20 Great Physicists Who Changed How We Understand the World
With their extraordinary minds, physicists have come up with theories, ideas, and discoveries that help people completely change their perception of the world around them as well as the vast universe.
Physics is vast, present everywhere from human daily life to activities in the most distant parts of the universe. The research works of these world-famous physicists have contributed to changing human perception of the world.
1. Galileo Galilei (1564-1642)

He is considered one of the greatest scientists and physicists of all time and the " father of modern physics ". He was the first to assert that "all objects fall freely with the same constant acceleration ". This is one of his most famous achievements.
Galileo Galilei was also the one who created and developed the telescope to help people observe astronomical phenomena in the universe. Thanks to the results obtained, he discovered that " the sun is the center of the solar system" , the surface of the moon has jagged mountains and the existence of a black hole in the sun.
2. Isaac Newton (1643-1727)

Most of us know Isaac Newton for his 3 Newtonian laws of motion and his law of universal gravitation. Besides, he also introduced the law of conservation of momentum and the dispersion of light through a prism. These are basic knowledge used to teach in schools.
One of his groundbreaking ideas about the universe was that the motion of objects in the sky must obey the same physical laws as the motion of objects on earth.
3. Michael Faraday (1791-1867)

Michael Faraday made groundbreaking discoveries in the study of magnetism and electricity. He discovered electromagnetic induction in 1831 and invented the world's first electric transformer.
In 1839, he proposed a fundamental relationship between electricity and magnetism.
His name is given to many concepts and units such as Faraday's constant and Faraday's law of induction.
4. James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879)

In 1864, James Clerk Maxwell published his work on the dynamical theory of the electromagnetic field. This theory showed that magnetism, electricity, and light are all manifestations of the same phenomenon: the electromagnetic field.
5. Wilhelm Rontgen (1845-1923)

In 1895, Wilhelm Röntgen accidentally discovered electromagnetic radiation in a range of wavelengths from which X-rays were created. Today, X-rays are widely used in medicine and many other industries.
6. Marie Curie (1867-1934)
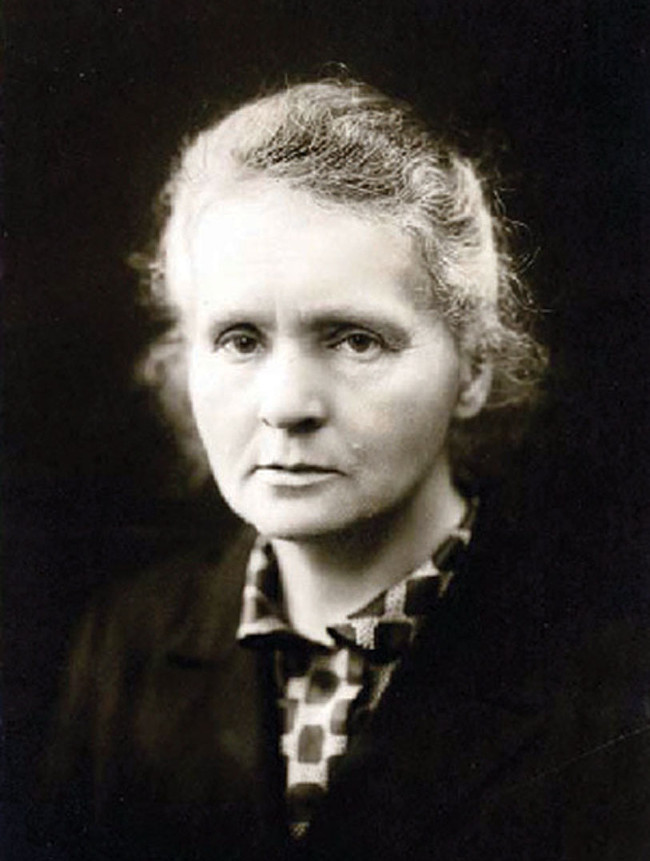

In 1896, Marie Curie discovered radioactivity (found by the properties of X-rays) and introduced the technique of isolating isotopes. At the same time, she and her husband, Pierre Curie, discovered two radioactive elements, radium and polonium.
7. Joseph John Thomson (1856-1940)
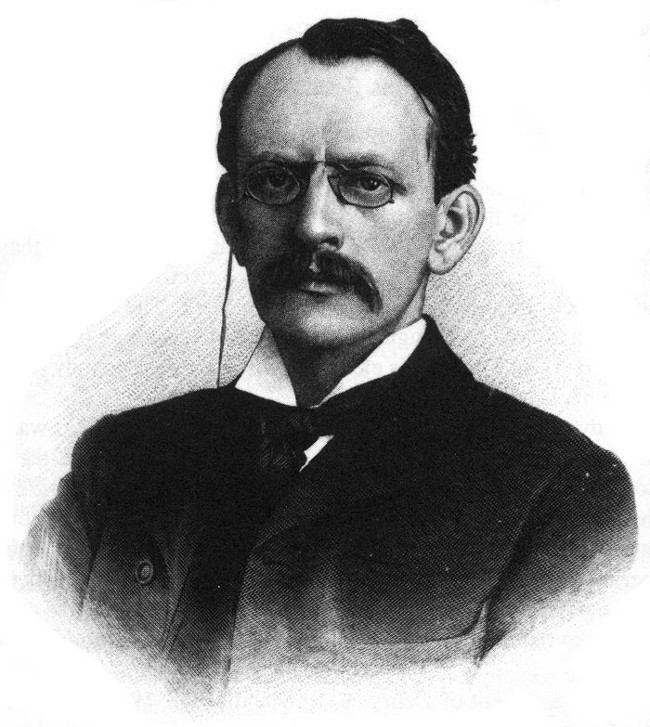

