing, you have to do the same thing to connect the solder joint with the CPU, this process if not careful will damage the CPU and surrounding components.
And as far as I know, after replacing the CPU, it is quite troublesome to intervene in the driver, so replacing and upgrading the CPU for Laptop is usually not recommended (of course for those CPUs that are soldered to death). on the mainboard).
As for the CPU on the PC, it is different, replacing and upgrading the CPU is extremely easy. Because most CPUs on PCs are removable, as long as the standard and mainboard support them, they can run comfortably.
#5. Do heavy work, don't think about Laptop

Through the above, we can see that Laptops are born for jobs that need mobility and neatness.
If you ask: why do manufacturers make powerful configuration versions, large sizes for what?
In my opinion, it is simply an economic issue, the products offered will attract a temporary set of customers called Laptop likes. That is, this group of customers knows the limitations and inadequacies of laptops, but they still use them because they simply like them.
As for users with moderate conditions like us, it is best if you have determined to do heavy work, you should not spend a large amount of money on a Laptop, but instead you should invest in a PC. most certain.
Otherwise, when using the laptop to do heavy work, please plug in the charger to use it, the power is strong enough to help the computer achieve better performance than when using the battery.
Every device is born for the purpose of serving people, it cannot be said that Laptop with the above limitations we consider it unnecessary.
Born and existed to this day, it proves that Laptops always have a place and will become more and more solid in the future when the need to work online, as well as people's demand for flexible use, is increasingly being promoted. .
Only a group of people who specialize in doing heavy work, requiring really high computer configuration, should switch to a PC to do it. Otherwise, I find the performance on the laptop has met most of the user's work needs.
Through this article, I believe you have a better understanding of the basic difference between CPU on Laptop and CPU on PC, right? Hope you have more useful information.