Logical functions (logical) in Excel
Logical functions are used a lot during data processing in Excel. If you do not know all of the common logical functions, follow the article below. The article summarizes the syntax and functions of functions in logical function groups in Excel.

1. AND
Syntax:
= AND (logical1, logical2, .)
Inside:
- logical1, logical2, . is one or more logical expressions that can be TRUE or FALSE.
Description:
The function returns TRUE if all arguments are evaluated as TRUE and returns FALSE if one or more logical values are defined as FALSE.
For example:

2. IF
Syntax:
= IF (logical_test, value_if_true, value_if_false)
Inside:
- logical_test: any value or expression that can be TRUE or FALSE.
- value_if_true: is the value you want to return when logical_test is TRUE. If logical_test is TRUE and value_if_true is omitted, the function will return 0 (zero).
- value_if_false: is the value that you want to return when logical_test is FALSE. If logical_test is FALSE where value_if_false is omitted (without the comma after the value_if_true argument), the function returns the logical value FALSE. If logical_test is FALSE where value_if_false is omitted (comma is followed by value_if_true argument), the function returns 0 (zero).
Description:
The function returns a value if the condition you specified is TRUE and returns a different value if that condition is evaluated as FALSE.
For example:

3. IFERROR
Syntax:
= IFERROR (value, value_if_error)
Inside:
- value: expression to check for errors.
- value_if_error: return value if value error, the following error types: # N / A, #VALUE, #REF, # DIV / 0 !, #NUM !, #NAME? or #NULL !.
Description:
The function returns the value_if_error if the value is evaluated as an error, otherwise the result of the formula is returned.
For example:
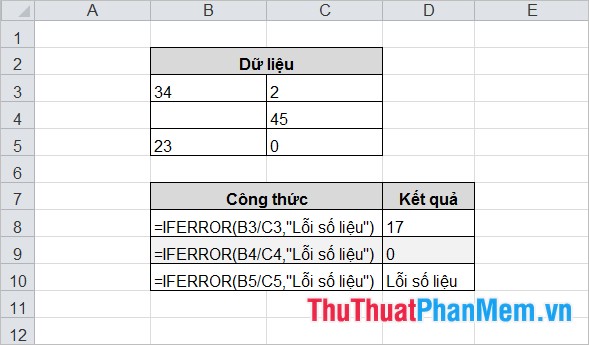
4. NOT
Syntax:
= NOT (logical)
Inside:
logical is an expression, a condition of type logic.
Description:
The function that returns the result is a negation of the logical expression, NOT returns TRUE if the logical expression is FALSE and vice versa.
For example:
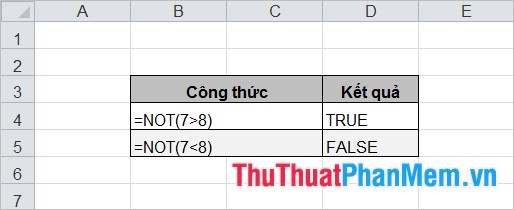
5. OR
Syntax:
= OR (logical1, logical2, .)
Inside:
- logical1, logical2, . are the expressions and conditions that you want to check TRUE or FALSE.
Description:
The function returns TRUE if one or more logical is TRUE, returns FALSE if all logical is FALSE.
For example:

6. FALSE () and TRUE ()
Syntax:
= FALSE () = TRUE ()
No arguments. You can enter FALSE or TRUE directly into a formula or function when calculating. Excel will interpret itself as a logical value of FALSE or TRUE value.
For example:
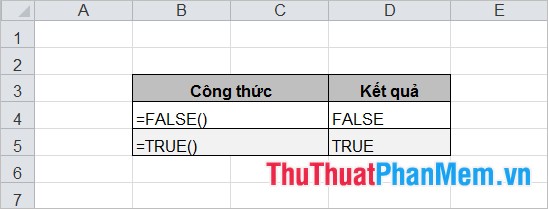
The article has introduced to you the functions in the logical function group in Excel, hope the article will help you. Good luck!
You should read it
- VAR.P function - Function that calculates variance based on the entire set, ignoring logical values and text in Excel
- How to use the IFS function in Excel 2016
- IFERROR function in Excel, formulas, and usage
- MINA and MAXA functions in Excel
- How to create and delete tables in Excel
- Answering these 10 puzzles in 7 seconds proves that your brain is extremely special!
 Spacing, spacing words in Word
Spacing, spacing words in Word How to use the RANK function in Excel
How to use the RANK function in Excel Change the width of columns and the height of rows in Excel
Change the width of columns and the height of rows in Excel Daverage function in Excel - Daverage function calculates the average value with a given condition
Daverage function in Excel - Daverage function calculates the average value with a given condition IF function in Excel
IF function in Excel Split data in columns in Excel
Split data in columns in Excel