Before the discovery of electrons by Joseph John Thomson, atoms were understood to be the smallest particles and basic building blocks of matter and had never been seen.
Joseph John Thomson was the one who discovered and proved that there exist smaller particles that make up matter than atoms, namely electrons.
8. Max Planck (1858-1947)
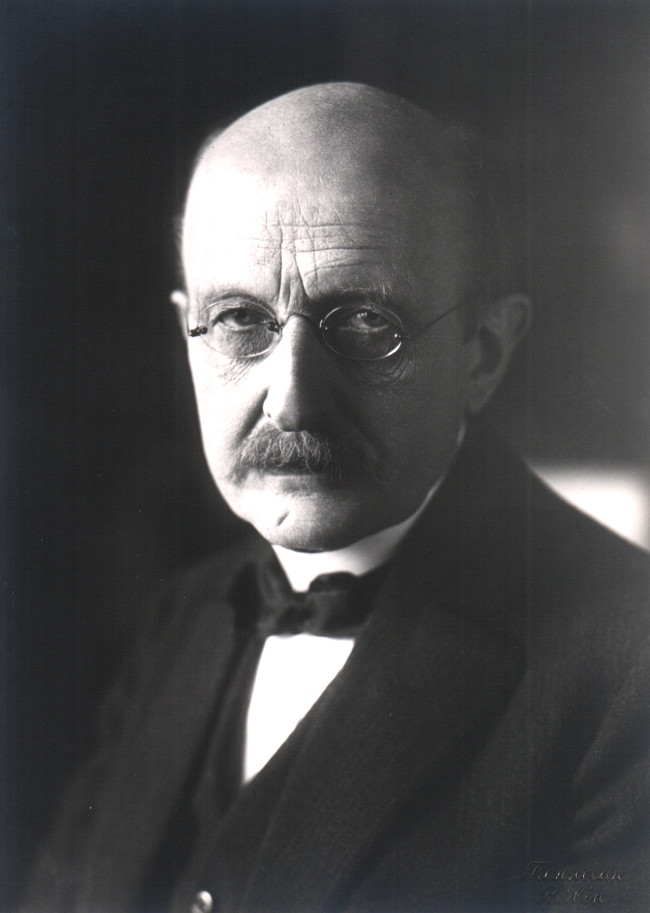
Max Planck is the "father" of quantum mechanics. In 1900, Max Planck introduced the concept of quantum, a discrete and smallest quantity of a physical entity.
He was the one who established the value for the Planck constant: ε =hv, which is a fundamental constant of physics that appears in problems of quantum physics.
9. Albert Einstein (1879-1955)
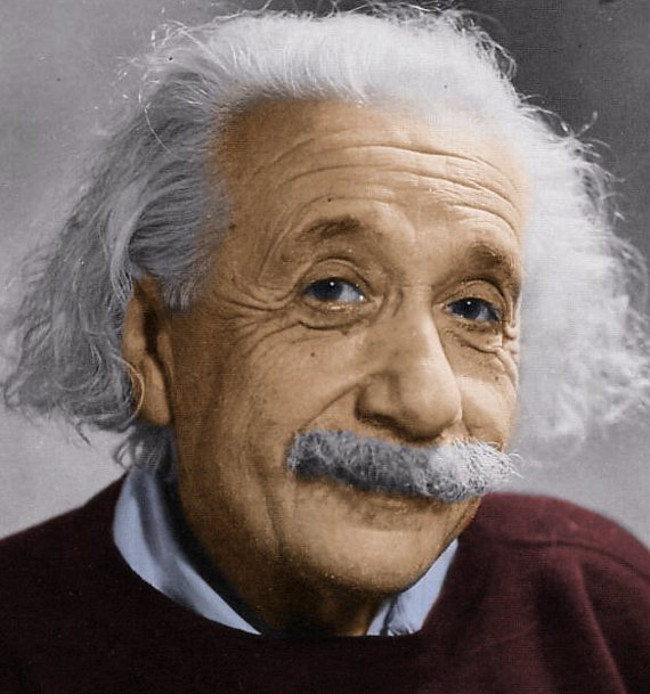

