Sleep vs Hibernate: how different and when to use it?
It is not always possible to shut down the computer. We have 2 more effective solutions to temporarily "shut down" the machine, which are two Sleep and Hibernate modes. In short, Sleep will put the computer into a temporary "sleep" state and still have electrical current running inside the device. Meanwhile, Hibernate will store all data temporarily into HDD / SSD and then shorten the power. But in particular, what is the use case for each feature, how are they really different and how are the benefits of each?
- Should Shut Down, Sleep or Hibernate laptop?
The main content is like this, and the details invite you to see below

Sleep mode
On Windows and OS X called Sleep, on Linux it is called Suspend. You can activate this mode through the operating system's power button ( if you don't see the Sleep button, see the end of the article ). But if you use a laptop, you have an easier and faster way to put it into sleep: just fold the laptop lid and you're done. With the new Windows tablet, you also have a sleep button on your computer.
When sleep mode is used, the computer will switch to a state that uses very little power. Power will no longer be delivered to most PC components, except RAM, storage drives ( probably HDD or SSD ), and connection ports ( usually USB ).
RAM needs electricity because actually when you sleep, the RAM is still active. All files you are open, operating system settings, even running applications, still exist in RAM. That's why if you open the laptop lid, everything immediately appears as if you slept, nothing was lost ( except that some peripheral devices may be disconnected. , it takes a few seconds for them to reconnect ).
And to store the above information, RAM must have power, but as soon as you disconnect power from RAM, the data will be erased due to the specific mechanism of this type of device ( called volatile memory, on the contrary With HDD, SSD is non-volatile, ie without power, the data can still be saved .
In sleep mode, because the power is still provided to the connection port, for many laptops you can still charge your phone, tablet even when the device is " sleeping ". But there are some manufacturers that will not allow this, you should check the manual that comes with the device for specifics.
So when sleep is the application still running or not? The answer is yes and no. Some modern operating systems like OS X 10.8 onwards and Windows 8 onwards will allow applications to run in the background as soon as we sleep, but at that time the app can only do some simple things like receive new emails or chat messages, download new posts from Twitter / Facebook on their own . but they don't work properly. This way of activating an implicit run requires the developer to embed it in their app, and for most regular apps, for example, Word, Excel, PowerPoint or games, it will stop working at sleep. .
For Macs and Windows machines running Windows 8 and above, sleep is not wasting too much battery, according to my experience, if you sleep on the machine all day, it will only cost about 1-5% of the battery. Change the recovery time to start working extremely fast, without waiting for a long time like shutdown or hibernate ( discussed below ).
Hibernate or hibernate mode
Hibernate is available in Windows and Linux, but it is not enabled in OS X. Basically, we can see Hibernate as a solution in contrast to Sleep: Sleep keeps power for a few components, and Hibernate is not. The power will be completely removed from the system like when you shutdown, you can even remove the battery and remove the charger from the laptop without any problems.
But there is one very important difference: before the machine turns off completely, the operating system will transfer data from RAM to an SSD or HDD ( Sleep mode does not have this stage ). These data also include all the files you are open, the operating system settings, even the running applications, for the later restoration. But why spend more time for data transfer? As I said above, if the power is turned off, the RAM will lose data but the SSD / HDD is not, and because Hibernate will disconnect the power from all PC components, the data transfer is necessary.
When you press the power button to turn on the computer, the operating system will also run up. But instead of the operating system having to reload everything from scratch, in the " first stages ", the data from the HDD / SSD will be converted back to RAM again, so that the computer knows what the status is when you hibernate. so that to restore to correct. This step is of course more time consuming than recovering from sleep, but in return during the shutdown period, saving battery power more than electricity is completely not used. When the recovery machine from hibernate, which app is using, which file is open, which background image is displayed . will appear again exactly as it was.
Speaking of OS X, users don't have a " Hibernate " option as clearly as Windows or Linux users. Instead, it will be activated automatically with 2 different names:
- Safe Sleep : for Macs that use HDDs. This mode will be activated when the laptop battery is too low or when the device is left idle for a very long time ( it is unclear how long Apple idea )
- Standby Mode : used for Macs using SSDs. This mode is activated if your Mac has been sleeping for more than 3 hours. Apple said that a fully charged Mac could exist in Standby Mode for more than 30 days without plugging in the power.
If you want to use hibernate on a Mac similar to Windows and Linux, please use SmartSleep.
