Summary of technical functions in Excel
The following article introduces in detail the technical functions in excel.
1. CONVERT function
Description: The function converts back and forth between measurement units. For example, converting units in weight, mass, length, time, energy .
Syntax: CONVERT (number, from_unit, to_unit) .
Inside:
- number: the value you want to convert.
- from_unit: The original unit of value you want to convert.
- to_unit: The unit of measurement you want to convert to.
For example: Convert (5, g, ozm): Convert 5g to Ounce mass units.
Standard for writing conversion units:



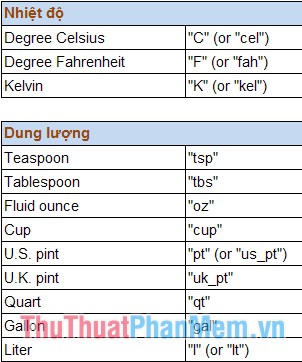
2. BESSELI function
Description: Returns the BESSELI function of the In (x) transform.
Syntax: BESSELI (x, n) .
Inside:
- x is the value to calculate the Besseli function.
- n is the order of the function, if n is a decimal number => the function takes the rounding value of n.
Attention:
- If n function returns the value #NUM!
- x, n must be numeric values if entered incorrectly => #VALUE error message.
Example: BESSELI (2.5,3) => Variable Besseli function In (x) first order at value 1.5 => result = 0.47437.
3. The BESSELJ function
Description: Returns the BESSELJ function of the variable Jn (x).
Syntax: BESSELJ (x, n) .
Inside:
- x is the value to calculate the Besselj function.
- n is the order of the function, if n is a decimal number => the function takes the rounding value of n.
Attention:
- If n function returns the value #NUM!
- x, n must be numeric values if entered incorrectly => #VALUE error message.
For example: BESSELJ (2.5,3) => The Besselj function transforms first-degree jn (x) at value 1.5 => result = 0.2166.
4. The BESSELK function
Description: Returns the BESSELK function of the Kn (x) transform.
Syntax: BESSELK (x, n) .
Inside:
- x is the value to calculate the Besselk function.
- n is the order of the function, if n is a decimal number => the function takes the rounding value of n.
Attention:
- If n function returns the value #NUM!
- x, n must be numeric values if entered incorrectly => #VALUE error message.
Example: BESSELK (2.5,3) => Variable Besselk function In (x) first order at value 1.5 => result = 0.268227.
5. BESSELY function
Description: Returns the BESSELY function of the variable Yn (x).
Syntax: BESSELY (x, n) .
Inside:
- x is the value to calculate the Bessely function.
- n is the order of the function, if n is a decimal number => the function takes the rounding value of n.
Attention:
- If n function returns the value #NUM!
- x, n must be numeric values if entered incorrectly => #VALUE error message.
For example: BESSELY (2.5,3) => The Bessely function transforms Yn (x) first order at the value 1.5 => result = -0.75605.
6. The BIN2DEC function
Description: The function performs conversion of binary numbers to decimal numbers.
Syntax: BIN2DEC (number) .
Inside:
number is the value to convert.
Note: If number is more than 10 characters => function value returns an error! NUM.
7. DEC2BIN function
Description: The function performs conversion of decimal values to numbers in binary.
Syntax: DEC2BIN (number [, places]) .
Inside:
- number is the value to convert, places arbitrary parameters.
- places is the number of characters you want to use in the return value.
8. The BIN2HEX function
Description: The function performs a number conversion from binary to hexadecimal.
Syntax: BIN2HEX (NUMBER [, PLACE]) .
Inside:
- Number is the binary value you want to convert.
- Place (the arbitrary value): is the number of characters of the returned result, if omitted excel, get the minimum number of characters enough to return the result.
Attention:
- Place is a natural and non-negative numerical value.
- If the value you want to convert is more than 10 characters => the #NUM !.
- If the conversion value is negative, the function ignores the place parameter and returns the result with 10 characters in hexadecimal.
- If the result has a larger number of characters than the specified in place => error #Num!
- If you enter place as a decimal value, get the integer part of the place.
9. Ham HEX2BIN
Description: The function performs conversion of numeric values from hexadecimal to binary.
Syntax: HEX2BIN (number [, place]) .
Inside:
- number is the value you want to convert.
- place: arbitrary value, specifying the number of characters of the returned result.
Attention:
- Enter the number value in quotation marks eg HEX2BIN ("F").
10. BIN2OCT function
Description: The function converts binary numbers to octal numbers.
Syntax: BIN2OCT (number [, places]) .
Where: number is the value you want to convert, place is an arbitrary value that is the number of characters of the returned result.
Note: Notes are similar to the above functions.
11. OCT2BIN function

Description: The function converts numbers from octal to binary.
Syntax: OCT2BIN (number [, places]) .
Inside:
- number is the value to be converted.
- places: number of characters of the returned result, arbitrary parameters, if omitted excel, the minimum value is sufficient to denote the result.
Note: Notes are similar to the above conversion functions.
