Manage Hibernate Mode in Windows 7
If you do not use Hibernate hibernation in Windows 7 , you can save some disk space by disabling it. Here we will look at a few different ways to manage the Hibernate option in Windows 7.
Enable or disable Hibernate Via Command Prompt
Using the Command Prompt is the easiest way to enable or disable hibernation. Click on Start and type CMD in the search box and it will be listed by program. Right-click on the icon and select Run as administrator .
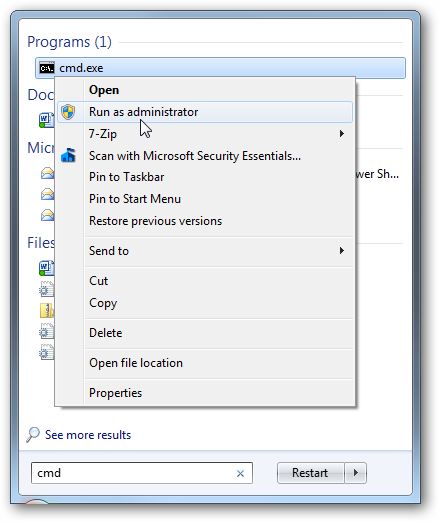
The Command Prompt opens and you will use the following to enable Hibernation .
powercfg / hibernate on
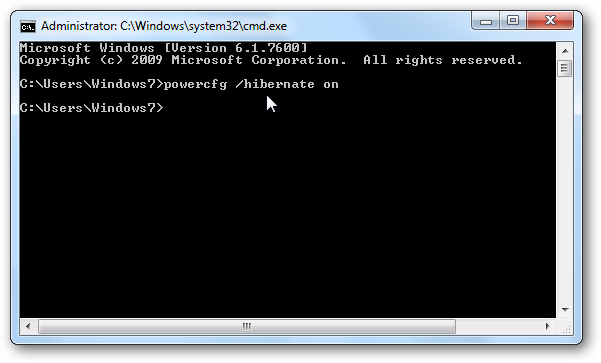
Type the following to disable hibernation.
powercfg / hibernate off

Managing Hibernation Through the Control Panel
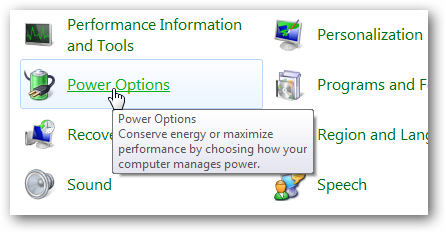
Click on Start and open Control Panel then click on Power Options .
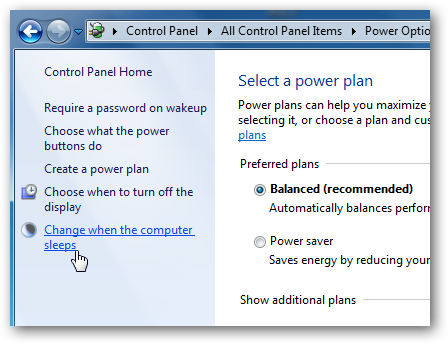
On the left, click Change when the computer sleeps.
Now click Change advanced power settings.
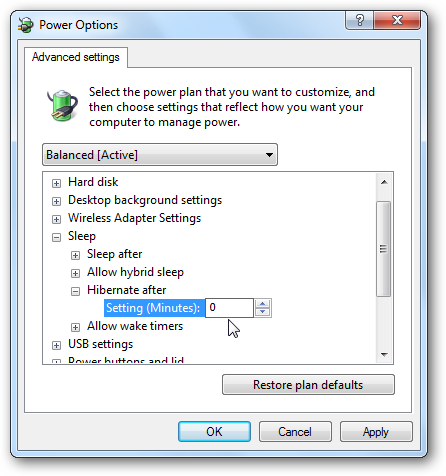
In the Advanced Power Options window expand the Sleep section then you will see the Hibernate after section and change the minute to 0 to turn it off. Or you can specify the number of minutes you want to pass before it goes into hibernation. After you have made your selection click on Apply and Ok then close out of the remaining screens.
Disable Hibernate Through Regedit
Note : Changing the registry value can cause your computer to become unstable or stop working and is only recommended for experienced users.
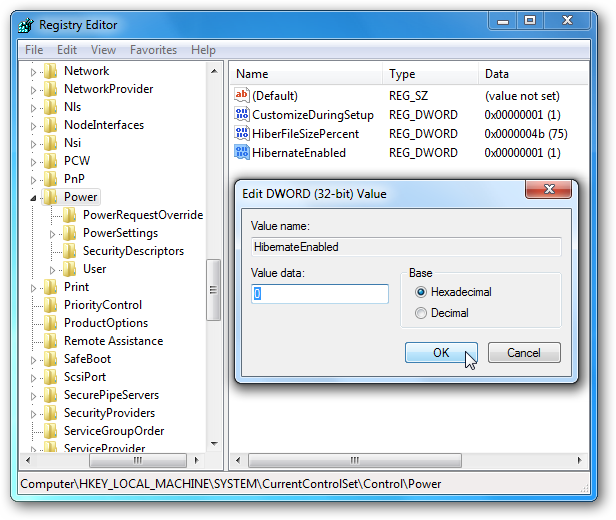
Now that the recommendation is on the go . you may want to disable Hibernate mode completely through a registry fix.Open the Registry and navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE SYSTEM CurrentControlSet Control Power and change both HiberFileSizePercent and HibernateEnabled to zero value data. After you have made the changes exit the Registry Editor and restart the computer.
If you always turn off your computer or never do it, you can turn off Hibernate mode to gain some hard disk space. On Windows 7 (32-bit) our machine with a 300GB hard drive, disabling hibernation gets us just over 3 GB of more disk space. That may not sound like a lot of high-capacity drives today, but if you don't need Hibernation , why not reclaim that space?