How to Change the Timezone in Linux
Method 1 of 4:
Using the Command Line
-
 Open Terminal. Select the Terminal program from your Linux programs, or press Ctrl+Alt+T on your keyboard.
Open Terminal. Select the Terminal program from your Linux programs, or press Ctrl+Alt+T on your keyboard. -
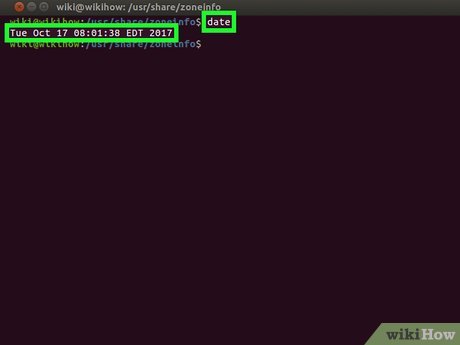
 Check your current time zone. Type date into Terminal and press ↵ Enter. The terminal will display the date in
Check your current time zone. Type date into Terminal and press ↵ Enter. The terminal will display the date inWeekday Month Day Time TimeZone Yearformat.- For example, you might see something like
Wed Mar 7 07:38:23 EDT 2017wherein "EDT" refers to the current time zone (Eastern Daylight Time).
- For example, you might see something like
-
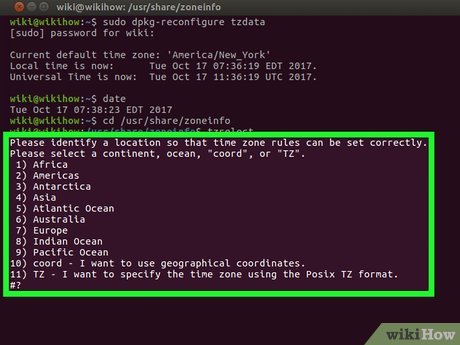
 Check available time zones. Type in cd /usr/share/zoneinfo and press ↵ Enter, then type in tzselect and press ↵ Enter to display a list of locations.
Check available time zones. Type in cd /usr/share/zoneinfo and press ↵ Enter, then type in tzselect and press ↵ Enter to display a list of locations.- The /usr/share/zoneinfo directory may vary depending on your Linux distribution.
-
 Select a continent or ocean. Type in a selection number that pertains to your general location, then press ↵ Enter.
Select a continent or ocean. Type in a selection number that pertains to your general location, then press ↵ Enter. -
 Select a country. Type in a selection number from the on-screen list and press ↵ Enter.
Select a country. Type in a selection number from the on-screen list and press ↵ Enter. -
 Select a time zone. Type in a selection number to select the preferred time zone region and press ↵ Enter.
Select a time zone. Type in a selection number to select the preferred time zone region and press ↵ Enter.- If your city is not listed in the time zone list, pick a different city from your same time zone.
-
 Confirm the local time. In the following prompt, confirm that the local time is correct by typing 1 and then pressing ↵ Enter.
Confirm the local time. In the following prompt, confirm that the local time is correct by typing 1 and then pressing ↵ Enter.- If the time isn't correct, type in 2 and press ↵ Enter, then select a new continent and repeat the process.
-
 Verify that your time zone has been set. Run the date command again and check that the time zone corresponds to the one you just changed to. If you see you new time zone listed, you have successfully changed your computer's time zone.
Verify that your time zone has been set. Run the date command again and check that the time zone corresponds to the one you just changed to. If you see you new time zone listed, you have successfully changed your computer's time zone. -
 Set your clock to stay synced with internet time servers if you like. Most modern distributions have NTP already installed. If your Linux distribution does not, you will need to install the NTP server package. Use the following commands to install it, depending on your Linux distribution:
Set your clock to stay synced with internet time servers if you like. Most modern distributions have NTP already installed. If your Linux distribution does not, you will need to install the NTP server package. Use the following commands to install it, depending on your Linux distribution:- Ubuntu/Mint/Debian: sudo apt install ntpdate
- CentOS: sudo yum install ntpdate
sudo /sbin/chkconfig ntpd on - Fedora/RedHat: sudo yum install ntpdate
sudo chkconfig ntpd on - Enter ntpdate server link && hwclock –w after the installation command, making sure to enter the link to the website in place of server link.
Method 2 of 4:
Using the Timezone Selection Menu
-
 Open Terminal. Select the Terminal program from your Linux programs, or press Ctrl+Alt+T on your keyboard.
