Things to know about 5 in 1 vaccines and 6 in 1 vaccines
Before giving the child for injection, many mothers wondered why it is necessary to inject, where to inject, the side effects are dangerous, 5 in 1 vaccine is better or 6 in 1 vaccine is better? So, in order to answer these questions, please join us to find out the information immediately below.
- 10 common diseases in children in the fall, symptoms and prevention
- It is the parents' habits that affect the development of young children
- Simple way to prevent mosquito bites for young children
Vaccine for children and what to know
- Vaccination purpose
- Things to know about Quinvaxem vaccine
- How do side effects affect health?
- Children who do not get the Quinvaxem vaccine
- Things to know about Pentaxim and Infranrix service vaccines
- Injection schedule
- Order of vaccination of vaccines
- What moms need to know when giving her vaccinations
- How to monitor and care for children after injection
- How to handle when your child has a fever after injection?
- During the injection process, what should be observed?
Vaccination purpose
The purpose of the general vaccination to prevent 6 dangerous diseases in children is leukocytes, tetanus, pertussis, HiB, hepatitis B and polio . In particular, each vaccine has different ingredients.
Vaccines 5 in 1 of the expanded Vaccine Quinvaxem (parents take the baby to the local health station to inject) prevent 5 above diseases, except paralysis. Therefore, if the child is vaccinated, it will be supplemented with the oral vaccine to prevent polio.
5-in-1 vaccines of Pentaxim services can prevent these 5 diseases, except for hepatitis B. Children need supplementation of single hepatitis B vaccine after Pentaxim injection.
Infanrix hexa 6-in-1 vaccine can fully prevent these 6 diseases.
Things to know about Quinvaxem vaccine
5 in 1 vaccine (Quinvaxem vaccine), is a combination vaccine that prevents 5 important and potentially fatal or handicapped diseases such as diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, hepatitis B and Hib (inflammation lungs - Haemophyllus influenza type B pus meningitis, which is accredited by the World Health Organization.
Quinvaxem has been selected by the World Health Organization in the vaccination program funded by the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunizations, used to vaccinate children in Asian countries and poor countries starting in 2006. Quinvaxem vaccine has been included in the expanded vaccination program in Vietnam since June 2010 in the context of foreign aid.
It can be said that this is a valuable vaccine source with a price suitable to poor countries, receiving aid for vaccines, hundreds of millions of children have been given free use of disease prevention.
There was also a series of Quinvaxem incidents when production in 2010 that WHO announced. Currently, WHO still recommends injecting the two vaccines that Vietnam is injecting for free.
According to the recommendation of the World Health Organization, no vaccine is absolutely safe, the post-injection reaction of Quivaxem vaccines in particular and vaccines in general can range from mild, moderate and severe. Reactions may be systemic or at the site of vaccination and are specific to each vaccine, as well as reactions to other drugs or vaccines when given. However, severe reactions are very rare.
In Vietnam, 43 cases of reaction after vaccination after Quinvaxem were reported, which were evaluated by the World Health Organization experts, of which 9 were evaluated as related to vaccines on a total of 14 million injections. These 9 cases all recovered, the reaction manifestations include high fever, convulsions within 48 hours after vaccination; anaphylaxis; Muscle hypotonia syndrome and allergic reaction manifestations.
It is important to limit dangerous situations for children requiring strict adherence to professional guidelines, regulations in the production and preservation of vaccines, examination, counseling, immunization designation, practice safe vaccination, monitor the health of children after vaccination so as to be able to detect abnormalities soon after vaccination and timely treatment. Parents need to work closely with medical staff so that children are fully immunized, on schedule and safely.

How do side effects affect health?
Most local and systemic reactions are mild and appear only within 2-3 days after vaccination such as:
- Swelling / redness / pain at the injection site.
- Mild fever below 38 degrees.
- Disturbing crying more annoying than usual.
- Eat / suck less.
After vaccination, pay attention to children, breastfeed more often, feed when they are awake, do not put anything on the injection site. Monitoring closely the temperature of the child, when the fever fever needs to measure temperature, cool, use fever-reducing medicine for children as directed by medical staff.
