Difference between function and formula in Excel
One of the core features of Excel is the ability to perform calculations using functions and formulas. Although these terms are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings. Let's explore the differences in the following article!
What is Excel formula?
In Microsoft Excel, a formula is an expression used to perform calculations or manipulate data in a spreadsheet. Formulas can perform basic arithmetic operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as more complex operations. The primary function of a formula is to process input data—such as cell references, numbers, or text—and return a result.
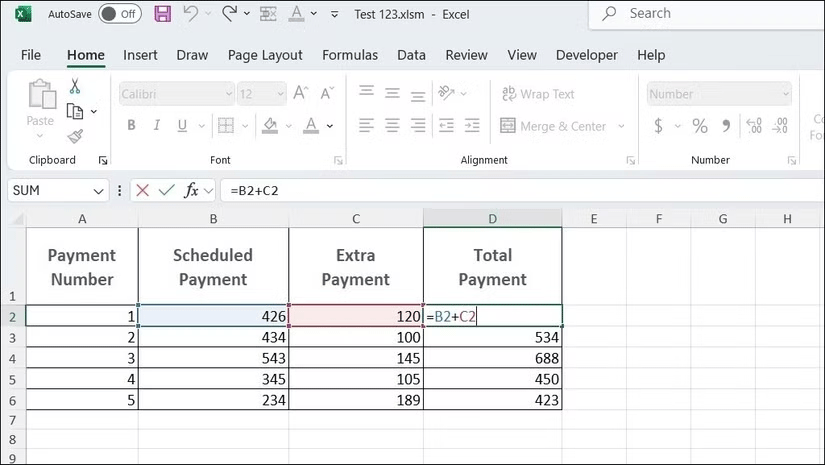
Formulas in Excel always begin with an equals sign (=), which tells Excel what the following expression is for. For example, if you want to sum the values in two cells, you can enter the formula =B2+C2 , where B2 and C2 are cell references.
What is Excel function?
An Excel function is a predefined, built-in formula designed to perform specific tasks efficiently. Functions simplify complex operations by allowing users to enter values, called arguments, and obtain results without having to write detailed formulas themselves.
Excel provides a large library of functions to meet a variety of needs, including mathematical and statistical calculations, text manipulation, logical testing, date and time operations, and financial analysis. Functions work within formulas, so a formula begins with an equal sign (=), followed by the function name and parentheses containing the arguments.
For example, the SUM function is a popular choice for quickly adding numbers. Instead of writing =A1+A2+A3+A4+A5 , you could simply use =SUM(A1:A5) . Note that both are formulas, but only the latter uses a function, in this case the SUM function.

Difference between function and formula in Excel
Although formulas and functions may seem similar, they serve slightly different purposes and can often be used in combination to perform a variety of calculations.
Formulas offer maximum flexibility because you can customize them to suit your specific needs. For example, a formula like =A1+B1*2 allows you to specify exactly how the values in those cells interact, giving you complete control over the calculation process. This flexibility is especially useful when you need to combine multiple calculations into a single formula.
In contrast, functions are built-in tools designed to simplify and speed up common tasks. Instead of building complex logic from scratch, you can use functions to perform specific calculations with minimal effort. For example, instead of manually calculating the average value with a formula like =(A1+A2+A3)/3 , you can use the AVERAGE function ( =AVERAGE(A1:A3) ) to complete the task more efficiently.
The main difference between the two is that a formula is a custom expression created by the user, while a function is a pre-written calculation in Excel that you can use in formulas. Functions exist to reduce the risk of errors and save time in Excel, especially when performing advanced calculations.
Of course, not every calculation has a built-in Excel function. For example, Excel functions can convert text to uppercase and lowercase, but there is no Excel function that converts text to sentences. In such cases, you will need to create your own formula, combining built-in Excel functions to get the desired result.
Understanding the difference between formulas and functions may seem abstract at first, but it's an important concept to grasp before diving into Excel and coming up with solutions to unique spreadsheet challenges.
You should read it
- How to use formula suggestions in Excel on the web
- MS Excel 2007 - Lesson 6: Calculation in Excel
- The square root formula in Excel - The square root function in Excel
- 5 useful Microsoft Excel formulas for calculating taxes
- How to use the IF function in Excel
- IFERROR function in Excel, formulas, and usage
- Basic Excel functions that anyone must know
- How to use MAXIFS function in Excel 2016
- How to use Hlookup function on Excel
- How to use the LEN function in Excel
- How to use the SUM function to calculate totals in Excel
- INDIRECT function in Excel - How to use INDIRECT function and examples using INDIRECT function
Maybe you are interested
Long-haul flight experience everyone needs to know 5 Google TV Settings to Change Immediately Instructions to log out of Facebook remotely when hacked account 1000 free music tracks to create Facebook, Instagram videos 4 lessons learned from the success of the female boxer Ronda Rousey Unexpected factors can make you miss job interviews (the last part)