In 1905, Albert Einstein published a paper on the theory of relativity, in which he described that the speed of light is always constant, and at the speed of light, time stands still and mass is infinite. He came up with the formula E=mc2.
In 1915, Einstein published his general theory of relativity, a fundamental theory about the nature of time, space, and gravity. It describes gravity as a result of the curvature of spacetime.
10. Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937)
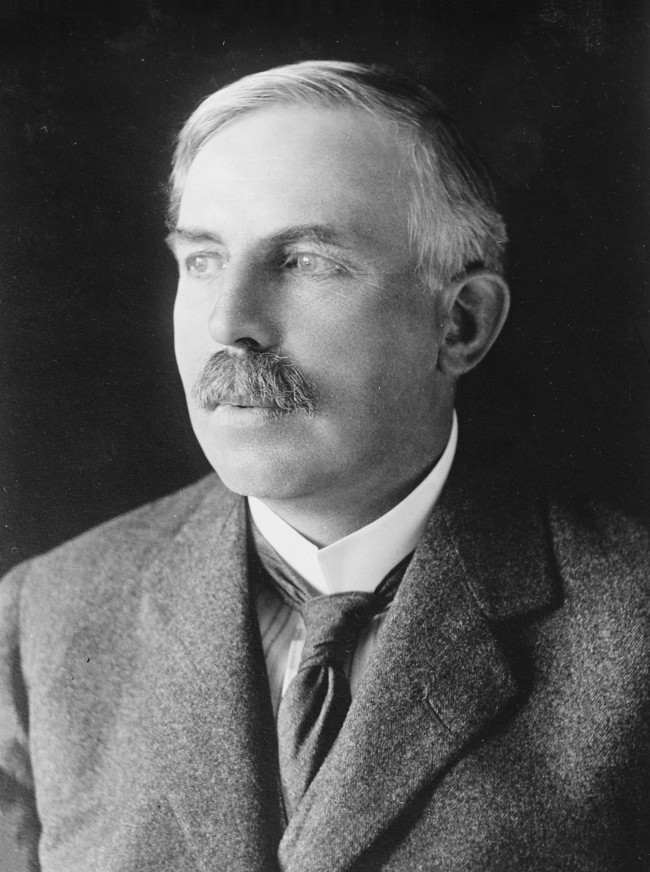

Ernest Rutherford was a physicist who worked on radioactivity and atomic structure. In 1911, he published one of his two most important works, the atomic model. He demonstrated that the nucleus in the center accounted for most of the mass of the atom.
His second important work was the discovery of the proton in 1920.
11. Neils Bohr (1885-1962)
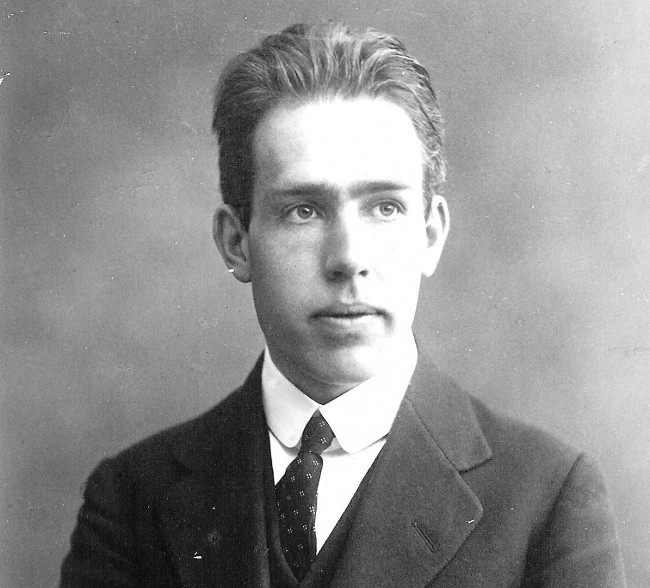