Open Terminal. Select the Terminal program from your Linux programs, or press Ctrl+Alt+T on your keyboard. -
 Enter the time zone menu command. Depending on your Linux distribution, this command will vary:
Enter the time zone menu command. Depending on your Linux distribution, this command will vary:- Ubuntu and Mint - sudo dpkg-reconfigure tzdata followed by the admin/user password.
- Redhat - redhat-config-date
- CentOS and Fedora - system-config-date
- 'FreeBSD and Slackware - tzselect
-
 Select your geographic area. Use the arrow keys to select the geographic area the country is found in, then press ↵ Enter.
Select your geographic area. Use the arrow keys to select the geographic area the country is found in, then press ↵ Enter. -
 Select your city/region. Select the city or region corresponding to your time zone, then press ↵ Enter. This will change the time zone on your system. [1]
Select your city/region. Select the city or region corresponding to your time zone, then press ↵ Enter. This will change the time zone on your system. [1]
Method 3 of 4:
Using the Graphical User Interface in Ubuntu
-
 Click the "System Menu" icon. It's a downward-facing triangle in the upper-right corner of the screen. A drop-down menu will appear.[2]
Click the "System Menu" icon. It's a downward-facing triangle in the upper-right corner of the screen. A drop-down menu will appear.[2]
-
 Click the "Settings" icon. This wrench-and-screwdriver-shaped icon is in the lower-left corner of the drop-down menu. Doing so opens the Ubuntu Control Center.
Click the "Settings" icon. This wrench-and-screwdriver-shaped icon is in the lower-left corner of the drop-down menu. Doing so opens the Ubuntu Control Center. -
 Scroll down and click Details. It's at the bottom of the sidebar that's on the left side of the window.
Scroll down and click Details. It's at the bottom of the sidebar that's on the left side of the window.- Make sure that your mouse is over the left-hand sidebar when scrolling.
-
 Click Date & Time. You'll find this tab on the left side of the window.
Click Date & Time. You'll find this tab on the left side of the window. -
 Turn off Automatic Time Zone. Click the blue "Automatic Time Zone" switch in the middle of the page to do so.
Turn off Automatic Time Zone. Click the blue "Automatic Time Zone" switch in the middle of the page to do so.- If the "Automatic Time Zone" switch is grey, skip this step.
-
 Click Time Zone. It's near the bottom of the window. Doing so opens the Time Zone menu.
Click Time Zone. It's near the bottom of the window. Doing so opens the Time Zone menu. -
 Select a time zone. Click your approximate location on the world map to do so. You should see the time change to match the selected area's time zone.
Select a time zone. Click your approximate location on the world map to do so. You should see the time change to match the selected area's time zone. -
 Close the window. This will save your settings and update your time zone accordingly.
Close the window. This will save your settings and update your time zone accordingly.
Method 4 of 4:
Using the Graphical User Interface in Mint
-
 Open the Menu. Click Menu in the bottom-left corner of the screen.
Open the Menu. Click Menu in the bottom-left corner of the screen. -
 Click the System Settings icon. It's made of two grey cogs. You'll find it on the left side of the Menu window.
Click the System Settings icon. It's made of two grey cogs. You'll find it on the left side of the Menu window. -
 Click Date & Time. It's in the "Preferences" group of options.
Click Date & Time. It's in the "Preferences" group of options. -
 Click Unlock. You'll find this on the right side of the window.
Click Unlock. You'll find this on the right side of the window. -
 Enter your user password when prompted. Type in the password that you use to log into your computer.
Enter your user password when prompted. Type in the password that you use to log into your computer. -
 Click Authenticate. It's at the bottom of the prompt. Doing so unlocks the Date & Time menu.
Click Authenticate. It's at the bottom of the prompt. Doing so unlocks the Date & Time menu. -
 Select a time zone. Click a vertical slice of the map to pick that time zone. You should see the clock on the right side of the page immediately change to reflect the selected time zone's time.
Select a time zone. Click a vertical slice of the map to pick that time zone. You should see the clock on the right side of the page immediately change to reflect the selected time zone's time. -
 Click Lock. It's on the right side of the window. Doing so saves your time zone preferences and locks the Date & Time menu.
Click Lock. It's on the right side of the window. Doing so saves your time zone preferences and locks the Date & Time menu.
Share by
David Pac
Update 04 March 2020