Cursor in C / C ++
Pointer - Pointer in C / C ++ language is easy to learn and interesting. Some tasks in the C / C ++ language are made easier by pointers, and other tasks become more flexible, such as in memory allocation, which cannot be performed without using a pointer. Therefore it is necessary to master the cursor when becoming a complete C / C ++ programmer. Now start with the simplest steps.
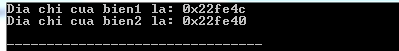
As you know, each variable in a given memory area and each memory location has its address defined so that it is easy to access using the operator (&) corresponding to its address in memory. Looking at the example below, it will print the address of the variable defined:
#include using namespace std ; int main () { int bien1 ; char bien2 [ 10 ]; cout << "Dia chi cua bien1 la: " ; cout << & bien1 << endl ; cout << "Dia chi cua bien2 la: " ; cout << & bien2 << endl ; return 0 ; } Running the above C / C ++ program will produce the following results:
What is a pointer?
A pointer is a variable in which its value is the address of another variable. For example, the address of the device. Like variables and constants, you must declare the pointer before you can use it to store any address of the variable. The general form of cursor declaration is as follows:
kieu_du_lieu * ten_bien ;
Here, kieu_du_lieu is the basic pointer data type, it is valid type in C language and ten_bien is the value name of the cursor. The * character part used in declaring pointers is the same as what you use for multiplication. However, in this declaration, the * character is designed to use pointer variables. Here are some valid declarations of pointers:
int * sv ; // tro toi mot gia tri nguyen double * nv ; // tro toi mot gia tri double float * luong ; // tro toi mot gia tri float char * ten // tro toi mot ky tu
The actual data type of the value of all pointers, be it integer, float, character, or other type, is like, some hexadecimal represent a memory address. The only difference of pointers of different data types is the data type of the variable or constant that the pointer points to.
How to use pointers in C / C ++
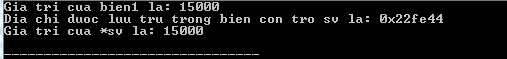
There are several important operations, which will help us work with pointers on a regular basis: a) we define pointer variables, b) assign the address of the variable to a subset and c) finally access Address variable values in pointer variables. This is done by the operator * returning the value of the variables contained in the address specified by this operator. Here are the uses of the above operations:
#include using namespace std ; int main () { int bien1 = 15000 ; // khai bao bien. int * sv ; // bien con tro sv sv = & bien1 ; // luu tru dia chi cua bien1 vao bien con tro sv cout << "Gia tri cua bien1 la: " ; cout << bien1 << endl ; // In dia chi duoc luu tru trong bien con tro sv cout << "Dia chi duoc luu tru trong bien con tro sv la: " ; cout << sv << endl ; // Truy cap gia tri co san tai dia chi cua bien con tro cout << "Gia tri cua *sv la: " ; cout << * sv << endl ; return 0 ; } Running the above C / C ++ program will produce the following results:
Details about pointers in C / C ++
Pointers have many concepts but are quite easy to learn and very important in C / C ++ language programming. Here are the important concepts about pointers in C / C ++, which are clearly presented to you, when you click on the corresponding link.
Concept DescriptionNull pointer in C / C ++
C / C ++ supports null pointers, which are a constant with a value of 0 defined in some standard librariesArithmetic pointer in C / C ++
There are 4 algebra operators that can be used on pointers: ++, -, +, -Pointers and arrays in C / C ++
What is the relationship between pointer and array? You check now.Cursor array in C / C ++
You can define arrays to hold pointers.Pointers to pointers in C / C ++
C / C ++ allows you to point to a pointer .Pass cursor to function in C / C ++
Pass a parameter by reference or address: both for passed parameters can be changed in the function called by the called function.Returns the pointer from the function in C / C ++
C / C ++ allows a function to return a pointer to a local variable, static variable, and also dynamically allocated memory.According to Tutorialspoint
Previous lesson: String (String) in C / C ++
Next article: Cursor NULL in C / C ++