Neils Bohr, a famous Danish physicist is known for his theory of atomic structure published in 1913. He showed that an atom has a nucleus at the center with electrons revolving around it. Neils Bohr played an important role in the birth of quantum mechanics.
12. Wolfgang Pauli (1900-1958)
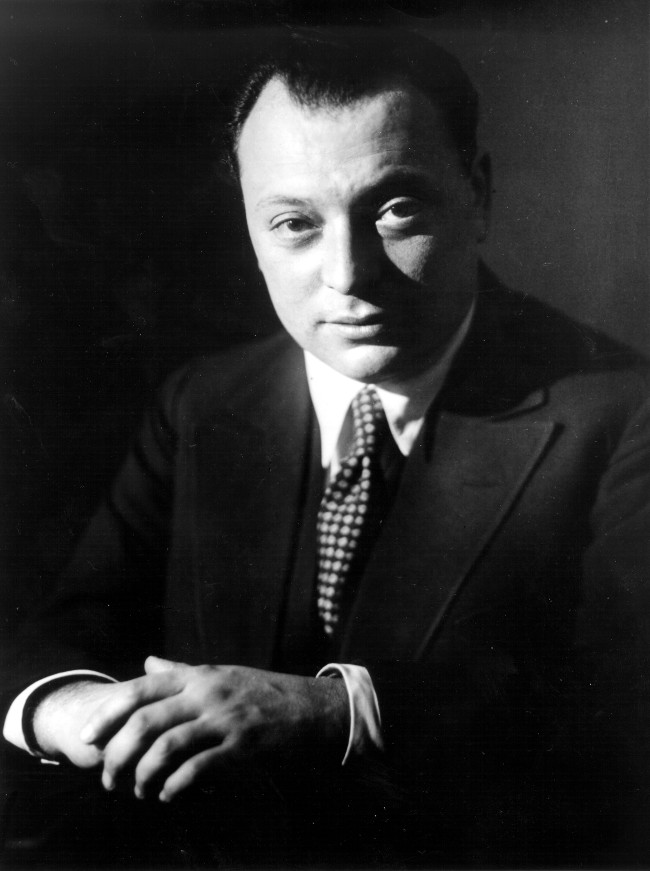

Wolfgang Pauli's famous research works are on quantum theory and spin theory.
In 1925, Wolfgang Pauli discovered the Exclusion Principle, the key to understanding the properties of nebulae and stars. He was the one who proposed the existence of neutrinos, particles that are very light and have difficulty interacting with matter, in 1931.
13. Erwin Schrödinger (1887-1961)
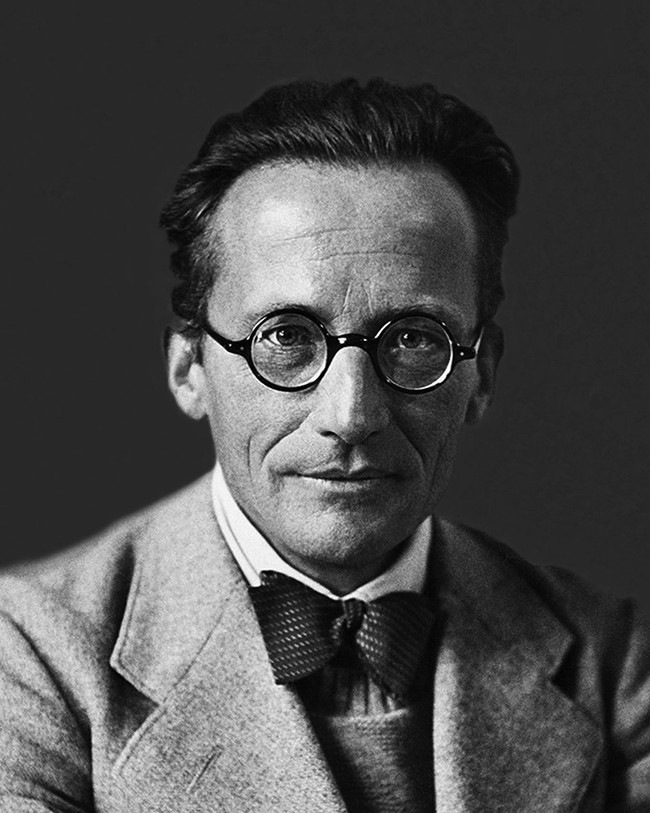

