Instructions for using Command Prompt
Deep in Windows is a command-line world that is obscure.In this article, we will show you how to solve errors and make your computer more secure.
The moment before Windows appears, when you turn on a computer we will see nothing but C:> prompt along with a mouse cursor. This is known as the command prompt (or sometimes Dos prompt). In order for the computer to do the job, users will have to fill in the cmd command from the internal memory.
However, this method of using the computer is really unattractive and some people even want to go back to using Dos prompt.
Still, do you believe that the command line still exists on all versions of Windows? Why so? The reason is that the commands are still a fast and powerful way to manage many aspects of Windows without having to use a complicated graphical interface.

As the content in the article will write, the command line can be a useful tool to fix and monitor, monitor errors and even improve security.
However, we have to admit that command line commands are free tools; Although they are not always necessary, learning the basics helps users discover the mysteries of the inner workings of Windows.
Before embarking on implementation, there are 2 things you should remember. First, this article is not for beginners or those who are afraid to change. Secondly, backing up your computer before doing it: we are not responsible for any problems that arise when you use the command line.
Windows Command Prompt
Before Windows appeared, the operating system called MS-Dos - shortened by Microsoft Disk Operating System - dominated the computer world. It will provide a link between users and computer hardware and based on writing, only requires the keyboard to operate.
Technically, MS-Dos uses a command-line interface (CLI) format, while Windows exploits graphical user interfaces (GUI).
The previous version of Windows operating system XP needs MS-Dos to operate because Windows itself cannot access the computer's BIOS. BIOS stands for English phrase (Basic Input / Output System) which means basic import / export system.
Users can choose to run Dos or Windows when the computer starts up and obviously everyone selects Windows.
Windows XP introduces a tool called Command Prompt , which currently exists in both Windows 7 and Windows 10. It is quite similar to MS-Dos but it is actually just an MS-DOS emulator running inside. Windows.
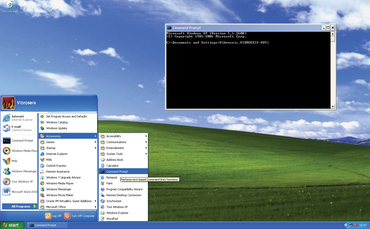
In addition to the technical side, Command Prompt allows access to a few unknown tools and settings. Because it does not need graphics, Command Prompt is very fast and in some cases it can be used to perform tasks that Windows cannot perform.
Of course, there are still a few shortcomings, many of which are the mysterious nature of the commands. Microsoft offers a comprehensive list of commands, how to use them and many different options. Click here to get the list of Windows XP and click here to get the version for Windows Vista / 7.
When Windows Explorer is the best
Although Command Prompt is a powerful tool, we don't think it is the easiest or the best method to perform tasks. Some commands seem a bit complicated, either because of a long string of characters or too many parameters.
It is very likely that errors will not be noticed by users when typing so it is better to use Windows Explorer to manage files daily.
Besides, the command line related tasks are also potentially dangerous - there are a number of dialog boxes confirming ' No, Yes or Cancel ' and no Undo commands (files deleted in the Commpand Prompt cannot be recovered). from the Recycle Bin), so sometimes the actions taken cannot be recovered.
Unfortunately misuse of wrong parameters and files can also be overwritten - even corrupting Windows system files.
Start with the BIOS
Remember we mentioned the BIOS above? Although not really a command-line tool, but Bios is a very important part of Windows and depends on the manufacturer and the computer model, it may include some very useful security tools.
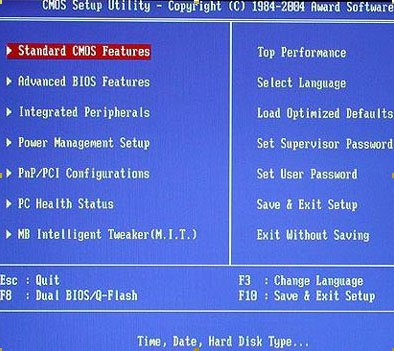
To find them, restart the computer, then press the BIOS key to access it - usually the F2 or Delete (Del) keys. When the BIOS screen appears, find the section labeled Security and navigate to it with the arrow keys.
In most cases, there will be options to help the user set the Supervisor password and User password. If you set the User password, this password needs to be entered before Windows works (of course, Windows also has a password).
If you set the Supervisor password, this password needs to be entered before accessing the BIOS - improving security.
Although there are many ways to reset or disable these passwords, this technique is beyond the capabilities of most current techniques, so they will provide additional useful security capabilities. For the same reason, users should take utmost care when using these tools: forget your password and you can be completely locked out of your computer. So be careful.