Children who do not get the Quinvaxem vaccine
Do not give Quinvaxem vaccines to children if there is a history of strong reactions to previous injections or strong reactions to diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus (DPT) or hepatitis B vaccines such as:
- 40ºC fever within 48 hours after vaccination.
- Shock within 48 hours after vaccination.
- Crying persists for more than 3 hours within 48 hours after vaccination.
- Seizures are accompanied by fever or no fever within 3 days after vaccination.
- Do not give injections to babies under 6 weeks of age because the vaccine may not be effective because of immunity from the mother.
- Delay the injection if the child is sick, fever or has acute illnesses.

Things to know about Pentaxim and Infranrix service vaccines
In addition to the 5-in-1 vaccine originating from Korea, included in the EPI program (free injection for children under 1 year old at commune / ward / township clinics, in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City) another 5-in-1 vaccine originating from France (known as Pentaxim, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, Hib, polio) and a 6 in 1 vaccine (called Infranrix, preventing diphtheria, Whooping cough, tetanus, hepatitis B, polio, Hib) originated from Belgium.
Both types are not included in the EPI program but are used in service vaccination.
The most fundamental difference between two vaccines for service vaccination with the free vaccination vaccine (Quinvaxem vaccine) is in the component of preventing pertussis :
Vaccines 5 in 1 Quinvaxem of Korea with pertussis ingredients are all-cell vaccines, and French and Belgian vaccines are cell-free, so there is no body of pertussis bacteria but replaced by antigen peculiar, so will be more pure.
Professor Nguyen Tran Hien, Director of the National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology Mr. Hien said that many parents think of giving their children safer injecting services because it is actually imported vaccines. from Europe, refined ingredients or also cellless vaccines.
This vaccine is 10 times safer than the vaccine in the expanded vaccination program we are applying. It reduces unwanted effects after injection.
In Quinvaxem vaccine containing dead pertussis bacteria is purified and the reaction is usually caused by the protein in the bacteria (including fever, redness at the injection site, can be removed after 1-2 days, more severe than anaphylactic shock).
Regarding the concern regarding the pertussis prevention component, he knew that, before putting Quinvaxem '5 in 1' into the Expanded Immunization program, the Ministry of Health had consulted and was told by the WHO that the vaccine This whole cell is still effective in preventing disease with acceptable hazard rates.
The 6 in 1 vaccine is called Infanrix hexa, in addition to preventing 5 important diseases at the same time as the 5 in 1 vaccine and preventing the sixth disease, polio. Includes: diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, hepatitis B and Hib (Haemophyllus influenza type B meningitis).
A more special feature of Vaccine 6 in 1 is: Whooping cough component in vaccine 6 in 1 is a cell type, so it is safe, has less fever and less side effects than vaccines with pertussis ingredients. cell.
Infanrix hexa vaccine has been used in Vietnam since 2006, helping to reduce the number of necessary injections from 9 to 3 to protect children from diseases that can be vaccinated. Infanrix hexa vaccine has been licensed to circulate in 70 countries around the world.
It must be confirmed that disease prevention is always better than cure. Vaccines are the most effective preventive measure to protect people who do not get sick and avoid major epidemics affecting human health and life. In addition, vaccination will prevent disease when exposed to patients.
Injection schedule
Three basic shots are given at least 28 days apart and the first shot is given at two months of age. The baby needs to be re-vaccinated for the fourth shot at 18 months (or more than 6 months from the 3rd shot) if he had previously received a 5-in-1 vaccination of expanded vaccination. The injection schedule may fluctuate with reality (children who are sick, out of medicine .), may be a little slower with the plan but should not be too late (wait for the service medication) because of the risk of getting sick before get enough dose. Vaccines containing 5 in 1 and 6 in 1 should not be given too early (before the baby is 2 months old or go earlier than the doctor's appointment), as the vaccine will be ineffective and must be re-injected.
