MS Excel 2007 - Lesson 6: Calculation in Excel
TipsMake.com - The difference between the tables in Excel and Word is the ability to calculate data, support the calculation functions that Word cannot do.
Excel supports many calculation functions, logic functions for calculating, filtering, collating and analyzing data. This is also a feature that makes Excel an indispensable tool for office jobs. In this article, TipsMake.com will show you how to use the overview calculation function in Excel 2007. You can refer to the basic Excel functions article, and the tutorial series for using each function on TipsMake.com. For details on how to do it.
A formula is a series of mathematical commands used in Excel to perform operations. Formulas are started in the formula box with a "=" sign.
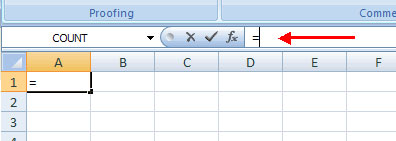
There are many components and formulas in excel
References : Reference or range of cells you want to use in the calculation
Operators : Operators (+, -, *, /, .) specify the operation to be performed
Constants (constants): Numbers or text values that are not changed
Functions : Defines predefined formulas in Excel
To create a basic formula in Excel
• Select the cell you want to apply the formula to
• Type the = sign and then the formula
• Click Enter
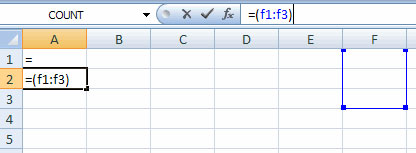
Calculation with Excel functions
A function is a built-in function in Excel's formula. A function with names and arguments (arguments are mathematical functions) is enclosed in parentheses. Common functions in Excel:
- Sum ( sum function): Computes all cells in the argument
- Average (average function): Calculates the average of the cells in the argument
- Min (minimum value function): Find the smallest value
- Max (maximum value function): Find the largest value
- Count (count function): Find the number of cells that contain a numeric value in an argument area
To calculate a function:
• Click the cell where you want the function to be applied
• Click the Insert Function button
• Select the function you want to apply
• Click OK
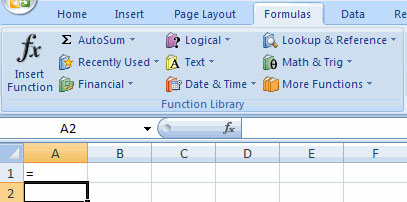
• Complete the Number1 box with the first cell in the area you want to be calculated
• Complete the Number2 box with the last cell in the area you want to calculate
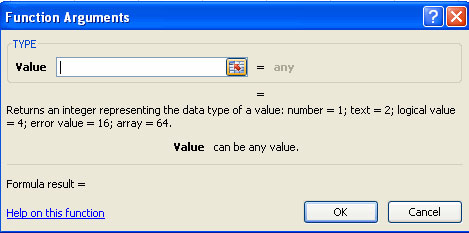
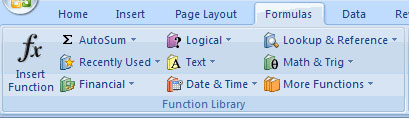
Functional library
The function library is a large set of functions available on the Formula tab of the Ribbon. These functions include:
- AutoSum : Calculate the sum of an area easily
- Recently Used : All the most recently used functions
- Financial (financial type): returns cash cycles and adds financial functions
- Logical : And, If, True, False, .
- Text : Text based on function
- Date & Time : Calculating functions on days and hours
- Math & Trig : Math functions
Relative, absolute and mixed references
Calling cells by their column and the label of the row (like 'A1') is a relative reference. When a formula contains relative references and it is copied from one cell to another, Excel does not create an exact copy of the formula. It will change the cell address associated with the row and column that they are moved to.
For example: If a simple formula in cell C1 '= (A1 + B1) is copied to cell C2, the formula will change to ' (A2 + B2) " to match the new line. This change, the cells must be called by the absolute reference, the absolute reference is completed by placing the $ sign in the cell address in the formula Continue with the given example: the formula in cell C1 will be read '= ($ A $ 1 + $ B $ 1)' if the value of C2 is also the sum of cells A1 and B1, both the column and row of cells are absolute and will not change when copying.
Mixed references can also be used where only lines or columns are fixed. For example, in the formula '= (A $ 1 + $ B2) , the row of cell A1 is fixed and the column of cell B2 is fixed.
Calculate between multiple Worksheet
You may want to use a value from one cell in many other worksheets in the same workbook in a public domain. For example, the value of cell A1 in the current worksheet and cell A2 in the second worksheet can be used to add the format 'sheetname! Celladdress' . The formula for this example will be '= A1 + Sheet2! A2' where the value of cell A1 in the current worksheet is added to the value of cell A2 in the worksheet named 'Sheet2'.
Next lesson: MS Excel 2007 - Lesson 7: Creating Macros in Excel 2007
Last lesson: MS Excel 2007 - Lesson 5: Edit Worksheet
See more:
- How to use the Power function in Excel
- How to use the Round function in Excel
- How to use the COUNT function in Excel
- How to use Excel's VALUE function
- How to use Vlookup function in Excel