GAMMA.DIST function - The function returns the gamma distribution in Excel
The following article introduces you to the GAMMA.DIST function - one of the functions in the statistical function group is very popular in Excel.

Description: The function returns the gamma distribution , using this function to study the skewed distribution variables . Support functions from Excel 2010 onwards.
Syntax: GAMMA.DIST (x, alpha, beta, cumulative)
Inside:
- x: The value you want to calculate the gamma distribution .
- alpha: The parameter value to the distribution .
- beta: Value The parameter value to the distribution , if beta = 1 -> function returns the standard gamma distribution .
- cumulative: Logic values that define the function format include:
+ cumulative = True -> Returns the cumulative distribution function.
+ cumulative = False -> Returns the probability density function.
Attention:
- If one of the function's x, alpha, and beta arguments is not a number form -> the function returns the #VALUE! Error value
- If x <0 or alpha ≤ 0 or beta ≤ 0 -> the function returns the #NUM! Error value
- The equation for calculating the gamma probability density function is:
[fleft ({x, alpha} right) = frac {1} {{{beta ^ alpha} Gamma left (alpha right)}} {x ^ {alpha - 1}} {e ^ {- frac {N} {beta }}}]
- The equation for calculating the standard gamma probability density function is:
[fleft ({x, alpha} right) = frac {{{x ^ {alpha - 1}} {e ^ {- N}}}} {{Gamma left (alpha right)}}]
- When alpha = 1 -> function returns exponential distribution with:
[alpha = frac {1} {beta}]
- For n positive integers, if alpha = n / 2 , beta = 2 , cumulative = true -> the function returns the value (1 - CHISQ.DIST.RT (x)) with n degrees of freedom.
- If alpha is a positive integer, the function GAMMA.DIST is called the Erlang distribution .
For example:
Find the GAMMA probability distribution and density in the data table below:
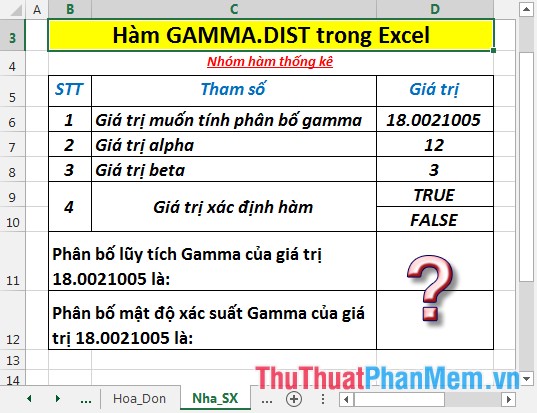
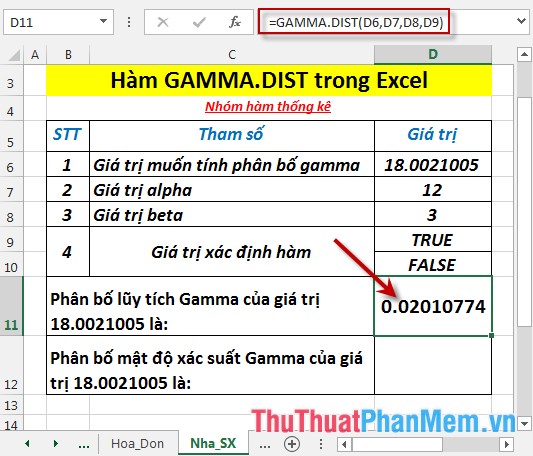
- Calculate the cumulative gamma distribution . In a cell to calculate, enter the formula : = GAMMA.DIST (D6, D7, D8, D9)

- Press Enter -> GAMMA cumulative distribution is:
- Calculate the gamma probability density distribution . In a cell to calculate, enter the formula: = GAMMA.DIST (D6, D7, D8, D10)
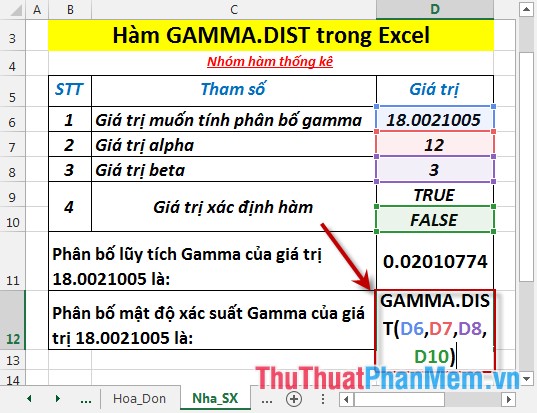
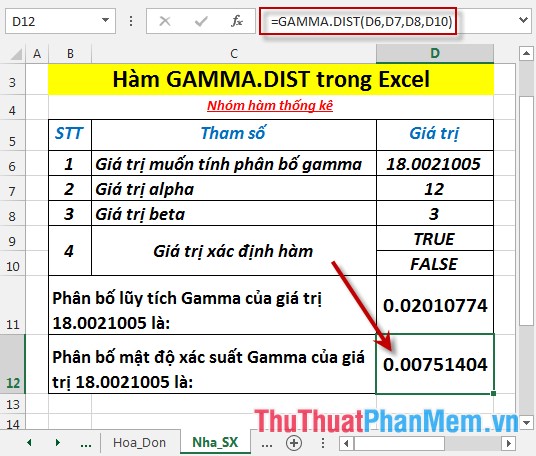
- Press Enter -> Gamma probability density is:
Above are instructions and some specific examples when using the GAMMA.DIST function in Excel.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ POISSON.DIST function - The function returns the Poisson distribution in Excel
- ★ BETA.DIST function - The function returns the Beta distribution in Excel
- ★ HYPGEOM.DIST - The function returns the hyperbolic distribution in Excel
- ★ F.DIST - The function returns the probability distribution F in Excel
- ★ T.DIST.RT - The function returns the Student's t-distribution on the right in Excel