Instructions for using pstree command on Linux
Pstree is a powerful and useful command to display processes running in Linux. Like the ps command, it shows all the processes that are currently active on your login system. The main difference is that when running the pstree command, processes are organized into tree sorting instead of lists like using the ps command. This tree displays processes in a parent-child relationship. The parent process is the process of creating all child processes below it.
The pstree pf structure is similar to the hierarchical directories on Unix systems like Linux and macOS. Using this structure, you can quickly navigate through the process tree to see which processes create or control each other, allowing the exact removal of processes that cause problems or are not controlled by the kill command. .
Run the command pstree
To run the basic form of this command, open the Terminal window and type the following command, then press Enter :
pstree

This command will display a list of all processes running on the system. The top process (in this case, systemd) is the parent process. The processes below it are created or opened via systemd. And branches from these processes show similar relationships, like family trees.
Here is the basic structure of pstree:
parent ———— child (1) ———— subchild (1) | | --subchild (2) | | -child (2)
By default processes generated from the same parent process will be ordered alphabetically. There are many other ways to sort in pstree using flags, we will discuss below.
Use pstree with flags
Like most Terminal programs, pstree can combine with different flags to create more complex output. To display process identification information, you can use the -p flag, display process identification number or PID.
pstree -p
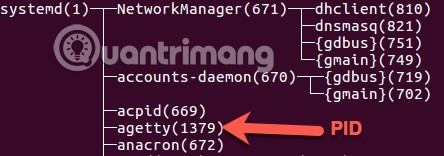
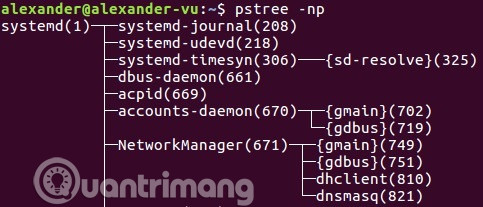
You can sort progress by PID instead of name with -n flag.
pstree -np
You may have noticed, the pstree output is usually cut off at the terminal window. Therefore, you can 'pack' long result lines with the - l flag.
pstree -l
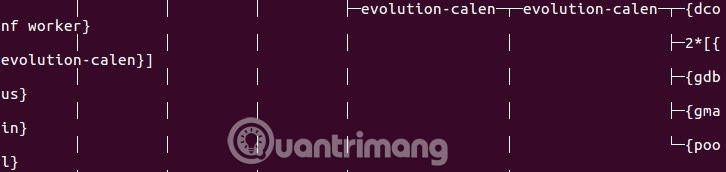
However, this operation will make it difficult for users to read the output.
See also: Store the output of a Linux command into a file
Show parts of the process tree
You can also view only a part of the process tree. There are two ways to do this. First, use the -s flag, allowing you to see the parent process of the child process you specify. You can call this process by its PID.
pstree -s 780

You can also view processes generated by the current user. If there are multiple users on the system, you will know who is doing what on your system. To see the processes generated by the user, just type the user name after the main command.
pstree alexander
This command will display any commands executed by that user's account, via the user program run or through the command they execute.
Each version of Linux may have different ways to use this command, but this is the most basic guide. To get help with the version you are using, type man pstree in the command line and press Enter to open the instruction page.
I wish you all success!
See more:
- Basic Linux commands everyone needs to know
- Certain deadly commands never run on Linux
- Guide to network operation for Linux users: 11 commands to know