In 1926, Erwin Schrödinger introduced the Schrödinger wave equation, the fundamental equation of quantum physics, which describes wave mechanics.
In 1935, he came up with one of the most famous thought experiments in history, 'Schrödinger's Cat'.
14. Paul Dirac (1902-1984)
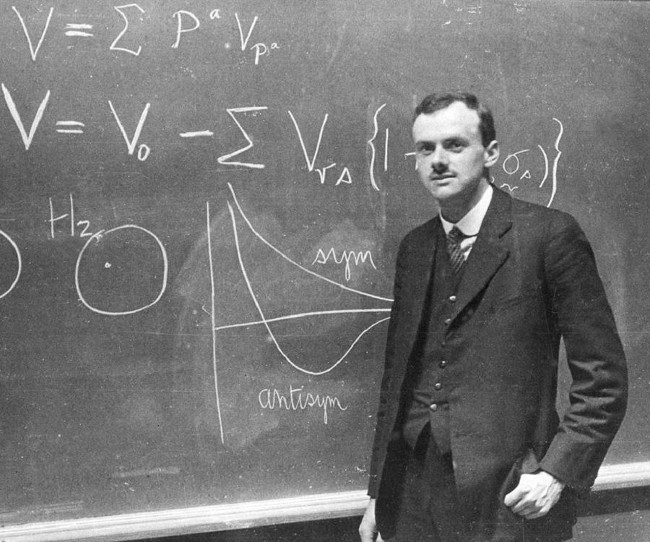
Paul Dirac's most highly regarded work was predicting the existence of antimatter, particles with equal but opposite charge to electrons, like the positron (or antielectron) in 1928.
15. Werner Heisenberg (1901-1976)
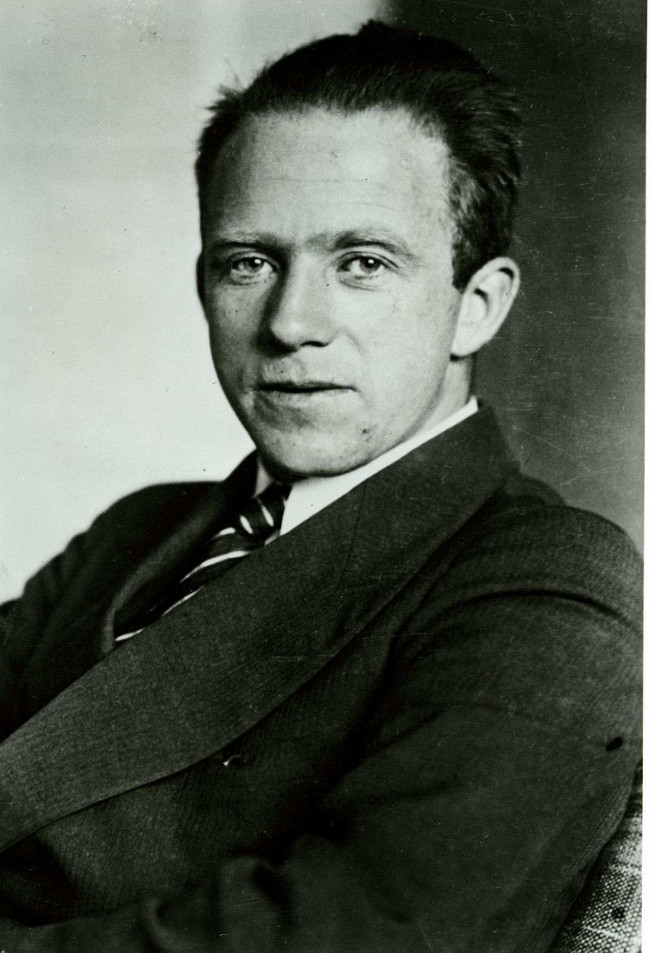

Werner Heisenberg is famous for his 1927 uncertainty principle, a key principle of quantum mechanics. This principle places fundamental limits on the accuracy of experimental measurements in quantum mechanics.
16. Enrico Fermi (1901-1954)
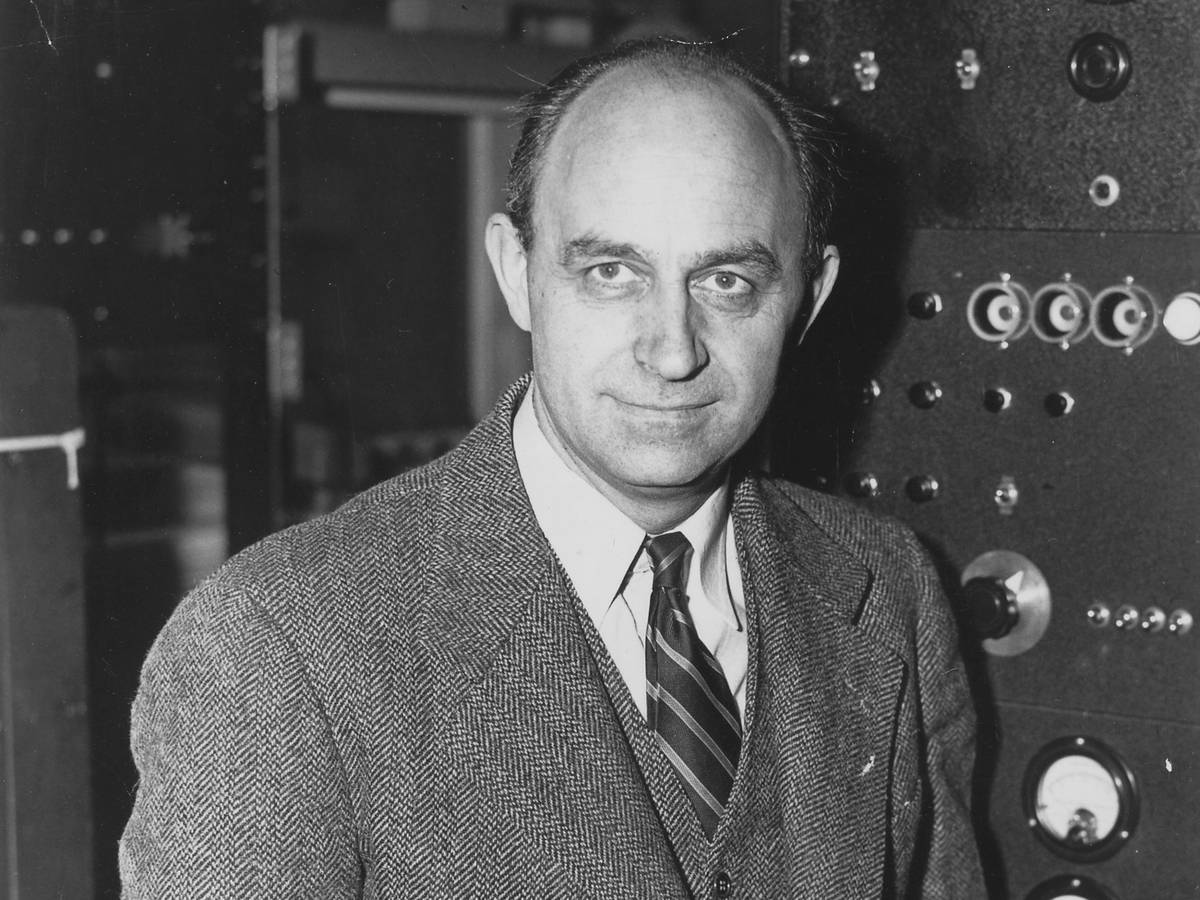

