What is Chikungunya virus? What you need to know about the global outbreak of Chikungunya
Chikungunya is a virus transmitted by mosquito bites. Here's what you need to know about the Chikungunya outbreak in China that's causing concern around the world.
What is Chikungunya virus?
Chikungunya fever (CHIKV) is a virus that is transmitted to people through mosquito bites—specifically, by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. Chikungunya infection occurs when a mosquito carrying the virus bites a person. The virus is not transmitted from person to person through physical contact or saliva, although it can be transmitted through blood.
The virus causes symptoms such as fever and joint pain, which can be severe. The name Chikungunya means 'bending over' because of the joint pain it causes. There is currently no medication to treat Chikungunya. Treatment focuses on controlling symptoms. Most people recover within about a week, but some people have lingering joint pain.
People travelling to areas with active Chikungunya outbreaks should take extra precautions to avoid mosquito bites. It is especially important to avoid further mosquito bites for about a week after you have been infected with the virus. This is because an uninfected mosquito can bite you and then become infected, spreading the virus further.
Prevalence of Chikungunya
Experts believe the number of cases is underreported because its symptoms are similar to other diseases. Previously confined to Africa and Asia, the virus has now spread globally, affecting more than 110 countries worldwide.
Are Dengue Fever and Chikungunya Fever the Same?
No, they are not the same virus. But the same mosquito transmits both diseases. Dengue fever has similar symptoms to chikungunya. Zika is another virus with similar symptoms and transmission. For this reason, a specialist may suspect all three viruses if a person has certain symptoms and has recently traveled abroad.
Symptoms and causes of Chikungunya
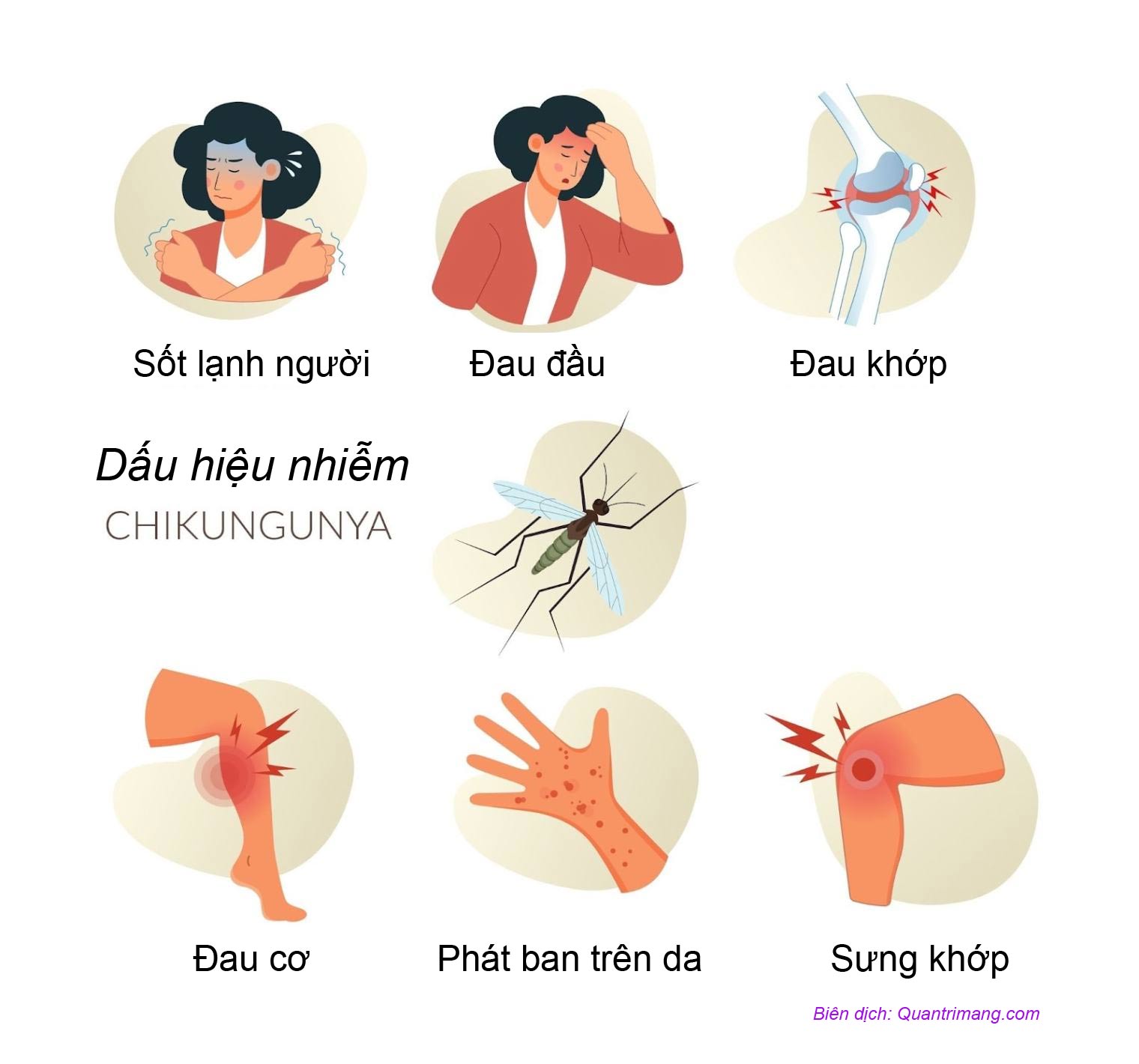
Signs of Chikungunya virus infection
Symptoms of chikungunya fever usually appear three to seven days after being bitten by an infected mosquito, although some people have symptoms as early as two days or as long as 12 days after being bitten.
Fever and joint pain are the most common symptoms of chikungunya. The severity of symptoms can vary from person to person. Many people experience severe joint pain. The fever often starts suddenly. Some people may have symptoms so mild that they mistake the virus for another illness or do not see a doctor.
