How did 'LoveBug' change the world of malware?
Also at this time 20 years ago, Filipino student Onel A. de Guzman silently spread a new computer virus that not only crippled millions of computer systems around the world, but also become the catalyst for the growth and growth of the billion-dollar 'ransomware industry' we know today.
The piece of malware that the Filipino student created two decades ago was called LoveBug, also known as ILOVEYOU or VBS / LoveLetter, sounded not very dangerous, and indeed this malware has a structure. The structure is quite simple, but the damage it causes is not 'simple' at all. Initially, Onel A. de Guzman only intended to generate malicious code to collect the passwords of a few local internet providers where he lives. However, LoveBug quickly spread out of control all over the world, infected more than 45 million devices (about 10% of computers connected to the Internet globally at the time) and became one of the malicious codes causing damage. heaviest in history with 5.5 to 8.7 billion dollars in related costs.
Besides the devastating destructive power, the factor that makes LoveBug's popularity lies in the impact it brings to the malware world, especially it is considered as the agent that paved the way for the emergence of challenges. ransomware (ransomware) is rife today.
The appearance of ransomware
11 years before LoveBug was born, the field of information technology witnessed the first case of ransomware infection, the AIDS Trojan. The malware had a sophisticated transmission mechanism, that was through floppy disks sent to HIV researchers around the world as part of the medical knowledge-sharing program at the time. It works by encrypting the file names and then asking the victims to send checks to the PO Box in Panama to regain access to the data.
The man behind AIDS Trojan, Dr. Joseph Popp, was quickly arrested. At the same time a new concept called 'ransomware prevention' has also been developed. Because AIDS Trojan uses synchronized encryption, good computer experts can fully recover encrypted files without the victim having to pay. This launched an interesting but equally cat-and-mouse game between the security industry and hackers.
However, the appearance of LoveBug can be seen as a turning point that changes the world of malware in general and ransomware in particular, moving from a small scale of attack to 'mass destruction'. Just click open the sexy attachment "LOVE-LETTER-FOR-YOU.TXT.vbs" (Love letter for you / me), the code automatically scours into your contacts in Outlook and send out the letters. Replication. The recipient will not be suspicious when the letter with the full emotional title is sent from the address of his relative and accidentally becomes the next victim. In this way, this malicious code quickly brought down personal and business computer systems around the world in a short time.
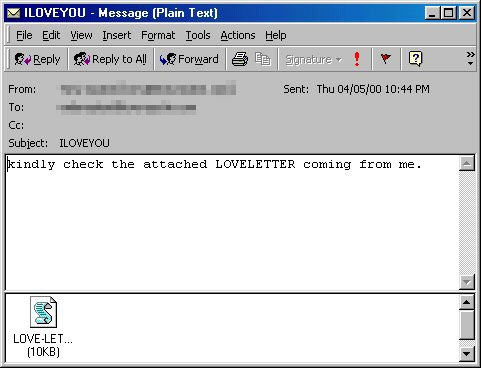 Malicious attachment
Malicious attachment Of course the security industry has also responded strongly. The best computer experts in the world have come together to find a way to crack the encryption and share it widely to help victims not pay any ransom. Since then, the cat and mouse game has become more and more demanding with increasingly complex ransomware strains such as CryptoLocker, CryptoDefense or CryptoLocker2.0. Hackers actively build more sophisticated attack strategies, while the security industry is constantly introducing new and equally sophisticated defenses.
What has mankind learned?
After decades, ransomware has become more sophisticated and popular, and has also diverted its main attack on businesses that pay large sums of money, with an average of 110,000. USD. However, the ransom is only a small part of the impact of the attacks. The financial loss to fix during and after a ransomware attack is what could kill the business: the system crippled, the production line stopped working, the prestige collapsed .
However, data protection technology is also becoming more modern, with 4 areas now an integral part of every ransomware prevention strategy, including: Protection, detection, feedback and recovery.
- Protection: Increasing security knowledge for end users and deploying remote anti-malware systems is the key to success. Along with that is the need to develop a backup strategy and archive data methodically.
- Detection: Respond as quickly as possible with a ransomware attack, which is also a springboard for effective recovery. Intrusion detection, anti-malware and detection of abnormal traces on the system are factors that can keep businesses safe.
- Response: As soon as it became known that it was under attack, the enterprise had to quickly shut down the entire system to stop internal infection. In parallel with that is urgently determining the time of infection occurring on each affected system.
- Recovery: Enterprises need to develop an effective system recovery strategy and return to their normal state before being attacked as quickly as possible.
You should read it
- ★ [Infographic] 7 effective ways to protect businesses from Ransomware
- ★ No anti-virus software can detect this extremely dangerous new Ransomware on Android
- ★ Acronis Ransomware Protection, a completely free anti-ransomware solution for Windows
- ★ Theory - What is Ransomware?
- ★ Detect and prevent Ransomware with CyberSight RansomStopper