Enrico Fermi is famous for his work on the first nuclear reactor in the Manhattan Project. He also made major contributions to quantum theory, as well as nuclear and elementary particle physics.
17. J. Robert Oppenheimer (1904-1967)
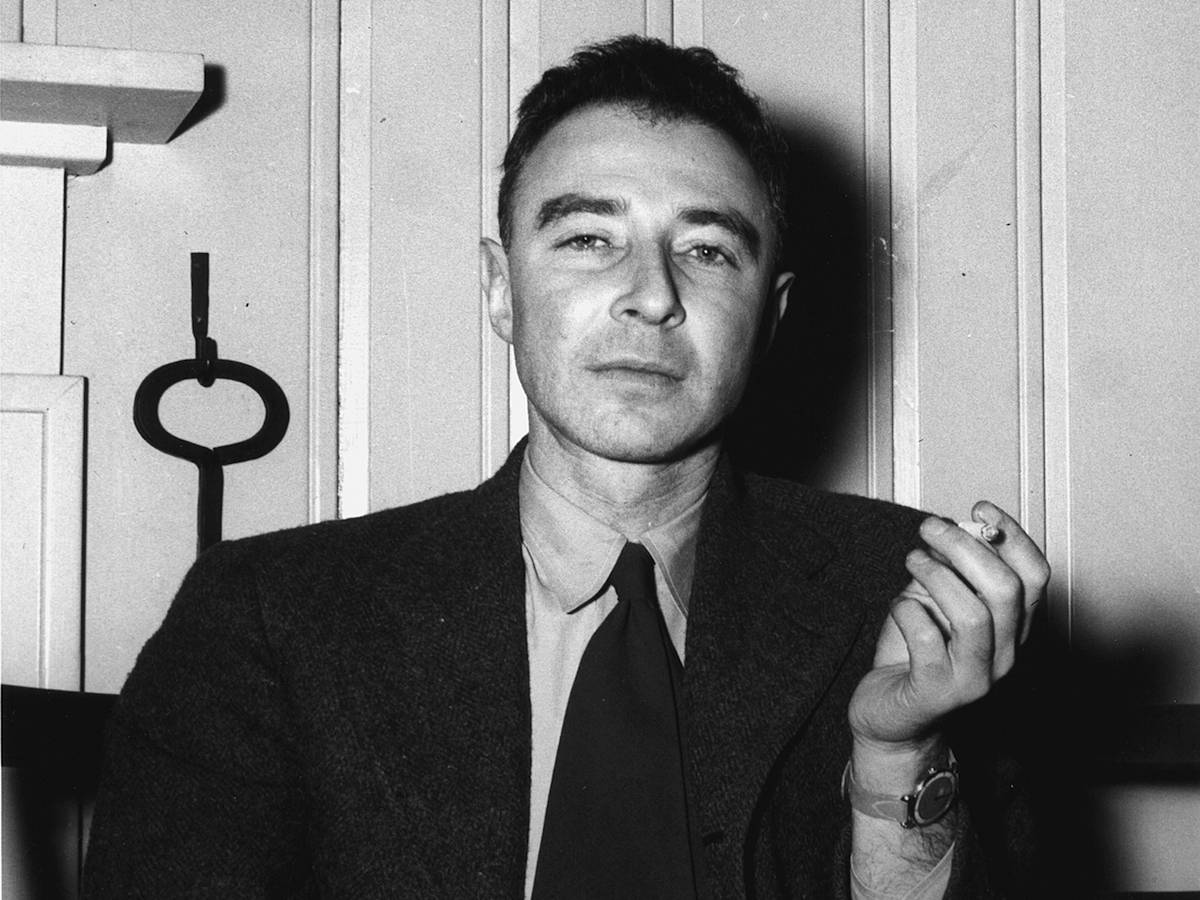

