How to Install Python Packages in Raspberry Pi OS Bookworm
Having trouble installing the Python package using the "pip" tool in Raspberry Pi OS Bookworm? There are some additional steps you need to take, involved in creating the Python virtual environment. Here's how!
How to Search for Python Packages Using Apt
The first thing to check is whether the Python package you need is available for installation using the system-wide apt package manager. You can search for packages in the official repository using the apt search command. For example:
apt search numpy
Note the package name, in this case python3-numpy (for Python version 3), then install it using apt (with sudo prefix to get the superuser privileges needed for installation):
sudo apt install python3-numpy
If the Python package you need is not available using the apt package manager, or you require a newer version of that package, you will need to use the Python-specific pip tool to install the package - within the Python virtual environment.
How to create a Python virtual environment
To install a Python package using the pip tool in Raspberry Pi OS Bookworm, you first need to create a virtual Python environment using venv. The author calls his project "muo-project", but you can use any name you want:
python -m venv muo-project
It will take some time to complete, depending on the Raspberry Pi model you are using. You will then need to change directories to the newly created environment directory, containing the full Python distribution, and activate it:
cd muo source bin/activate
The Python virtual environment is now ready to use and a system prompt will be added before its name - in this case muo-project. This indicates that you are no longer using the system version of Python, but the version inside your virtual environment. So any changes you make to it or the modules you install will not affect the system Python.
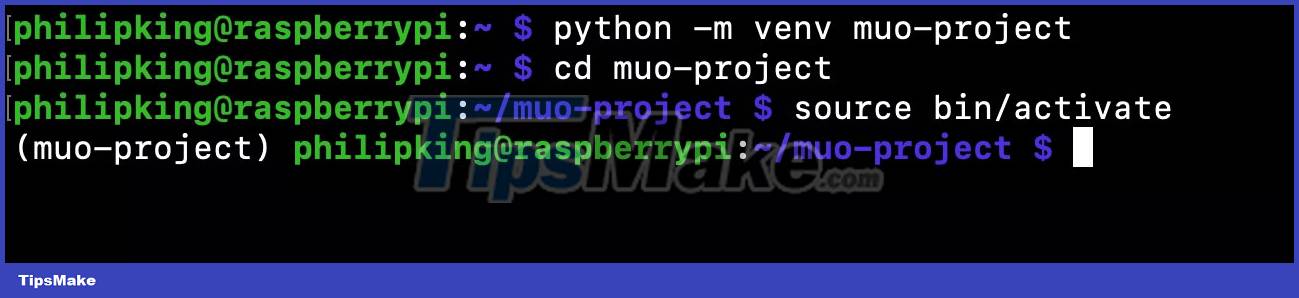
Note that if you restart your Raspberry Pi, you will need to re-enable the Python environment to use it again.
Note: If you want to create a Python virtual environment with a copy of all currently installed Python modules at the operating system level, you can do so by adding the flag --system-site-packages in Comeinand. For example:
python -m venv --system-site-packages muo-project
Install Python package using Pip
From within your active Python virtual environment, you can now install any packages you need using the pip command. For example, to install the Stressberry system stresstest tool:
pip install stressberry
It will then install the module, along with any dependencies it requires, in your Python virtual environment. Note that the module will only be available within and not system-wide.
Although installing Python packages in Raspberry Pi OS Bookworm using the pip tool requires additional steps, the advantage is that they then only work in a virtual environment and therefore cannot interfere with or break the system .
You should read it
- Install Python Package with PIP on Windows, Mac and Linux
- How to install Pip in Ubuntu
- How to Install Python Packages on Windows 7
- How to Install Scipy
- How to install Python on Windows, macOS, Linux
- How to Set Up a Python Environment for Deep Learning
- How to use Raspberry Pi Imager to install Raspberry Pi OS
- How to install Android on a Raspberry Pi
- Package in Python
- How to start Raspberry Pi 3 from USB
- How to Install Python on Windows
- Learn Pi Imager, How to Use Raspberry Pi Imager
Maybe you are interested
Brain research explains the difference in the impact of technology on men and women Instructions to turn on, turn off the keyboard sound on Android The easiest way to connect speakers to TVs GOM Saver: photo and video compression tool on Android saves storage space for being infected Run 2 applications at the same time on the BlackBerry Passport screen 5 software to rename files in batch
