Discover Dragonblood security vulnerability in WPA3
Security researchers have recently discovered several new security flaws in the WPA3-Personal protocol, allowing potential attackers to unlock Wi-Fi network passwords, and from there gain access to Encrypted network traffic, being exchanged back and forth between connected devices.
More specifically, according to a press release from the Wi-Fi Alliance, devices affected by these security flaws in the WPA3 Wi-Fi standard will "allow side-channel information collection on" The device runs the attack software, and will also not be able to perform certain encryption operations correctly, or lead to the use of inappropriate encryption elements'.

- Danger: Hackers can target medical devices, change medical examination and treatment results
Basically, WPA3 uses the Wi-Fi Device Provisioning Protocol (DPP) protocol instead of the shared password to log new devices into the network. This is a protocol that allows users to scan QR or NFC codes to log devices into the wireless network, replacing the traditional password usage method. In addition, unlike WPA2, all network traffic on WPA3 will be encrypted after connecting to a network system using WPA3 WiFi Security.
The WPA3-Personal protocol will replace the Pre-shared Key (PSK) in WPA2-Personal with simultaneous authentication (Authentication of Equals - SAE) to provide a more robust password-based authentication method.
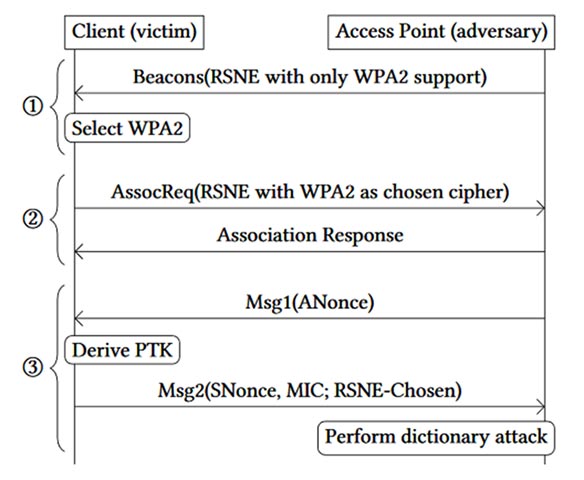
Although WPA3-Personal is designed to replace WPA2 - a 14-year-old 'aging' protocol that is currently less secure, the Authentication of Equals (SAE) authentication method of the new protocol (also known as Dragonfly), although it is theoretically superior, it seems to be "stained" by some fundamental errors in the design process, causing user data to be exposed, and of course They will be at high risk of becoming the 'prey' of crooks. According to security researchers, the most optimal method used by an attacker to exploit this vulnerability is to use password partitioning attacks.
- Reveal personal data of more than 1.3 million people from a vulnerability in web application
Dragonblood attacks can be used to steal sensitive information
According to the study, two research experts Mathy Vanhoef (NYUAD) and Eyal Ronen (Tel Aviv & KU Leuven University) mentioned in their study: 'Basically, Dragonblood attacks are like those dictionary attack, and allows crooks to recover passwords by abusing buffer-based side-channel leaks (cache-based side-channel leaks). Side-channel attacks are often aimed at password encryption. '
In addition, the researchers also mentioned the need to build a website dedicated to analyzing attacks using the WPA3 Dragonfly handshake vulnerability, which could be abused to steal. Sensitive information is transmitted over Wi-Fi networks such as credit card numbers, passwords, private chat messages, emails, .
- Hackers antivirus application preinstalled on Xiaomi phones into malware
As explained in the summary of the research paper: "These attacks can be highly effective while the deployment cost is quite low, such as the 8-digit brute-force type password. Normal self costs less than $ 125 for Amazon EC2 use cases. "
Since the Dragonfly handshake used by Wi-Fi networks requires a user name and password to control access, it can also be used by the EAP-pwd protocol, causing all attacks. Dragonblood found to have an effect on WPA3-Personal is ready to be used against EAP-pwd.
"In addition, we have discovered some serious bugs that appear in most EAP-pwd deployment products. This allows an attacker to impersonate any user and thus access the network. Wi-Fi without knowing that user's password Although we believe that EAP-pwd currently used is not so popular, this could in theory still cause a serious security risk for many people, and demonstrate the risks when Dragonfly is deployed incorrectly, 'researchers said.
- Insider attacks are becoming more and more popular and difficult to detect
The KRACK WPA2 vulnerability has also been found
In general, the vulnerabilities found in WPA3-Personal have two types, namely side-channel leakage and downgrade attack, and both can be used by potential attackers to detect the password of the Wi-Fi network.
Security expert Mathy Vanhoef and his team have also discovered KRACK attacks (short for 'short for key reinstallation attack'), directly affecting the WPA2 protocol. At the time of discovery, KRACK affected "all protected Wi-Fi networks".

- The alarming increase in the number of attacks targeted at IoT devices
Device manufacturers started deploying security patches
'A more open process will help prevent (or clarify) the possibility of downgrade attacks against WPA3-Transition mode. However, although WPA3 still fixes certain errors, we still consider it a significant improvement over WPA2 ', the researchers concluded.
According to the report of the Wi-Fi Alliance, all of the above problems can be mitigated or prevented through software updates without having to implement any impact on the functionality of devices. There is no evidence that these vulnerabilities have been exploited on a mass scale, and manufacturers with affected devices have also begun to deploy patches to solve the problem.