7 steps to successfully overcome Windows network
In this article, I will show you 7 steps to overcome the success of Windows network. Besides, what to check for local computers and Windows infrastructure such as DNS, DNCP and default ports .
Although there is only one small home network with a Windows computer or a large enterprise network with thousands of Windows and server computers, troubleshooting network connectivity is always a challenge for administrators. network member. The complexity in troubleshooting will increase with the number of devices and the scope of Windows infrastructure. However, with some troubleshooting steps introduced in this article, you can successfully fix a Windows network for the first time.
Step 1 - Capture the infrastructure
To successfully fix the problem, the first thing you need to do is capture the network infrastructure (what is connected to what and how it is designed). If your network is an enterprise network using Windows computers, chances are you'll get a network map. Ideally it will be the case that you design your own network, but it is not always that lucky for you.
Step 2 - Learn about the network
If you don't know the network infrastructure design and don't have reference documents, you can start troubleshooting by learning about the network infrastructure from the best diagnostic tools. There are many things you can know by using IPCONFIG or information in the Windows Network Connection window.
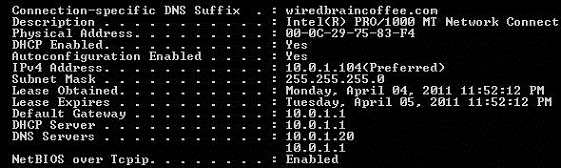
Figure 1: IPCONFIG
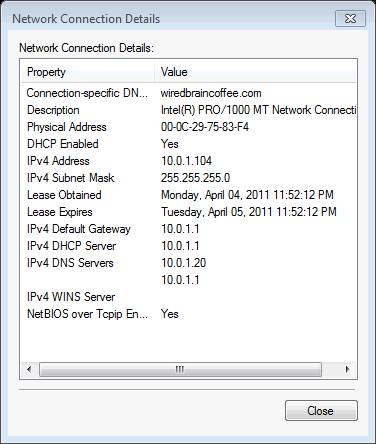
Figure 2: Details in Windows Network Connection
From these two tools, you can know many things like:
- Network interface is still active or having trouble (physical network connection)
- How to obtain an IP address - DHCP or static
- Whether or not an IP address or an IP address is automatically assigned (address starts with 169.254.xx or APIPA)
- Default port
- Configure DNS server
All this information is valuable in solving Windows network problems.
In the figures shown above, the network there is working fine and no problem occurs. However, what happens if IPCONFIG shows the problem here? The steps below, we will focus on some general networking issues and some solutions.
Step 3 - Network connection is down
If you look at the OSI model, the physical layer (layer 1) is underneath. If class 1 does not work, there is no signal transmitted here. The best way is to solve the problem from the bottom up (meaning from grade 1 to higher grades).
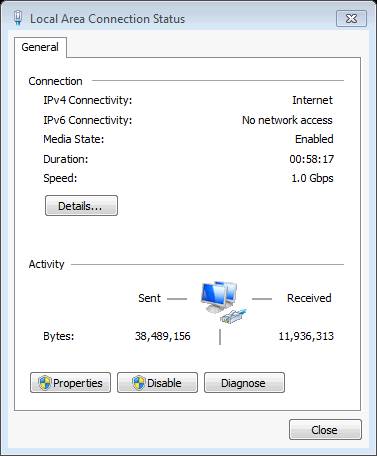
Figure 3: Network connection status
In the image above, you can see the Media State line is Enabled. This is very normal, but if Media State has disabled status then all you need to do is:
- Check the network cable - is it unplugged, broken or cut?
- Check the switch - see if the network cable is connected to it? Is the port active?
Make sure all of the above work well before moving on to the steps below.
Step 4 - No IP address
Whether you don't have an IP address (0.0.0.0) or a self-assigned IP address (APIPA, starting with 169.254.xx), there's absolutely no problem. You will have to receive an IP address before using the network. If set to use DHCP (usually set by default) and the DHCP server has a problem, that's why you don't have an IP address.
Options to solve the problem:
- Solve the problem with the DHCP server
- Static assignment of non-conflicting IP addresses, located on the correct subnet, .
Step 5 - Do not DNS server
If no DNS server is configured, you can only communicate on the network with an IP address. You can now use the 'ping' command to check the default gateway, DHCP server and other servers on the network. However, you will not be able to perform any checks by name.
Options to solve the problem:
- Determine why the DHCP server does not provide an IP address
- Configure IP addresses if you know them
- Configure a public Internet DNS server like Google's DNS servers (8.8.4.4)
In other words, if you can't ping configured DNS servers, you need to check them - they may be suspended or data packets are blocked at the firewall.
Step 6 - No default Gateway
If you do not configure the IP address for the default gateway, you will not be able to communicate on another IP subnet (Internet for example) or you will not be able to communicate on your local LAN. Thus, when there is no IP for the default gateway, you can only work normally with local servers. In fact, configuring the default gateway is completely optional if you don't need access to the outside network.
You can manually configure the default gateway or determine if the DHCP server does not provide an IP address.
Alternatively, if you have defined the default gateway but cannot communicate with it (even with the ping command), you need to check your local router.
Step 7 - Configure the wrong Subnet Mask
If you misconfigured the IP subnet mask, you will get some unpredictable results. Now you need to reconfigure it yourself (if you are using a static IP address) or check the DHCP server to see why it provides the wrong subnet mask for you.