10 great astronomers have made the most important contribution to the astrophysical field of humanity
The list below honors 10 of the greatest astronomers of all time like Galilei, Einstein, Claudius Ptolemy, Hawking . Let's find out what important contributions they have made to the field. Astrophysics of humanity.
- 6 famous inventions but made scientists regret for life
- Eccentric habits of 10 world geniuses
1. Claudius Ptolemy (90-168)
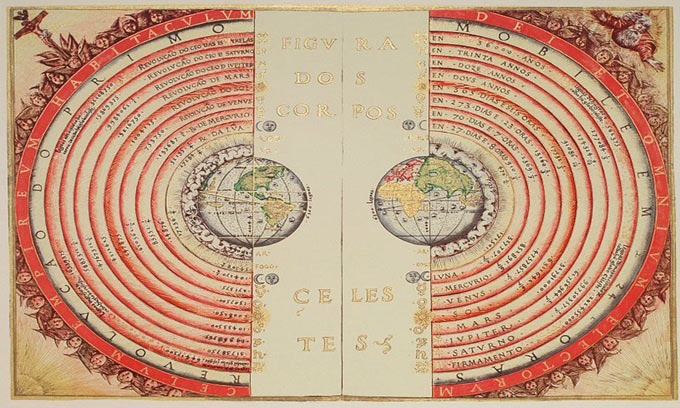
Photo: Bartolomeu Velho.
Claudius Ptolemy was a geographer, mathematician and astronomer whose ancestors were Greek but lived and worked in Egypt.
In the 2nd century, Ptolemy published the Almagest, a classic work that gave a comprehensive treatise on the movement of his stars and planets. In the book, Ptolemy also mentions the central position of the Earth's solar system.
Ptolemy's system provided information boards that allowed the prediction of planets. Ptolemy also gave the first list of 48 constellations, their names still exist today.
More than 12 centuries later, Ptolemy's thought was accepted but his proposed model was inaccurate and replaced by heliocentric theory.
2. Nicolaus Copernicus (1473 - 1543)

Photos: Wikimedia
This Polish astronomer proposed the Sun model at the center of heliocentrism in his book 'De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium - The Rotation of Celestial Bodies'. This model of Copernicus broke the conception of the Earth at the center of the solar system that existed for centuries.
It wasn't until nearly a century later that Copernicus's idea was accepted. In 1632, Galileo made the claim that the Earth orbiting the Sun was based on Copernicus' work.
3. Johannes Kepler (1571 - 1630)

Photo: Ancient Origins.
He was a German mathematician, astrology and astronomer. Kepler was one of the pioneers in the Scientific Revolution of the 16th-17th century when he introduced laws of celestial motion based on Copernic's view of the solar system.
Kepler rejected Copernicus' hypothesis that the planets moved perfectly around the Sun and showed that the planets moving in elliptical orbit with the Sun were focal points. In addition, he asserts that planets do not move at the same speed in orbit, connecting a planet with the Sun sweeping through equal areas in equal intervals.
4. Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642)
 Photo: Edukalife.
Photo: Edukalife.
Galileo was an Italian physicist, astronomer, and mathematician who played an important role in the scientific revolution in the 17th century.
Galileo did experiments and improved telescopes so that he could discover four large moons of Jupiter.
5. Isaac Newton (1642 - 1727)
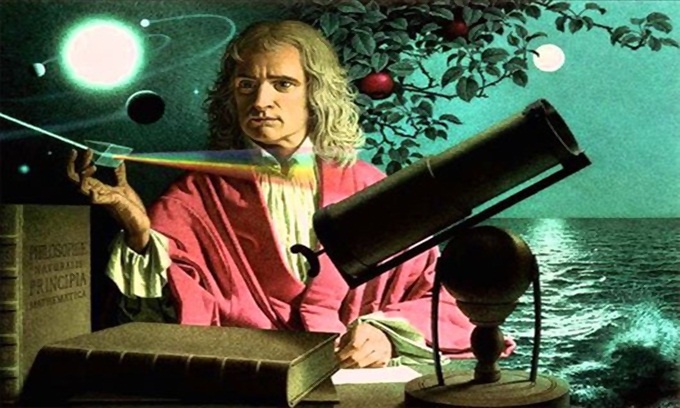 Photos: History Collection.
Photos: History Collection.
Many people believe that Isaac Newton is the most influential scientist in all sciences. He invented the calculus of calculus and made many important discoveries in the fields of optics, mechanics, experimental chemistry, alchemy and theology. The theory of universal gravitation and the three laws of motion (Newton's law) completely changed contemporary science.
Newton completely eliminated heliocentrism by pointing out the unity of Kepler's law of planetary motion and his theory of gravity.
6. Christiaan Huygens (1629 - 1695)