J. Robert Oppenheimer is best known for his work on the Manhattan Project, which directed the production of the first atomic bombs.
18. Richard Feynman (1918-1988)
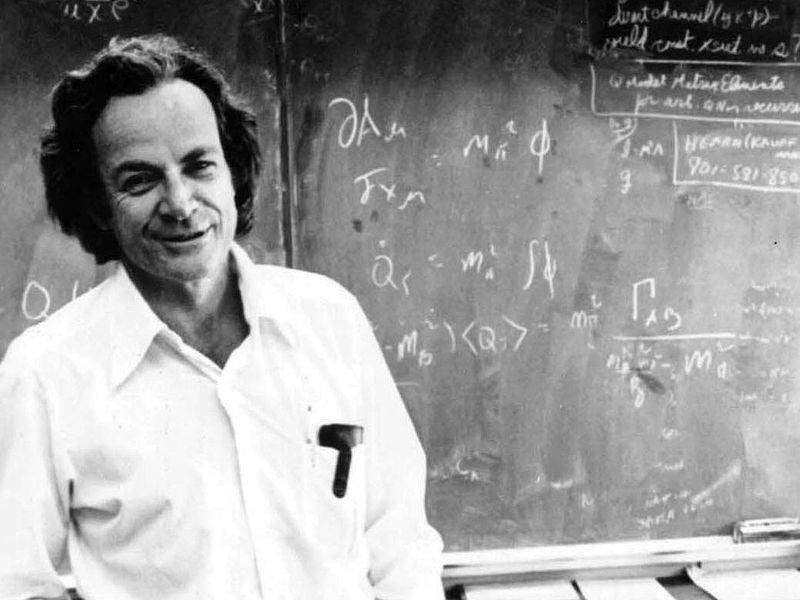

Richard Feynman is best known for his contributions to the theory of quantum electrodynamics, a theory that combines special relativity and quantum mechanics to seek a deeper understanding of the universe.
19. Murray Gell-Mann (1929-2019)
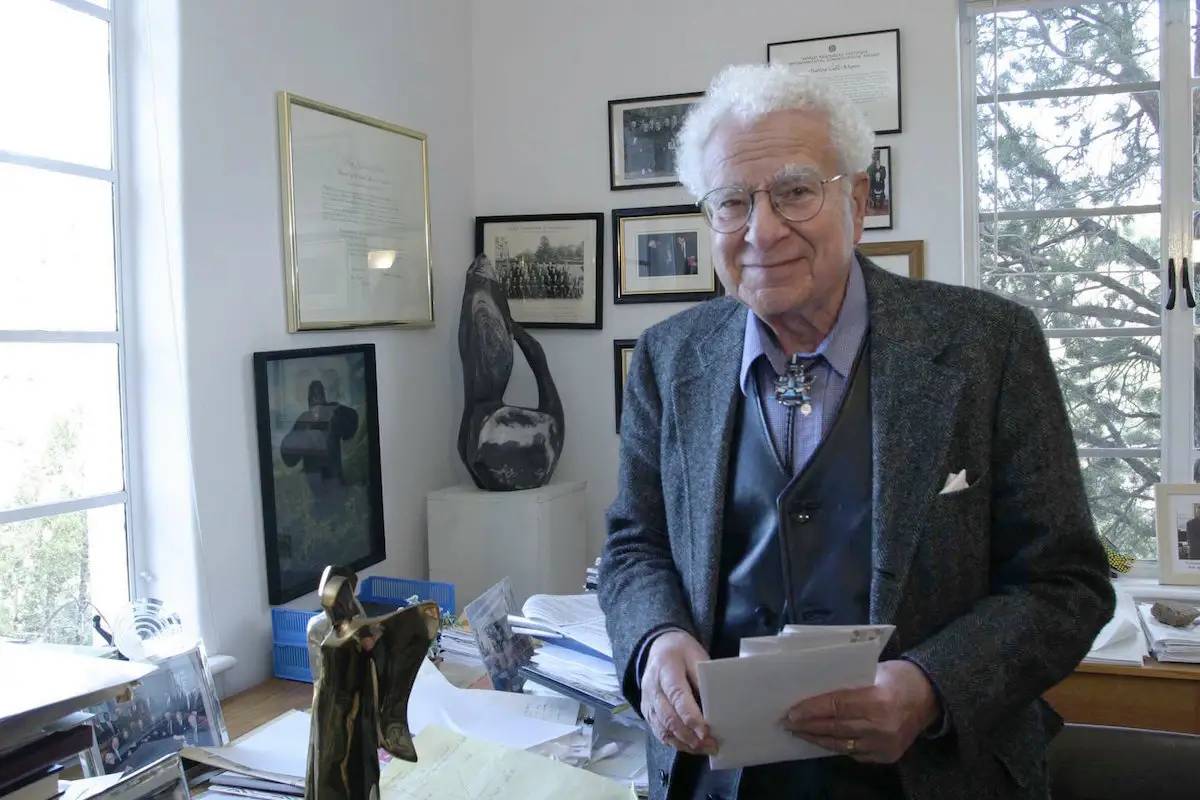

