Array (Array) in C / C ++
C / C ++ programming language provides data structures called arrays, stored in a set of data of the same type with fixed length. An array is used to store data sets, but it is useful if you think of an array of variables with the same type.
Instead of declaring variables in a discrete way, like variables so0, so1, . and so99, you can declare an array of values like so [0], so [1] and . so [99] to represent the separate values. A specific member of the array can be accessed via index (index).
All arrays include adjacent memory locations. The lowest address corresponds to the first member and the highest address corresponding to the last member of the array.
Declare an array in C / C ++
To declare an array in the C / C ++ language, you specify the type of variable and the number of elements required by that variable as follows:
Kieu Ten_mang [ Kich_co_mang ];
This is a one-dimensional array.Kich_co_mang must be an integer greater than 0 and Kieu must be valid in C / C ++ language. For example, declare an array of 10 elements called balance with type double, use the following statement:
char sinhvien [ 10 ];
Initialize arrays in C / C ++
You can initialize arrays in C / C ++ or each element or use a statement like this:
int hanghoa [ 5 ] = { 45 , 34 , 29 , 67 , 49 }; The number of values in quotation marks {} cannot be greater than the number of declared elements in square brackets [].
If you omit the array size, that array is large enough to hold the initialized values: You will create exactly one string with the same value as the above string by assigning each element one by one. Here is an example when assigning values to an element of an array:
int hanghoa [] = { 45 , 34 , 29 , 67 , 49 }; You can create the same array as you did in the previous example.
hanghoa [ 4 ] = 50 ;
The above statement assigns the 5th value of the array value 50.0. All arrays have the first index (0), this is called the basic index and the last element of the array has an index equal to the size of the array minus 1. Here is how to represent the image. illustrate the above declaration string through the index:
Access array elements in C / C ++
An array is accessed by indexing in the name of the array. Here is a way to access an array value:
int hocphi = hocphik60 [ 55 ];
The above statement takes the 56 element of the array and assigns this value to the variable hocphi. Here is an example of use with all the above descriptions:
#include using namespace std ; #include using std :: setw ; int main () { int n [ 10 ]; // n la mot mang gom 10 so nguyen // khoi tao gia tri cac phan tu cua mang n la 0 for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++ ) { n [ i ] = i + 100 ; // thiet lap phan tu tai vi tri i la i + 100 } cout << "Phan tu thu:" << setw ( 13 ) << "Gia tri la:" << endl ; // hien thi gia tri cua moi phan tu for ( int j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j ++ ) { cout << setw ( 7 )<< j << setw ( 13 ) << n [ j ] << endl ; } return 0 ; } Running the above C / C ++ program will produce the following results:

Array details in C / C ++
Arrays are a very important part of the C / C ++ language. Here are the key definitions related to a specific array that are more clearly presented to C / C ++ developers:
Concept DescriptionMultidimensional array in C / C ++
C / C ++ supports multidimensional arrays. The simplest pattern of this array is a two-dimensional arrayPointers to an array in C / C ++
You can point to the first element of the array simply by specifying the array name, not an indexPass arrays to functions as parameters in C / C ++
You can pass to a point function that points to an array by specifying an array name rather than an indexReturns array from function in C / C ++
C / C ++ allows a function to return an arrayMultidimensional array in C ++
C ++ supports multidimensional arrays. Here is the general pattern of a multidimensional array declaration:
kieu_du_lieu ten_mang [kich_co_1] [kich_co_2] . [kich_co_N];
For example, the following declaration creates an integer array of 3 dimensions: 5. 10. 4:
int hocphi [5] [10] [4];
Two-dimensional array in C ++
The simplest pattern of multidimensional arrays is a two-dimensional array. A two-dimensional array is essentially a list of one-dimensional arrays. To declare a two-dimensional integer array with size x, y, you should write the following:
kieu_du_lieu ten_mang [x] [y];
Here, kieu_du_lieu can be any valid data type and ten_mang will be a valid C ++ identifier.
A two-dimensional array can be as a table that has x rows and y columns. A two-dimensional array a contains 3 rows and 4 columns can be displayed as follows:

Thus, each element in array a is identified by an element name in the pattern a [i] [j], with a being the array name and i, j are subscript - the index is uniquely identified each part death in a.
Initialize a two-dimensional array in C ++
Multidimensional arrays can be initialized by defining values in square brackets for each row. The following is a row with 3 rows and each row contains 4 columns.
int a [3] [4] = {
{0, 1, 2, 3}, / * I don't know how to make a donation for the item 0 * /
{4, 5, 6, 7}, / * I don't want to give a blessing to the family that has 1 * /
{8, 9, 10, 11} / * I don't want to give a blessing to the other party 2 * /
}; Brackets, which indicate values are optional. The following initialization is equivalent to the above example:
int a [3] [4] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11}; Access elements of two-dimensional arrays in C ++
Two-dimensional array elements are accessed using indexes, eg row index and column index. For example:
int val = a [2] [3];
The above command will access the fourth element from the 3rd row of the array. You can check it again in the diagram above. Now that we look at the example below, we used nested loops to handle a two-dimensional array:
chứa
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// bring it back with 5 rows and 2 cots.
int a [5] [2] = {{0,0}, {1,2}, {2,4}, {3,6}, {4,8}};
The program of the experts in the field
for (int i = 0; i <5; i ++)
for (int j = 0; j <2; j ++)
{
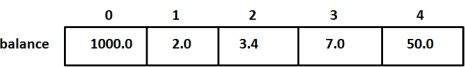
cout << "Family member a [" << i << "] [" << j << "] la:";
cout << a [i] [j] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
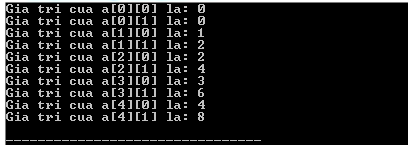
Running the above C ++ program will produce the following results:
As the above explained, you can have arrays with any number of dimensions, but most of the arrays you create will be one or two dimensions.
Pointers to an array in C ++
You may not understand this chapter until you have read the chapter about Cursor in C ++.
So suppose that you have a little understanding of pointers in C ++, so let's start: An array name is a constant pointer to the first element of the array. Therefore, in the declaration:
double phithuebao [ 50 ];
phithuebao is a pointer to & phithuebao [0], which is the address of the first element of the phithuebao array. Therefore, the following program segment assigns the address of the first element of phithuebao :
double * p ; double phithuebao [ 10 ]; p = phithuebao ;
Using the array name as the constant pointer is valid, and vice versa. Therefore, * (phithuebao + 4) is the official way to access data at phithuebao [4].
Once you save the address of the first element in p, you can access array elements using * p, * (p + 1), * (p + 2), . Below is the wallet example to refer to all the concepts mentioned above:
#include using namespace std ; int main () { // mang sau co 5 phan tu. double phithuebao [ 5 ] = { 1000.0 , 2.0 , 3.4 , 17.0 , 50.0 }; double * p ; p = phithuebao ; // hien thi gia tri cac phan tu trong mang cout << "Hien thi gia tri mang boi su dung con tro!" << endl ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++ ) { cout << "Gia tri cua *(p + " << i << ") la: " ; cout << *( p + i ) << endl ; } cout << "Hien thi gia tri mang boi su dung phithuebao lam dia chi!" << endl ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++ ) { cout << "*Gia tri cua (phithuebao + " << i << ") la: " ; cout << *( phithuebao + i ) << endl ; } return 0 ; } Running the above C ++ program will produce the following results:
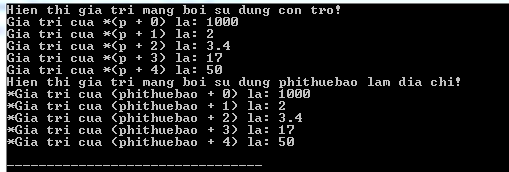
In the above example, p is a pointer to double, which means it can store the address of a variable of type double. Once we have the address in p, then * p will provide the available value at the address stored in p, as we have shown in the above example.
Pass arrays as function parameters in C ++
Returns an array from a function in C ++
C ++ does not allow you to return an entire array as a parameter to a function. However, you can return a pointer to an array by specifying the array name that is not an index. You will learn about pointers in the next chapter, so you can skip this chapter until you understand the concept of Cursor in C ++.
If you want to return a one-dimensional array from a function, you will have to declare a function that returns a pointer as in the following example:
int * tenHam () { . . . } The second point to remember is that C ++ does not support returning the address of the local variable to outside the function, so you will have to define the local variable as a Static variable.
Now suppose the following function will generate 10 random numbers and return them using an array and call this function as follows:
#include #include #include /* thu vien cho ham srand, rand */ using namespace std ; // phan dinh nghia cua ham de tao va tra ve cac so ngau nhien. int * soNgauNhien ( ) { static int r [ 10 ]; srand ( ( unsigned ) time ( NULL ) ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; ++ i ) { r [ i ] = rand (); cout << r [ i ] << endl ; } return r ; } // ham main de goi phan dinh nghia ham tren. int main () { // mot con tro tro toi mot so nguyen. int * p ; p = soNgauNhien (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++ ) { cout << "Gia tri cua *(p + " << i << ") la: " ; cout << *( p + i ) << endl ; } return 0 ; } Running the above C ++ program will produce the following results:

According to Tutorialspoint
Previous post: Number in C ++
Next lesson: String (String) in C / C ++