10 best features of Windows Server 2016
This article will introduce you to the 10 best features of Windows Server 2016.
1. Nano Server
The Nano Server boasts 92 percent smaller settings than the Windows Server graphical user interface (GUI) option. In addition, the following compelling reasons may cause you to start running Nano for Windows Server workloads:
- The Bare-metal operating system means that users will have less updates and reboots.
- Because users have to go into server roles from outside the Nano, the server will have a much reduced attack surface when compared to the Windows Server GUI.
- Nano is so small that it can be easily transferred via servers, data centers and physical sites.
- Nano stores the most popular Windows Server workloads including Hyper-V servers.
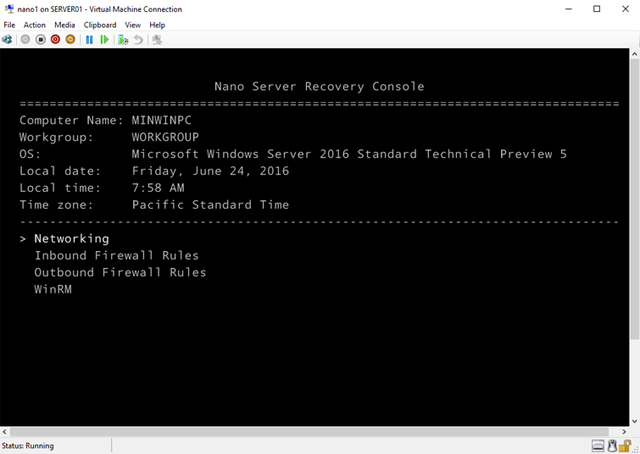
Nano is designed for complete remote management. However, the Nano includes a minimal local management interface called the "Nano Server Recovery Console" that enables initial configuration tasks.
2. Containers (containers)

Microsoft is working with the Docker development team to bring Docker-based containers into Windows Server. So far, containers have existed almost entirely in the open source Linux / UNIX world. They allow you to split applications and services quickly for ease of management. Windows Server 2016 provides two different types of services that contain Windows Sever:
- Windows Server Container. This type of container is intended for low-volume workloads and does not need to be considered when the container (container instance) service running on the same server can share some common resources.
- Hyper-V Container . This is not a Hyper-V host or virtual machine. Its Windows Server service 'is completely separate from other containers and other storage servers. Hyper-V contianers are suitable for high-confidence workloads.
3. Secure Boot Linux mode
Secure Boot mode is part of the integrated Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) specification that protects the server's boot environment against rootkit infection or other bootable malware.
The problem with Secure Boot based on Windows Server is that your server will have problems trying to create a Linux-based Hyper-V second-generation virtual machine because the Linux kernel driver is not a reliable device. Technically, the virtual machine's UEFI firmware displays the "Failed Secure Boot Verification" error and does not start.
The engineers of Windows Server and Azure seem to love Linux very much. So now we can deploy Linux virtual machines in Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V without any problems without having to disable the Secure Boot feature.
4. ReFS
Resilient File System (ReFS) has been around for a long time on Windows Server. In Windows Server 2016, users can finally use the stable version of ReFS. ReFS is a high performance, well-resilient file system used with Storage Spaces Direct and Hyper-V workloads.
5. Storage Spaces Direct feature
Storage Spaces is a great Windows Server feature that helps administrators create more flexible disk space. The Storage Spaces Direct feature in Windows Server 2016 is an upgrade feature from Storage Spaces that allows nodes in the failover cluter to use local memory within the cluter, without using storage fabric.
6. ADFS v4
Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) is a claimed Windows Server-based role support (Claims -based identity) (token). Statement-based identity is important because of the need for one-time authentication (SSO) between on-premises Active Directory and different cloud-based services.
ADFS v4 in Windows Server 2016 finally provides support for OpenID-based authentication, multi-factor authentication (MFA) and "combined conditional access". This technology allows ADFS to respond when user or device attributes do not comply with security policies at both end points of a trust relationship.
7. Nested Virtualization
Nested virtualization refers to the ability of a virtual machine to virtual server. Nested virtualization works when an enterprise wants to deploy additional Hyper-V servers and needs to minimize hardware costs.
8. Hyper-V virtual hardware
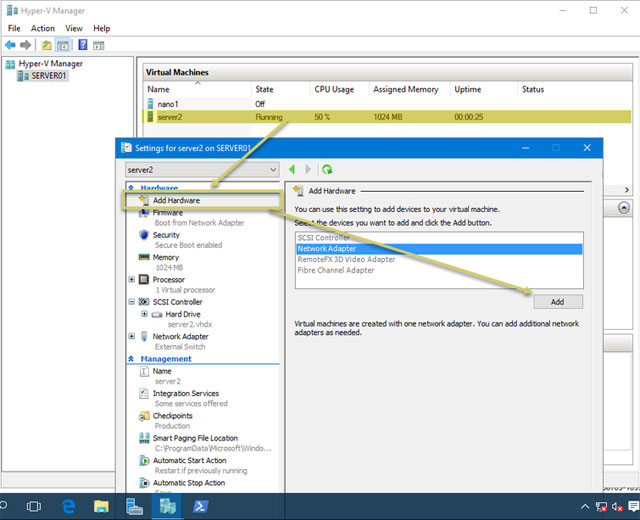
Hyper-V Server allows adding virtual hardware or adjusting RAM allocated to a virtual machine. However, before making these changes, the virtual machine must be turned off first. Now, in Windows Server 2016, we can add virtual hardware while virtual machines are online and running.
9. PowerShell Direct
In Windows Server 2012 R2, Hyper-V administrators often perform remote management for Windows PowerShell-based virtual machines in the same way as physical servers. In Windows Server 2016, PowerShell remote commands now have -VM * parameters that allow sending PowerShell directly to Hyper-V server virtual machines.
Invoke-Command -VMName 'server2' -ScriptBlock {Stop-Service -Name Spooler} -Credential 'tomsitprotim' -Verbose
We used the new -VMName parameter of the Invoke-Command commands to run Stop-Service commands on the Hyper-V virtual machine named server2.
10. Virtual machine protected (Shielded VM)
The new Host Guardian Service server role is to store the protected virtual machine feature. Windows Server 2016 protects virtual machines, allowing deeper, more sophisticated control of Hyper-V virtual machine access.
For example, a Hyper-V server may have virtual machines from multiple users and should ensure that different Hyper-V administrator groups can only access the specified virtual machines. By using BitLocker Drive Encryption to encrypt virtual machines' virtual hard disks, protected virtual machines can solve that problem.