Besides, look for options called ' Boot Sector Virus Protection '. When you enable this option, there will not be any software that will be able to write down important boot sectors of the hard drive like some viruses do. However, please note that some software - specifically partitioning software - has a good reason to do this. So be careful with fake announcements.
When completed, exit the Bios (usually using the Esc key) and choose to save the changes you just made.
How to open the command line tool
Now run Windows to access the command-line tool: you'll see it in the Accessories menu from All Programs on the Start menu. Or, users can use the Windows + R key, then type cmd.exe in the Open dialog box and click OK .
- 12 ways to open CMD - Command Prompt easily on Windows 10
In Windows Vista / 7, sometimes users will need to use admin permissions to open it. To do this, right click on the command line icon and select ' Run as administrator '.
- Instructions to open Command Prompt Admin on Windows
Inside the dialog box
Command Prompt has some disadvantages. In Windows XP, it boots and displays C: Windows folder (or 'directory', just like it usually calls in this environment) but in Windows Vista / 7, it opens in the user's home address book ( C: Users [username ]) unless the Administrator mode is used, when it opens in the C: Windowssystem32 address book. No matter where it is opened, this address book is considered a link.
However, in Windows Vista / 7 Command Prompt can be opened in any folder in Windows Explorer by pressing the Shift key while right-clicking on the folder, then selecting the ' Open command window here ' from the pop-up menu.
To switch to a folder or other path, the CD command is used - to change to the address book named C: My Directory , type cd c: My Directory and press Enter . To switch between drives, simply type the wildcard name for the drive and a colon (eg D :) then press enter.
For most commands, type /? later it (or help before) will display very detailed support information. ' Help ' will display a list of all available commands. When switching between commands it is necessary to put a / or - before (minus sign); Check the support text to see which commands to use.
Some special text characters are often used in the command line. The pipe character ¦ will send the result of a certain command to use with another command. In most keyboards, it is typed by pressing the Alt Gr key and the key on the left of number 1 on the keyboard.
Another character is often used, especially when working with files that are asterisks * , representing any sequence of characters.
For example, * .xls means that files with an extension file extension are XLS. Letter. * Means that any file named Letter, and *. * Means all files. The question mark represents a single character - so Letter?. * Will include Letter1.doc, Letter2.pdf, .
Pressing Enter is always the way to execute commands, so in order not to repeat it we will not mention it. To clear the screen, use the CLS command, to exit the command line, type exit (or simply click the red mark to close the software window).
Safe use of the Internet
One of the most powerful commands to execute in the command line is the net. It has a lot of extra commands. For example, executing the net user command , will list all account names, while the net config workstation will display the computer, user and workgroup names.
More convenient in terms of security, it is also used to prevent users from logging in at certain times. To restrict Janet users from using computers between 9am and 6pm during the week and 10am to 9pm on weekends, type net user Janet / times: MF, 09-18; Sa-Su, 10-21 .
The net accounts command is great for improving password security. It needs the command line to be opened as administrator (as explained above) and it will display the password information for the current user.
People tend to choose short passwords and stick with them for a long time. However, net accounts can be used to eliminate this habit. For example, to make each user set a password of at least 10 characters long and change their password within 90 days, type net accounts / MAXPWAGE: 90 / MINPWLEN: 10 .
Users who use a password too short will be notified that they need to create a new password at the next login. To remove this restriction, type net accounts / MAXPWAGE: unlimited / MINPWLEN: 0 . (Pay attention to the following paragraph 'accounts).
Windows also has a built-in Guest account, without a password it cannot be changed in Windows. Although this account is not enabled by default, its password protection will contribute to increased security.
In the administrator command line, type net user guest * , then type the password twice when a window appears (characters will not appear on the screen). To remove the password, press Enter twice when a password entry screen appears. Besides, this command is also used to change or remove the password of any user by changing the guest with the username needed.
Secure copy and backup faster
Although we have copy, del (delete) and move commands for files (type + /? To find out more), xcopy is a more powerful replacement command. Users can apply this command to a lot of work and it is even more reliable than using Windows Explorer.
For new users, it is possible to copy all folders or hard drives, including all hidden files, to new storage areas. It even copies selected files based on whether the file is older or newer than the copy.
For example, if you want to copy everything on the C: drive to the D: drive, use the xcopy c: d: / d / s command. After a few days, use the xcopy c: d: / d / e / s command to copy the newly created files. This is a fast and very safe way to back up.
There are still many other uses that users can use with xcopy - to copy hidden files (or file systems), use / h switches , and to copy only files that already exist in one location, use / u switch .