12. Ham COMPLEX
Description: The function converts real and imaginary factors into complex numbers of the form x + yi or x + ỵ.
Syntax: COMPLEX (real_num, i_num [, suffix] .
Inside:
- real_num: real coefficient is a numerical value.
- i_num: The imaginary coefficient is a numerical value.
- suffix: suffix of virtual coefficient of complex number if ignoring default is i, if not put in quotation marks.
Note: If 1 of 2 real_num and i_num values are not numeric => #Value error. Or, in case of input suffix outside the characters i and j, the error function #Value.
13. The DEC2OCT function
Description: Convert decimal numbers to octal numbers.
Syntax: DEC2OCT (number, places) .
Inside:
- number: is the decimal number to be converted to octal.
- places: is the number of characters of the returned result. If you enter places, the return result contains the leading zero if the result has fewer characters than places.
Attention:
- If number> 536,870,911 or number <-536870912, or places exceeds 40 characters or places the #NUM!
- If number, places are not numbers => the error message #VALUE!
14. The DELTA function
Description: Check if the 2 numbers are equal or not.
Syntax: DELTA (number 1, number 2) .
Inside:
- number1: is the 1 comparison value.
- number2: is the second comparison value.
If two values are equal => the value of the function returns 1, otherwise it returns 0.
Note: 2 values must be numeric values, if the error value type is entered in the #VALUE error function.
15. GESTEP function
Description: How the function is used to compare 2 values.
Syntax: GETSTEP (number, step) .
Inside:
- number is the value to compare.
- step: value to compare.
If number> step => GETSTEP returns 1, otherwise number
Attention:
- If you do not enter the test value, step by step the function automatically understands the value of step = 0.
- The two parameters of the function must be a numeric value otherwise the #VALUE error function will be displayed.
16. The IMAGINARY function
Description: The function returns the imaginary coefficient of a real number in a complex coefficient.
Syntax: IMAGINARY (number) .
Inside:
- number is a complex number to get a virtual coefficient.
17. IMDIV function
Description: The function performs the quotient of 2 complex numbers.
Syntax: IMDIV (inumber1, inumber2) .
Inside:
- inumber1 is the first complex number to be calculated.
- inumber2 is the second complex number to be calculated.
18. IMLN function
Description: The function performs the natural logarithm of a complex number.
Syntax: IMLN (inumber) .
Inside:
- inumber is a complex number that needs to be calculated naturally.
19. The IMLOG2 function
Description: The function performs base 2 logarithms of a complex number.
Syntax: IMLOG2 (inumber) .
Inside:
- inumber is a complex number to be calculated base 2's logarithm.
20. IMPRODUCT function
Description: The function performs the product of the product of 2 complex numbers.
Syntax: IMPRODUCT (inumber1, inumber2, inumber3, .) .
Inside:
- inumber are complex numbers to calculate.
Note: Complex numbers entered in quotation marks.
For example, IMPRODUCT ("3-2i", "24-9i").
21. IMSIN function
Description: The function performs calculating the sine value of a complex number.
Syntax: IMSIN (number) .
Inside:
- number is a complex number to be calculated.
22. IMSUB function
Description: The function performs the difference of two complex numbers.
Syntax: IMSUB (inumber1, inumber2) .
Inside:
- inumber1 is the first complex number.
- inumber 2 is the second complex number.
23. The IMABS function
Description: Calculate the absolute value of a complex number.
Syntax: IMABS (inumber) .
Inside:
- inumber is a complex number that needs absolute value calculation.
24. IMEXP function
Description: The function performs exponentiation e of complex numbers.
Syntax: IMEXP (inumber) .
Inside:
- inumber is a complex number whose base power is to be calculated e.
25. IMCOS function
Description: Perform the cosine calculation of a complex number.
Syntax: IMCOS (inumber) .
Inside:
- inumber is a complex number for cosine.
Note: The value of entering a complex number is enclosed in quotation marks.
26. IMLOG10 function
Description: The function performs base 10 logarithms of a complex number.
Syntax: IMLOG10 (inumber) .
Inside:
- inumber is a complex number to be calculated base 10 logarithms.
27. IMPOWER function
Description: The function performs exponentiation of a complex number.
Syntax: IMPOWER (inumber, number) .
Inside:
- number is a complex number for exponentiation, number is exponent.
28. The function IMREAL
Description: The function that performs the calculation returns the real coefficient of the complex number.
Syntax: IMREAL (inumber) .
Inside:
- inumber is a complex number to find the real coefficient.
Note: Enter a complex numeric value in quotation marks.
For example: IMREAL ("15-6i").
29. IMSQRT
Description: The function performs the square root of a complex number.
Syntax: IMSQRT (inumber) .
Inside:
- inumber is a complex numerical value to calculate square root.
30. IMSUM function
Description: The function performs calculations and returns the total value of 2 complex numbers.
Syntax: IMSUM (inumber1, inumber2, inumber3, .) .
Inside:
- inumber is complex numbers to be calculated with complex numbers to calculate up to 29 numbers.