Today I introduce to you the synthesis of matrix functions in Excel 2013. The article will guide in detail the syntax and specific examples for each matrix function. Hope to help you a lot.
1. Transpose function
- Meaning: The function returns the transposition matrix of a given matrix. You notice the function is correct with matrices with the same number of rows and columns.
- Syntax: Transpose (array [n, n]) .
Where: Array is a 2-dimensional array with a row and column index of n.
- For example:
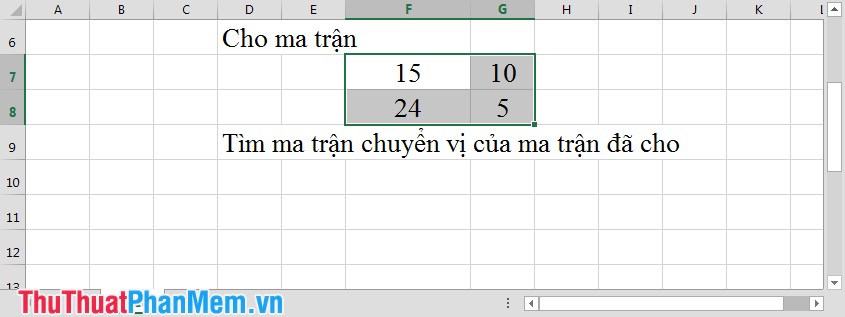
Step 1: In the cell you want to display the transposition matrix, enter the command as shown:

Step 2: Press Enter -> display the command you type False . Highlight the data area F11: G12 -> press F2 -> Ctrl + Shift + Enter .
Note: The original matrix has many rows and columns, then you highlight the corresponding data area with so many rows and columns.
2. Mdeterm function
- Meaning: The function returns the determinant of matrices.
- Syntax: Mdeterm (array [n, n]) .
Where: Array is a 2-dimensional array with a row and column index of n.
- For example:
Step 1: In the cell where you need to calculate the determinant, enter the following command:
Step 2: Press Enter, the result will be:
3. Minverse function
- Meaning: Returns the inverse matrix of the given matrix.
- Syntax: Minverse (array [n, n]) .
Where: Array is a 2-dimensional array with equal number of columns and rows.
- For example:
Step 1: In the cell you want to display the inverse matrix, enter the following command:
Step 2: Press Enter , highlight the data area C11: D12 -> press F2 -> Ctrl + Shift + Enter . The result is as shown in the picture:
4. Mmult function
- Meaning: Returns the product of 2 matrices.
- Syntax: Mmult (aray1, array2) .
Where: The number of columns of matrix 1 is equal to the number of rows of matrix 2.
- Example: Find the product of 2 matrices.
+ Step 1: In the box you want to display matrix products, enter the command as shown:
Step 2: Press Enter , highlight the data range K6: L8 -> press F2 -> Ctrl + Shift + Enter . The result is as shown below:
In this step, there is a small note in Step 2 if you highlight the number of rows and columns incorrectly, as shown in the figure:
Note: Here matrix 1 (3 rows, 3 columns) x matrix 2 (3 rows, 2 columns) => product matrix has a row index and a column index equal to matrix 2.
Good luck!
