How to Reset SA Password in Sql Server
Method 1 of 3:
Using Windows Authentication
-
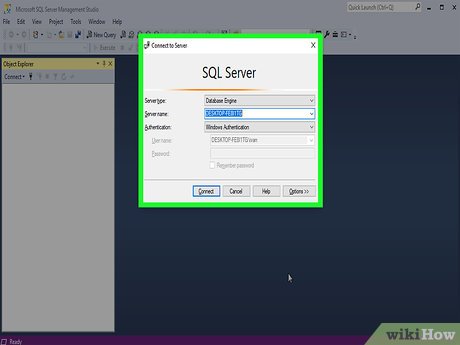 Understand how this method works. If Windows Authentication is enabled for your server, you can use it to log into your server without having to enter a password. After you're logged in, you can easily change the SQL server's password.[1]
Understand how this method works. If Windows Authentication is enabled for your server, you can use it to log into your server without having to enter a password. After you're logged in, you can easily change the SQL server's password.[1]- If Windows Authentication isn't enabled, you'll need to either use Single-User Mode or use Command Prompt to reset your password.
-
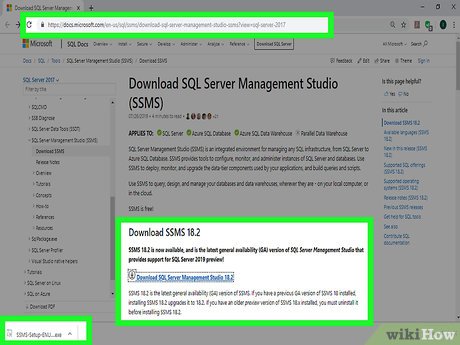 Make sure that SSMS is installed. SSMS is a user interface which allows you to change different aspects of your SQL Server settings in a window rather than in Command Prompt. If you don't have SSMS installed, do the following:
Make sure that SSMS is installed. SSMS is a user interface which allows you to change different aspects of your SQL Server settings in a window rather than in Command Prompt. If you don't have SSMS installed, do the following:- Go to the SSMS installation page in a browser.
- Click the Download SQL Server Management Studio 17.6 link.
- Double-click the downloaded SSMS setup file.
- Follow the on-screen prompts to install SSMS.
- Open SSMS. Type sql server management studio into Start, then click Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio 17 at the top of the Start window.
- Select the correct authentication. Click the "Authentication" drop-down box, then click Windows Authentication in the menu.
- Click Connect. It's at the bottom of the window. If Windows Authentication is allowed for your account, doing so will log you into your server's dashboard.
- Expand your server's folder. If your server's folder in the upper-left side of the window doesn't have several options below it, click the + icon to the left of it to expand it.
- Expand the "Security" folder. It's below the server's name.
- Expand the "Logins" folder. You'll find this in the group of options below the "Security" folder.
- Double-click sa. It's in the "Logins" group of options. Doing so opens your System Administrator properties window.
- Enter a new password. Type your new password into both the "Password" and the "Confirm password" text fields near the top of the window.
- Click OK. It's at the bottom of the window. Doing so will change your password and close the properties window.
Method 2 of 3:
Using Single-User Mode
- Understand how this method works. Even if you've locked out your only account, you can add a user and give them administrator permissions by using the Command Prompt. After doing this, you can use the new user's credentials to log into your SQL Server page, from which point you can change the SA password.[2]
- Make sure that SSMS is installed. SSMS is a user interface which allows you to change different aspects of your SQL Server settings in a window rather than in Command Prompt. If you don't have SSMS installed, do the following:
- Go to the SSMS installation page in a browser.
- Click the Download SQL Server Management Studio 17.6 link.
- Double-click the downloaded SSMS setup file.
- Follow the on-screen prompts to install SSMS.
- Open Command Prompt in administrator mode. Open Start, then do the following:
- Type in command prompt
- Right-click Command Prompt
- Click Run as administrator
- Click Yes when prompted.
- Stop SQL Instance from running. Type in net stop MSSQLSERVER and press ↵ Enter. This will stop the currently running SQL services.
- Restart SQL in Single-User Mode. Type in net start MSSQLSERVER -m"SQLCMD" and press ↵ Enter.