When using the address book name, users will have to close these commands with quotes. For example, xcopy ' C: Old Documents ' ' D: Backup Documents ' / e / s . (note, there is a space after xcopy).
Detect suspicious activities
So far, we have been looking for ways to use the command line to improve security and perform some quicker and safer tasks. However, knowing how to use and operate the computer with the command line will also help identify and identify security threats.
For example, finding a software or service that is connected to the internet is a time-consuming task in Windows - but the netstat command simplifies this task. On the administrator command line, type netstat -b to display all active connections: this software is responsible for each connection displayed in the Proto column.
The Foreign Address column will display the URL or IP address of the remote home page (details about any IP address will be captured from the IP test site or with the 'whois' Sysinternals tool).
Meanwhile, Windows' boot log creation tool provides a powerful way to find out which drivers and services operate in error or fraud, such as malicious software / driver installation services (spyware, virus, .). It does not specifically require the use of command instructions but understands how the command line works, making it easy to read and translate files created by boot-logging mode.
To understand this, restart your computer and press the F8 key before the Windows logo appears. When the Advanced Options menu appears, use the arrow keys to select Enable Boot Logging and press Enter . (In Windows XP, if any other menu appears, just select Enter to continue).
When Windows works, open the command line window with administrator privileges and type cd% windir% to switch to the Windows address book. Next, type start notepad ntbtlog.txt to open the boot-log file in Notepad.
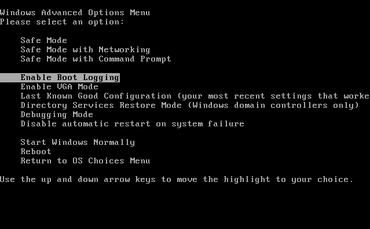
All drivers in the order of loading, repeating the full path, will be listed - and this information is much more useful when the concept of the address book path (mentioned above) is accepted. However, how useful is this in terms of security?
If the computer is working properly, save the log file somewhere to compare later when a problem arises. Close Notepad and go back to the command line. Type del ntbtlog.txt to delete the log file (if it does not delete, the next time it starts, the result will be added to the end of the current file).
If you think your computer has recently been infected with a virus, this method can be used to indicate new drivers or services that have suspicious activity: compare the boot-log file (ntbtlog.txt) before with the most recently created file.
Run Windows software with the command line
Nearly all Windows software can be booted with the command line. This may sound a bit crazy, but in fact it is very useful.
Many software that supports command line transfer can enable or disable some features, whether for convenience or for troubleshooting and security purposes. The recipe is to use the start command, followed by the name of the software. For example, to start Wordpad, type start write.exe . For Notepad, use start notepad.exe and for Word use start winword.exe .
Some software has a special diagnostic mode. To run Internet Explorer with all disabled add-ons, type start iexplore.exe -extoff and to open Excel in Safe Mode, type start excel.exe / s .
Besides, to discover the software name of an application, right-click its entry in the All Program menu and select Properties . Search the Target dialog box to find the file name with the .exe extension.
You may be disappointed but in fact there is no easy way to discover the transfer command for a specific software. If the software manufacturer does not provide information on their website, try searching the web with ' command-line options ' along with the name of the software.
Fight with infection
Similarly, the ongoing tasks of Windows are also listed when the user uses the tasklist command. This command displays the currently running software and the amount of memory they use. This is also a very useful way to detect malicious software - they can work without your knowledge.
Use tasklist / svc to list the related services with each software. The ( > ) character can be used to save this list into a file - for example, tasklist> tasklist.txt . Use this information to compare with a search engine like Google to find suspicious tasks or services.
Finally, a special Safe Mode option can load the command line instead of Windows Desktop, which is useful if the malware has disabled Safe Mode graphical mode (some fake antivirus software does this to makes it difficult for users to remove). On the Advanced Options menu select Safe Mode With Command Prompt .
One application for this is to run System Restore. From the command window, type cd% windir% system32restore .
After pressing Enter , execute the rstrui.exe command to run the System Restore wizard. To run Windows Desktop, type start explorer . To turn off the computer with the command, use shutdown -s to turn it off or shutdown -r to restart the computer.
Conclude
In this article, we showed you how to explore Windows 'underworld' to help improve computer security and perform some tasks. It may sound a bit outdated, but it is still one of the best ways to know what's going on with Windows. Spend some time to learn the basics that will be returned many times later when trying to prevent or solve security-related issues.
See more:
- Check and fix hard drive errors with CMD on Windows
- 21 Command Prompt tricks you may not know