How to Manage Users in Linux
Method 1 of 4:
Adding Users
-
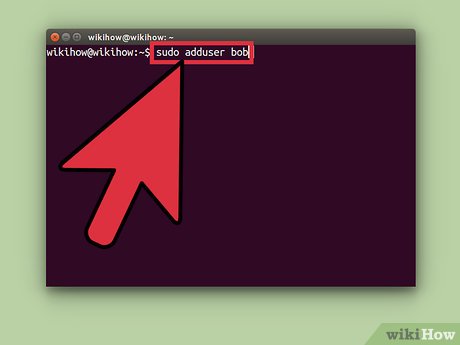 Type adduser -d /home/users/ into the command line.
Type adduser -d /home/users/ into the command line.- Example: adduser bob -d /home/users/bob
-
 Type passwd and press return to set a password for the new user.
Type passwd and press return to set a password for the new user.- Type the new password.
- Confirm the password.
Method 2 of 4:
Modifying Users
Changing Passwords
- Type passwd in the command line.
- Enter the new password for the user.
- Note: the cursor will not move however your password is being typed.
- Confirm the new password.
Method 3 of 4:
Removing Users
- Type userdel into the command line to delete a user.
- Example: userdel bob
- Type userdel -r to also delete their home folder and files.
Method 4 of 4:
Sudo and Su
Terms
- sudo: Switch User and Do
- Executes a command as root or another use while maintaining your current session.
- su: Switch User
- Switches your session to another user.
- Switches your session to another user.
Usage
- Type sudo before a command to execute the command as the root user. You will be prompted for a password.
- Example: sudo apt-get install telnet
- Type sudo before a command to execute the command as another user on the system. You will be promoted for that users password.
- Example: sudo bob telnet localhost 22
- Type su to switch your command line session to the root user. You will be promoted for a password.
- Type logout to switch back.
- Type su to switch your command line session to another user. You will be promoted for their password.
- Type logout to switch back.
Update 04 March 2020
You should read it
- How to set and change a user password in Linux
- How to manage user passwords from Terminal in Linux
- How to change Windows user account password using Command Prompt
- How to Change a Computer Password Using Command Prompt
- How to Hack Into a Windows User Account Using the Net User Command
- The command changes user in Windows
- How to Bypass Windows 7 Password
- Instructions for changing Windows passwords without having to remember the old password
- USER_NAME function in SQL Server
- How to reset WSL user password
- How to Reset SA Password in Sql Server
- SYSTEM_USER function in SQL Server
Maybe you are interested
TLDR: The Tool That Tells You If a YouTube Video Is Worth Your Time Make Terminal More Fun with These 8 Linux Tools! How did 'LoveBug' change the world of malware? How to create a two-screen switch mode shortcut on Windows 10 How to read UPC bar codes to identify US, Japanese or Chinese goods The art of creating great paintings from letters
