Will the performance of big.LITTLE x86 CPUs increase significantly on Windows 11?
Among them, there is a very remarkable test conducted by the famous technology news site Hot Hardware. The aim of the experts in this test is to find out what changes have been made (if any) by Microsoft to the Windows 11 scheduler, as well as how well the operating system will be compatible. with Intel's upcoming Big-Bigger Alder Lake CPUs. In fact, AMD's next-generation Ryzen processors are also expected to feature a 'hybrid big.LITTLE' architectural design. Therefore, this will be a very important aspect that can directly impact the overall user experience.
In terms of hardware, the device used in the test is a Samsung Galaxy Book S running a Lakefield Core i7-L16G7 CPU. For software, experts compared two versions: Windows 11 build 21996.1 and the latest 21H1 update for Windows 10 - to check the difference in performance and hardware compatibility. specific to the new operating system version.
The results show that there are only small, local improvements in performance depending on the specific workload. However, there seems to have been a marked improvement in browser performance, as follows.

The results of the Geekbench evaluation, with various short continuous tests, show a moderate increase in multi-threaded (MT) performance and a negligible improvement in the single-threaded test (ST):

In the test test Cinema 4D display performance with CInebench. The results show a rather modest increase of Windows 11 compared to Windows 10 when all CPU cores are fully loaded. However, the improvement is more pronounced in single load always, because tasks are constantly 'jumping' around between cores and being more affected by the scheduler's input.

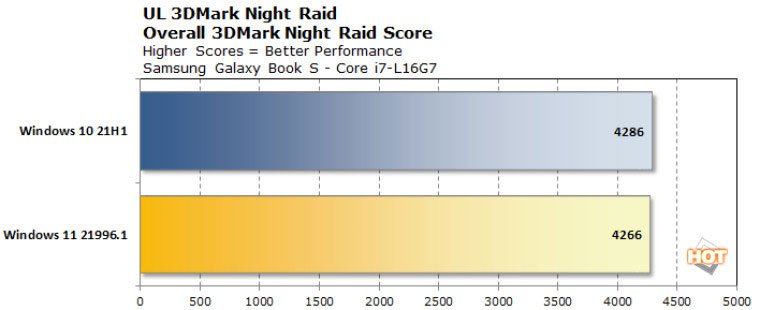
Another graphics-related workload was also tested in the form of 3DMark Night Raid, a lightweight DirectX 12 benchmarking tool. Notably, this is the only test that shows a (negligible) lower performance of Windows 11 compared to Windows 10.
Finally, PCMark 10 was used to test the performance of both CPU and GPU at the same time, as well as simulate a real PC usage scenario. The results show that Windows 11 gives better performance in all respects, on the same hardware setup.

Currently, it is still too early to make any definitive statements about the performance of Windows 11. However, the above practical tests show that we have reason to expect the appearance of a version of Windows. more comprehensive.
You should read it
- ★ Microsoft promises to improve Windows 11 performance in 2022
- ★ Microsoft claims Windows 11 PCs will have better performance thanks to the ability to optimize CPU, RAM and storage hard drive
- ★ How to download and install Windows Performance Toolkit in Windows 10
- ★ 11 ways to start the Performance Monitor performance monitor in Windows
- ★ How to increase gaming performance on Windows 10 April 2018