On Windows, there's something called Hybrid Sleep. It is a combination of Sleep and Hibernate. When Hybrid Sleep, the data about the app and the open file will be saved on both RAM and HDD / SSD, then the computer will enter a sleep state so you can still recover and start working again. Quick way. If the device is sleeping and the power outage is fine, the data on RAM will be lost but there is still data in the HDD / SSD so you can still restore the PC exactly like when recovering from hibernate. By default, Hybrid Sleep is enabled for desktop computers running Windows, and laptops are disabled.
The similarity and difference between Hibernate and Sleep
So now that you know the basic principles of Hibernate and Sleep, we can now summarize their similarities and differences as follows ( without the Hybrid Sleep case ):

When to use which?
Very simple:
- Use Sleep when you want a quick and convenient time to sleep and restore your computer when you need to store your laptop to move from home to work, between offices in the office, from home to work, to catch again are short-distance travel routes. Alternatively, you can use Sleep when you need to leave the PC for a short time, such as when going to lunch or meeting, for example.
- Use Hibernate when you know you will leave your computer for a long time, usually for hours or days. For example, you can hibernate your computer when you are about to go on vacation and throw your laptop at home. In such situations, waiting for hibernate recovery machine will not be too frustrating, the battery will not be wasted.
If you are concerned about the power consumption level when you sleep, you can go to Energy Star's website, a unit that certifies the level of electricity consumption for electronics and technology. You can use the machine code, for example the Dell Inspiron 15-7558, to check how much power the device will charge. However, these numbers are not so important, so just use the device freely.
Why don't I see the Sleep or Hibernate button?
This section is only for Windows users. If you click the operating system's Power button without seeing the Sleep and Hibernate option, one of the things below is probably the reason:
- Graphics card does not support sleep : The solution is to try to upgrade the card for the card, but if not, then buy a new card. But for computers, including laptops and desktops, sold in the last 5-7 years, this problem is no longer available because the new GPU supports sleep.
- Sleep and other power-saving modes have been disabled in the BIOS : The fixes are to shutdown the device, turn it back on, and once the device is running, press any Fx key repeatedly to enter the BIOS. Fx key is any key, depending on the company, like Dell is F12, Sony is F2, HP is usually F10, Lenovo is usually F1 or F2 ( may have to press the Fn button ), and Asus is also F2.
- If you only have Sleep without Hibernate, chances are your device will have Hybrid Sleep enabled
- Finally, you should also check in Control Panel to see if someone disables Sleep and Hibernate on your device:
- Go to Control Panel> Power Options> Change Plan Settings
- Press the " Change advanced power settings " line
- Select the " Change settings that are currently unavailable " option in the new window
- Find the " Sleep " line, there are enough options for Sleep and Hibernate
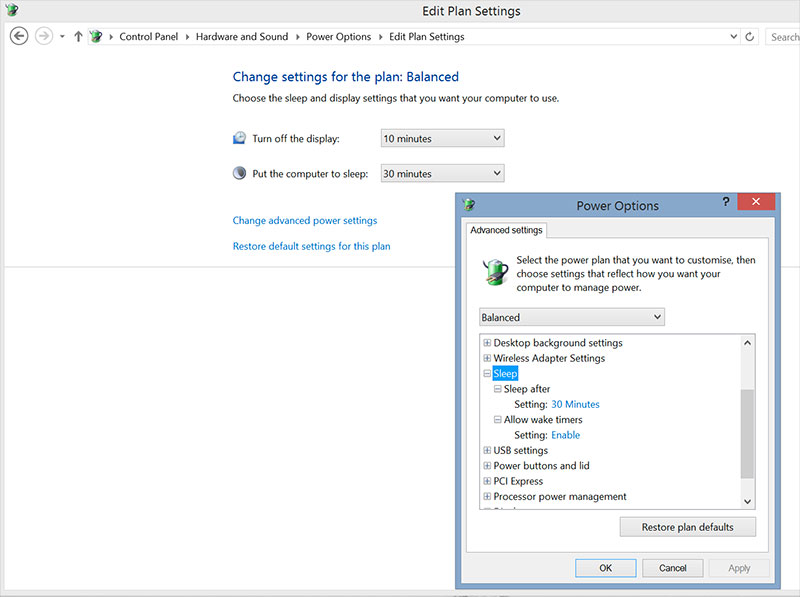
- Turn off, turn on Hibernate mode in Windows 7
- Instructions for enabling / disabling Hibernate mode on Windows 10
- Reactivate "hibernate" - Hibernate on Windows 8.1
Good luck!