Order of vaccination of vaccines
Vaccines 5 in 1 and 6 in 1 can be exchanged interchangeably, but parents remember to add 6 preventive ingredients to the baby. Depending on the ingredients to compensate, make sure you have enough injections, enough distance between the injections. Parents need to record the full schedule of injections, injections so as not to compensate for excess or lack of preventive ingredients. When such an excess occurs, the parents will spend more work, more money (if the service is injected) and may cause side effects.
What moms need to know when giving her vaccinations
Can vaccination be delayed? And how long is delay?
Having your child vaccinated according to the deadline of the national vaccination schedule is always the best advice for parents. However, it is true that vaccination can delay. In fact, the number of babies vaccinated on the day is not much. If the child has not been vaccinated, the mother can give the baby back injections later. However, remember to not delay too long and ask your doctor as well as inform your baby about the specific time before the injection.
What are the reactions to the child when vaccination is completed and how to prevent it?
When giving the child for vaccination, she should pay attention to giving her child more water than usual, but also need to pay attention to measuring the body temperature. Common adverse reactions are fever, crying or swelling of the injection site.
When should I not get injections?
When the child's health is not guaranteed or problems such as colds, fever, eczema, rash, jaundice, . I should not take my child to vaccinate.
If the child has a fever for the first time, does the nose have a fever? Should the child be vaccinated?
As a parent, everyone is very worried, distressing when they have a fever, tired after injection. However, the mother should not give up her child. The fact that a child has a fever depends on many factors, so it is very possible that the first child has a fever but the second nose will not be feverish. In general, it is still necessary to get the child to get vaccinated.
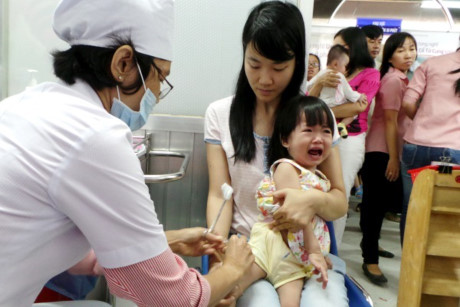
How to monitor and care for children after injection
After vaccination parents need to stay at the injection site and follow up within 30 minutes after the injection. Parents who take their children home should be aware that they should monitor their health continuously even when they are sleeping and at least for 1 day (24 hours).
If the child has abnormal signs after vaccination such as: high fever, convulsions, crying, prolonged crying, lethargy, breastfeeding, shortness of breath, cyanosis . immediately take the child to the hospital or facility Medical to be diagnosed and treated promptly.
How to handle when your child has a fever after injection?
After vaccination a few hours or a day, some children may have a fever: fever is usually mild, but sometimes high fever (over 39 degrees Celsius), accompanied by fussing. The mother should let the child stay in a cool place, wear loose, comfortable clothes, cool the child with a damp towel but do not apply ice or cold water. You can give your child a fever-reducing medicine.
What do I need to bring when I give my child vaccination?
For the mother to be vaccinated, it is important to bear in mind all the documents related to the previous vaccination of the child, the vaccination book, the medical examination book, and the nutrition book. Let your baby wear easy clothes. With toddlers, mothers can let them wear big T-shirts and loose pants.
During the injection process, what should be observed?
The mother should pay close attention
- Can my vaccine get the box from the refrigerator?
- Expiry date of vaccine, name and country of vaccine production.
- Is the reconstituted water tube and the medicine mixing procedure of the nurse performing?
What to ask your doctor before leaving the clinic
- What side effects can your baby have?
- What should I do if my baby has these side effects?
- What signs are worrying?
- When is my child vaccinated next?
Current vaccination recommendations for children
For the health of children, parents should:
- Take preventive measures for children to have the opportunity to get vaccinated on time.
- Take children to fully expand their immunization schedule, without delay.
- If the child has indicated a delay in the vaccination (due to illness or any other reason), contact the vaccination unit so that the child can continue vaccination.
You should read it
- ★ What is community immunity? The role of community immunity and vaccines?
- ★ WHO: Testing more than 20 different vaccines for corona virus
- ★ Video: Experience of the first person in the world to be tested on Covid-19 vaccine
- ★ Coronavirus vaccines: The drugs in development to treat COVID-19
- ★ Flu drugs are a new clinical trial that successfully causes fever