NORM.DIST function - The function returns the normal distribution with the standard deviation and the mean value specified in Excel
The following article introduces you to the NORM.DIST function - one of the functions in the statistical function group is very popular in Excel.

Description: The function returns the normal distribution with a specified standard deviation and mean. Functions widely used in hypothesis testing statistics. Support functions from Excel 2010 onwards.
Syntax: NORM.DIST (x, mean, standard_dev, cumulative)
Inside:
- x: The value you want to calculate the normal distribution, is a required parameter .
- mean: Arithmetic mean of distribution, is a required parameter.
- standard_dev: The standard deviation of the distribution, is a required parameter.
- cumulative: A logical value that determines the form of the function, which is a required parameter, including:
+ cumulative = True -> returns the cumulative distribution function.
+ cumulative = False -> returns the probability density function.
Attention:
- If mean, standard_dev is not an integer -> they are truncated to integers.
- If mean, standard_dev is not a number -> the function returns the #VALUE! Error value
- If standard_dev ≤ 0 -> the function returns the #NUM! Error value
- If mean = 0 , standard_dev = 1 and cumulative = TRUE -> the function returns the normal distribution.
- The equation for the standard density function (cumulative = True) is:
[f (x; mu, sigma) = frac {1} {{sqrt {2pi} sigma}} {e ^ {- left ({frac {{{{left ({N - mu} right)} ^ 2}} } {{2 {sigma ^ 2}}}} right)}}]
- If cumulative = True -> the formula is integral from negative infinity to x.
For example:
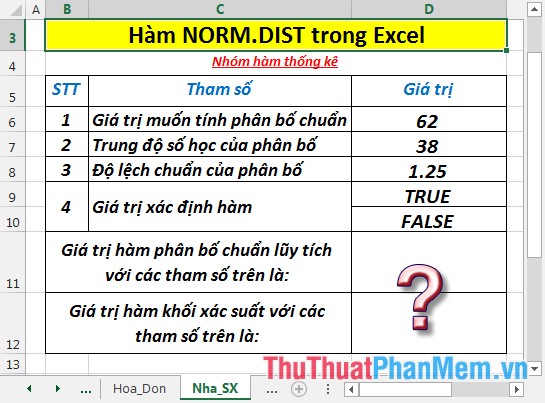
Find the cumulative and probability normal distribution with the values in the data table below:
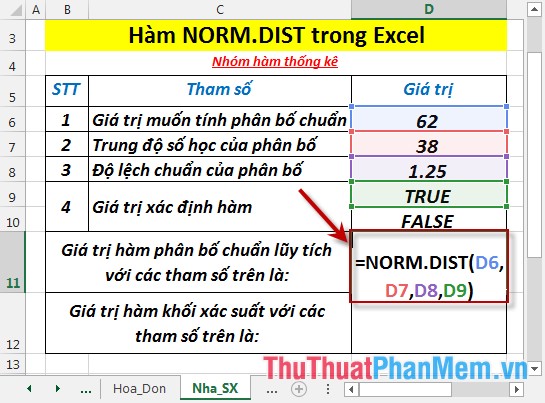
- Calculate cumulative standard distribution (corresponding to True value ) . In a cell to calculate, enter the formula : = NORM.DIST (D6, D7, D8, D9)
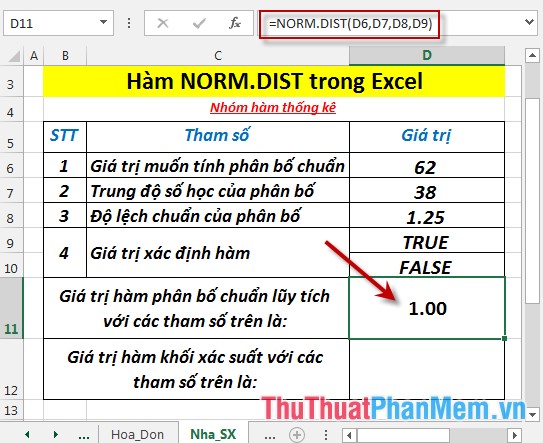
- Press Enter -> cumulative standard distribution is:
- Calculate the value of the probability block function (corresponding to the value of False) . In a cell to calculate, enter the formula : = NORM.DIST (D6, D7, D8, D10)

- Press Enter -> the probability function value is:
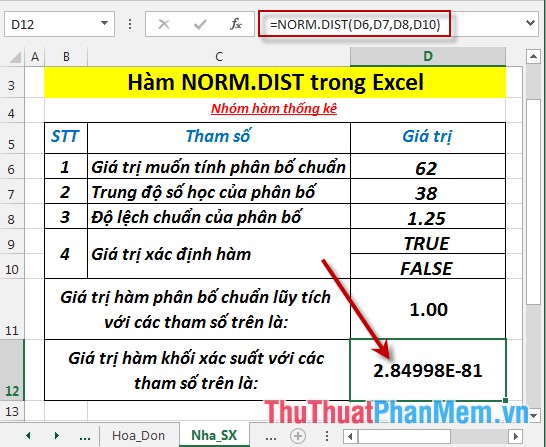
- There is a rather large difference in value between the cumulative standard distribution function and the probability distribution.
Above are instructions and some specific examples when using the NORM.DIST function in Excel.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ NORM.S.INV function - The function returns the inverse of the normalized distribution with an average value of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 in Excel
- ★ LOGNORM.DIST - Function returns the logarithmic distribution of x in Excel
- ★ POISSON.DIST function - The function returns the Poisson distribution in Excel
- ★ NORMDIST function - The function returns the normal distribution with the standard deviation and the average value specified in Excel
- ★ GAMMA.DIST function - The function returns the gamma distribution in Excel