- You won't see any indication that you're running in Single-User Mode at this point, but you should see the phrase "The SQL Server service was started successfully" appear.
- Connect to SQL. Type in sqlcmd and press ↵ Enter. Doing so opens the SQL command line.
- Create a new user and password. You'll do this with typed commands in the SQL command line:
- Type in CREATE LOGIN name WITH PASSWORD='password' where "name" is the account name and "password" is the new password.
- Press ↵ Enter.
- Type in GO and press ↵ Enter.
- Add the user to the System Administrator role. Type in SP_ADDSRVROLEMEMBER name,'SYSADMIN' where "name" is the account name, press ↵ Enter, and then type in GO and press ↵ Enter.
- Exit the SQLCMD command line. Type in exit and press ↵ Enter.
- Restart SQL in regular mode. You can cancel Single-User Mode by typing in net stop MSSQLSERVER && net start MSSQLSERVER and pressing ↵ Enter.
- You should see the "The SQL Server service was started successfully" phrase appear again; at this point, you can close Command Prompt.
- Open SSMS. Type sql server management studio into Start, then click Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio 17 at the top of the Start window.
- Select the correct authentication. Click the "Authentication" drop-down box, then click SQL Server Authentication in the menu.
- Log in with the new user's credentials. Click the "Login" drop-down box, then click the name of the user you just created.
- Enter the password. Type the user's password into the "Password" text box near the bottom of the window.
- Click Connect. It's at the bottom of the window. As long as you adequately entered your username and password, this will open your server's dashboard.
- Expand your server's folder. If your server's folder in the upper-left side of the window doesn't have several options below it, click the + icon to the left of it to expand it.
- Expand the "Security" folder. It's below the server's name.
- Expand the "Logins" folder. You'll find this in the group of options below the "Security" folder.
- Double-click sa. It's in the "Logins" group of options. Doing so opens your System Administrator properties window.
- Enter a new password. Type your new password into both the "Password" and the "Confirm password" text fields near the top of the window.
- Click OK. It's at the bottom of the window. Doing so will change your password and close the properties window.
Method 3 of 3:
Using Command Prompt
- Open Start. Click the Windows logo in the bottom-left corner of the screen. This will open the Start menu.
- Search for Command Prompt. Type in command prompt, then wait for Command Prompt to appear at the top of the Start menu.
- Right-clickCommand Prompt. Doing so will prompt a drop-down menu.
- Click Run as administrator. It's in the drop-down menu.
- Click Yes when prompted. This will confirm your decision to open Command Prompt in administrator mode. The Command Prompt window should open.
- Enter the first command. Type in osql -L and press ↵ Enter.[3]
- Enter the second command with your server's name. Type in OSQL -S server -E where "server" is replaced by your server's name, then press ↵ Enter.
- Create a new password. Type in EXEC sp_password NULL, 'password', 'sa' where "password" is replaced by the password that you want to use, then press ↵ Enter.
- For example, to set your password as "rutabaga123", you would type EXEC sp_password NULL, 'rutabaga123', 'sa' into Command Prompt.
- Execute the command. Type in GO, then press ↵ Enter. Type exit, then press ↵ Enter to exit OSQL.
- Attempt to log into SQL Server. Do so by using your administrator credentials and your new password. If you're able to log into SQL Server, your password was successfully changed.
Update 05 March 2020
You should read it
- How to Change How Long Until a Mac Asks for Your Password
- Turn off the domain password request feature in Windows Server 2003
- How to Unlock SQL Server Account
- How to Password Protect Files on a Mac
- How to Change Your Password on Windows
- SQL Server 2005 - Hack encrypted data by password
- Configure Windows Server 2008 to remotely access SSL VPN Server (Part 3)
- How to Use a Password Reset Disk (Windows)
- How to Change Your Password in Windows 8
- How to Bypass Windows 7 Password
- How to Change Your Apple ID Password
- 8 ways to secure SSH server connections on Linux
Maybe you are interested
How to Recognize Sent Messages in Apple Messages Invite to download the space theme wallpapers on the NASA XS inspired by NASA How to make delicious Cupcake at home How to preserve banh chung and banh Tet is long What is most important to men when they are in their 30s? 50 soft skills needed to be happy and successful for life (Part 2)