Other symptoms may include:
- Headache.
- Muscle pain.
- Swollen joints.
- Rash.
- Tired.
- Nausea.
Most people experience symptoms for about a week and recover completely. However, some people experience chronic joint pain after recovery.
What causes Chikungunya fever?
Chikungunya virus is spread through mosquito bites, not from person to person through bodily fluids or contact. This means that if you have chikungunya fever, you will not pass it on to a caregiver or family member.
There have been reports of health care workers becoming infected with the virus after coming into contact with the blood of an infected person. This means that blood-borne transmission is possible, but rare.
Who is most likely to get Chikungunya fever?
You are most likely to get chikungunya if you travel to a country with an active outbreak or known cases of transmission. So before you travel, find out about the area you are going to and see a doctor to see if you are at risk of getting chikungunya during your trip.
Pregnant women infected with Chikungunya virus do not transmit the virus to their unborn babies. There is also no evidence that the virus is transmitted to infants through breast milk. However, pregnant women close to their due date should avoid traveling to countries with known cases of infection because the virus can be transmitted to the baby during birth.
How is Chikungunya fever treated?
Treatment basically focuses on controlling the patient's symptoms. Specifically, it includes:
- Drink plenty of water.
- Get plenty of rest.
- Take acetaminophen for pain. Do not take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or aspirin until cleared by your doctor.
Most people feel better within a week of their first symptoms. However, some people report joint pain that lasts for months or years. Most evidence suggests that once you have had chikungunya, you will not get it again because your body builds up immunity to the virus.
Is there a cure for chikungunya fever?
No, there is no cure for chikungunya, but the illness is temporary. However, you can prevent it by getting vaccinated, avoiding mosquito bites, and being especially careful when traveling to areas where chikungunya outbreaks are common.
You should read it
- ★ Extremely creative room ideas around the world
- ★ American science officially found 42 genes that cause gum disease, periodontal disease
- ★ Finding new drugs again can improve the treatment of Parkinson's disease
- ★ How to prevent stomach viruses after exposure
- ★ WHO revealed an amazing number of people with hepatitis B and C