Photo: Biografie.
A Dutch astronomer with many contributions in astronomy, mathematics, and physics. In 1655, Huygens used his own made telescope to discover a thin, flat belt around Saturn's moon and Titan. That same year, he observed and sketched the Orion nebula shape, as well as proposed light wave theory.
7. Giovanni Cassini (1625 - 1712)

Photos: Wikimedia.
Cassini is a mathematician, astrology and astronomer born in Perinaldo, Republic of Genoa (Italy today).
In 1672, Cassini and his colleague Jean Richer used the parallax method to determine the distance from Mars and the Sun to Earth and allowed the first estimates of size. of the solar system.
Cassini was the first to observe and discover four Saturnian satellites (Iapetus, Rhea, Tethys and Dione) and discover the dividing line on Saturn's belt. His name is named for the Cassini spacecraft launched into space in 2004, tasked with studying Saturn and its natural satellites.
8. Charles Messier (1730-1817)

Photo: Famous People.
Charles Messier is a French scientist. When he was young, Messier began exploring and recording nebulae, since these objects were often mistaken for comets.
He made a list of objects in the sky at great distances such as star clusters and galaxies. In 1771, Messier published the first list of 45 objects, which he later added and expanded to 103 objects. Later, astronomers added lists with a total of 110 objects.
9. Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955)
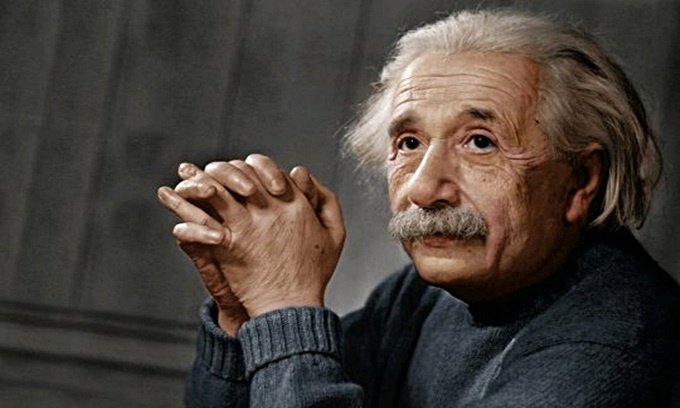

Photo: Francis.
Einstein was named the father of modern physics. His greatest achievement was the successful construction of general relativity and the famous formula E = mc2, where E is energy, m is mass and c is the speed constant of light, which has many influences. to astrophysics theory.
10. Stephen Hawking was born on January 8, 1942
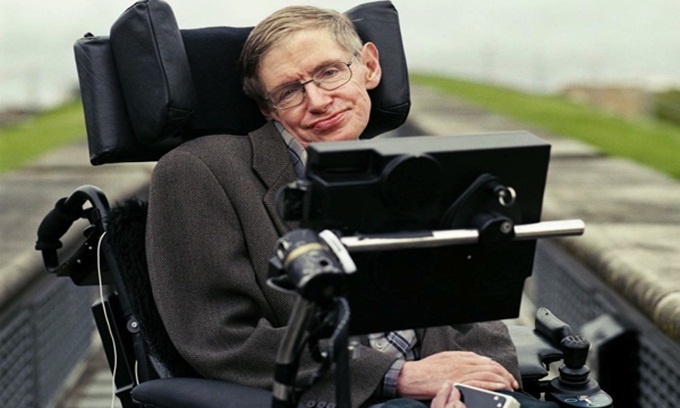

Photos: Wikimedia.
Hawking is a theoretical physicist and cosmologist who was born in Oxford and grew up in St Albans, England. He made great contributions in the field of space exploration, black holes, relativity and quantum gravity. The most striking is the collaboration with British physicist Roger Penrose to conclude that Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity describes time and space starting from the Big Bang and ending in holes. black.
You should read it
- ★ What do you know about the great genius Albert Einstein
- ★ Isaac Newton discovered that the gravitational force of a falling apple was anecdote
- ★ Stephen Hawking's life through photos
- ★ Download Stephen Hawking's space doctoral thesis - Download Properties of Expanding Universes
- ★ The mystery behind the stolen brain of Albert Einstein genius