NORMDIST function - The function returns the normal distribution with the standard deviation and the average value specified in Excel
The following article details the NORMDIST function - The function returns the normal distribution in excel.
Description: The function returns the normal distribution in excel with a standard deviation and a defined mean. Application of this function in testing hypotheses.
Syntax: NORMDIST (x, mean, standard_dev, cumulative) .
Inside:
- x : The value you want to determine the distribution, is the required parameter bt.
- mean : The arithmetic mean of the distribution, which is a required parameter.
- standard_dev : The standard deviation of the distribution, is a required parameter.
- cumulative : The logical value of the function, which is a required parameter. The following values are available:
+ Function has value TRUE => cumulative distribution function.
+ Function with value FALSE => probability mass function.
Attention:
- The equation of the function (with commulative = False) is:

- If the average value or standard deviation is not in the form of numbers => the function returns the #VALUE! Error.
- If average = 0 and standard deviation = 1, cumulative = True => function returns the normal distribution NORMSDIST .
- If the standard deviation is less than 0 => The function returns the value #NUM !.
- When the cumulative value = TRUE => distribution applies from negative infinity to the value x.
For example:
Calculate the distribution of the value 92.

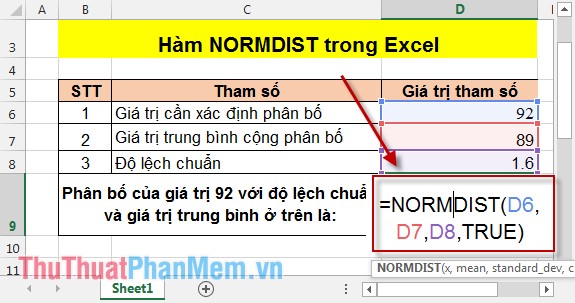
TH1: Cumulative value is TRUE
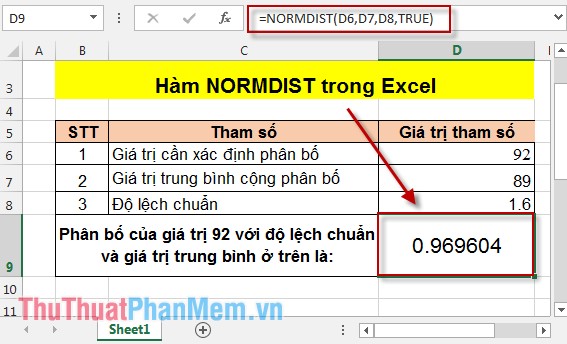
In the cell to calculate enter the formula: = NORMDIST (D6, D7, D8, TRUE) .
Pressing Enter has the result:
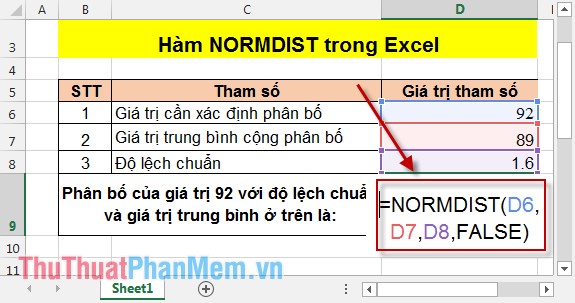
TH2: Cumulative value = FALSE
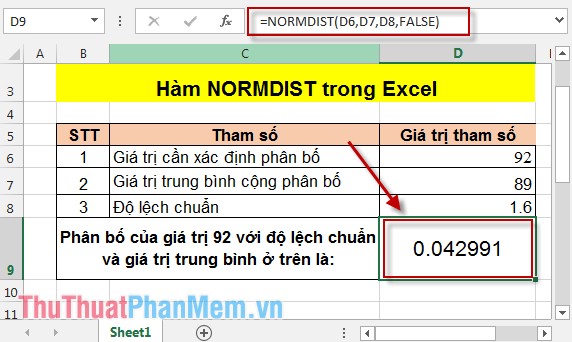
- In the cell to calculate, enter the formula: = NORMDIST (D6, D7, D8, FALSE) .
Pressing Enter results:
Case 3 : If the standard deviation = 1 and the mean value = 0, accumulate = True => NORMDIST (92) = NORMSDIST (92).
- NORMDIST function value (92):
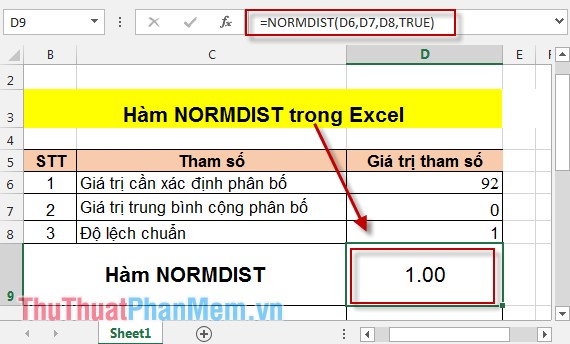
- NORMSDIST (92) value:
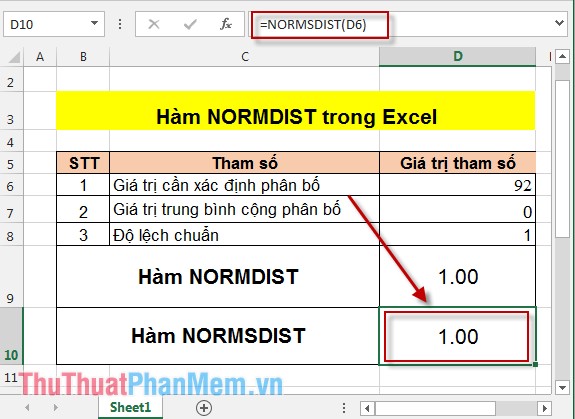
So if the standard deviation = 1 mean value = 0 and cumulative = true => NORMSDIST function is equal to the value of NORMDIST function.
The above details NORMDIST function and special case between NORMSDIST and NORMDIST functions. Hope this tool is helpful for you.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ NORM.S.INV function - The function returns the inverse of the normalized distribution with an average value of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 in Excel
- ★ NORM.S.DIST function - The function returns the normalized distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 in Excel
- ★ PHI function - The function returns the value of the density function for a normal distribution in Excel
- ★ STDEV.P function - The function returns the standard deviation based on the whole in Excel
- ★ SKEW function - The function returns the deviation of the distribution in Excel