In 1961, Murray Gell-Mann proposed a classification of eight subatomic particles, and in 1964 he proposed the quark hypothesis, which suggested that protons, neutrons, and other hadrons were actually made up of even smaller particles, called quarks.
20. Vera Rubin (1928-2016)
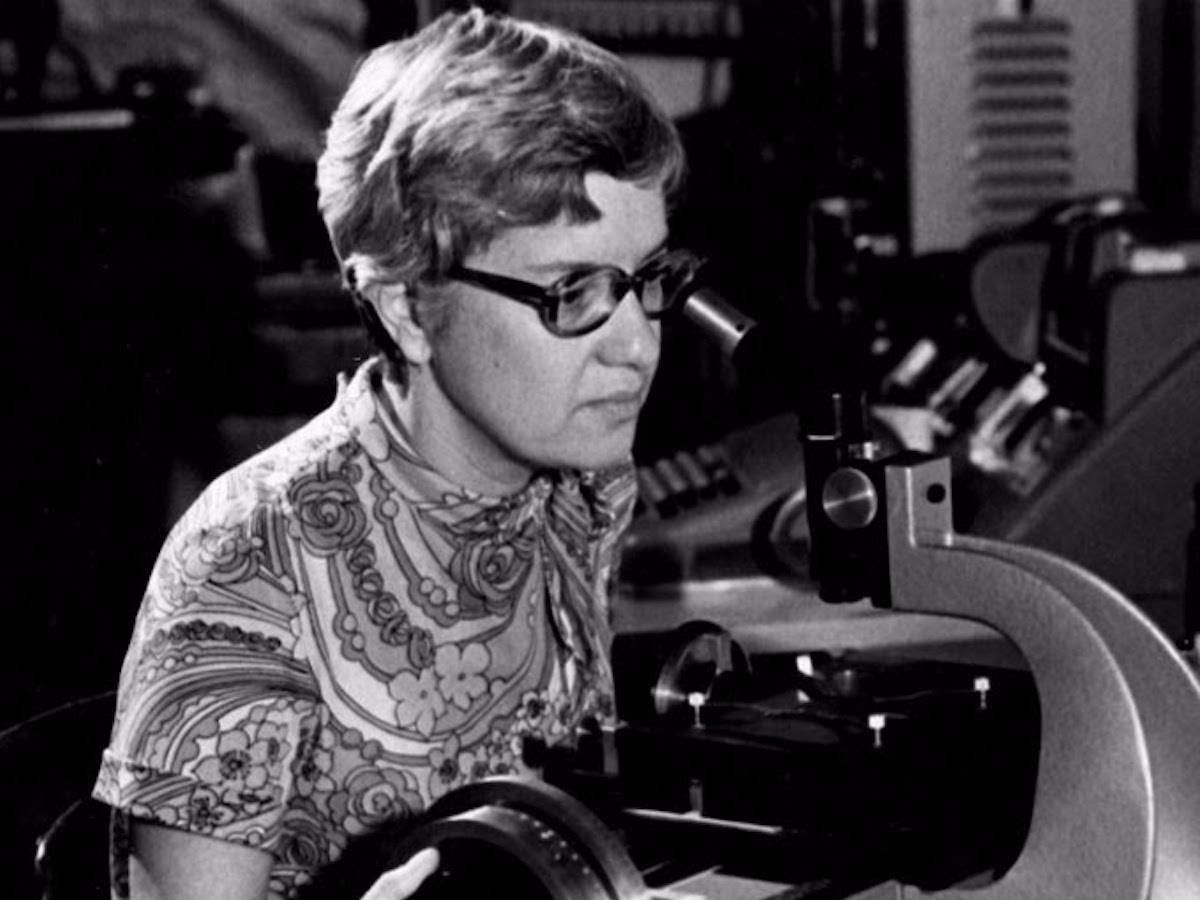

Although Vera Rubin was originally an astronomer, her studies of the rotation of galaxies led her to the first concrete evidence that 84% of the universe is made up of mysterious, invisible particles of dark matter. The search for these particles revolutionized the fields of particle physics and astrophysics.
You should read it
- ★ The mysterious journey of Galileo Galilei's missing fingers
- ★ What do you know about the great genius Albert Einstein
- ★ Isaac Newton discovered that the gravitational force of a falling apple was anecdote
- ★ 9 most famous Nobel prizes in history, contributing to change the world
- ★ The mystery behind the stolen brain of Albert Einstein genius