How to Kill a Process in Command Prompt
Part 1 of 2:
Viewing Processes Currently Running on Your Computer
-
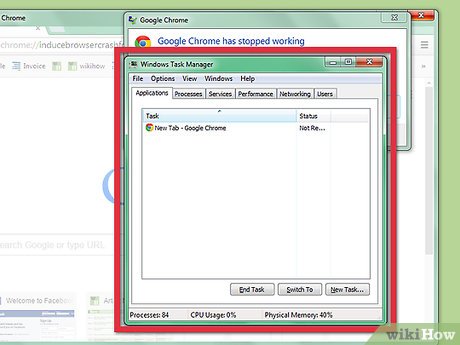
 Start Task Manager. Press the Ctrl key, the ⇧ Shift key, and the Esc key in consecutive order at the same time to open Task Manager.
Start Task Manager. Press the Ctrl key, the ⇧ Shift key, and the Esc key in consecutive order at the same time to open Task Manager. -
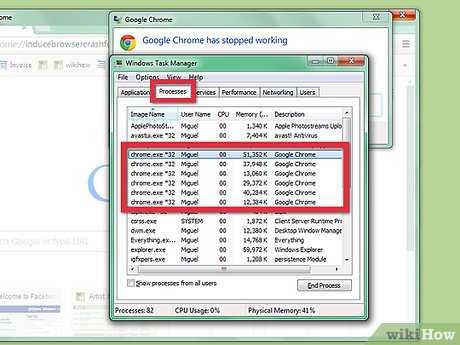
 View the names of the running processes and identify the problematic process. Click the Processes tab in Task Manager and find the name of the process that you want to kill.
View the names of the running processes and identify the problematic process. Click the Processes tab in Task Manager and find the name of the process that you want to kill.- Windows 8/8.1 users should click the Details tab.
- If a program that is currently running on your screen is frozen and you want to kill it, an easy way to find its name is to click the Applications tab (Processes tab in Windows 8/8.1), right click the window's name, then click Go to process (Go to details in Windows 8/8.1).
- If the Task Manager window does not display any tabs, double-click in the indicated space in the window to show them.
Part 2 of 2:
Killing Processes Currently Running on Your Computer
-
 Open the Start menu. Press the ⊞ Win key.
Open the Start menu. Press the ⊞ Win key. -
 Start Command Prompt as an Administrator. Right click the first result that appears in the Start menu and click Run as Administrator.
Start Command Prompt as an Administrator. Right click the first result that appears in the Start menu and click Run as Administrator.- If a User Account Control dialog appears, click Yes on it.
-
 Type taskkill /f /im into Command Prompt.
Type taskkill /f /im into Command Prompt. -
 Space at least once after completing the previous step, type a quotation mark, type the name of the process you want to kill, then type another quotation mark to top it off.
Space at least once after completing the previous step, type a quotation mark, type the name of the process you want to kill, then type another quotation mark to top it off. -
 Kill the process. Press the ↵ Enter key.
Kill the process. Press the ↵ Enter key.- Command Prompt should display a message similar to SUCCESS: The process "example.exe" with PID 0000 has been terminated.
Share by
Micah Soto
Update 04 March 2020
You should read it
- ★ How to scan viruses on Windows with Process Explorer
- ★ What is COM Surrogate or dllhost.exe and why does it run on the computer?
- ★ Instructions for using pstree command on Linux
- ★ How to fix the problem of too many background processes running on Windows PC
- ★ How to monitor network usage for Linux processes