SLOPE function - The function returns the slope of a linear regression line through data points in Excel
The following article introduces you to the SLOPE function - one of the functions in the group of statistical functions that is very popular in Excel.

Description: The function returns the slope of a linear regression line through data points. The slope is the vertical distance divided by the horizontal distance between any two points on that line, the rate of change along the regression line.
Syntax: SLOPE (known_y's, known_x's)
Inside:
- known_y's : An independent data point array or range.
- known_x's: The set of independent data points.
Attention:
- The value of the argument must be a number, name, array or reference containing numbers.
- If known_y's and known_x's are empty or have a different number of data points -> the function returns the # N / A error value .
- If the argument is a reference array containing text values or logic -> these values are ignored, but the value 0 is still counted.
- If argument values use invalid data types -> the function returns the #VALUE! Error value
- The slope equation for the regression line is:
[b = frac {{sum {left ({x - overline x} right) left ({y - overline y} right)}}} {{sum {{{left ({x - overline x} right)} ^ 2 }}}}]
Where x and y are the sample mean AVERAGE (known_x's) and AVERAGE (known_y's)
For example:
Calculate the slope of the linear regression line through data points in the following data table:
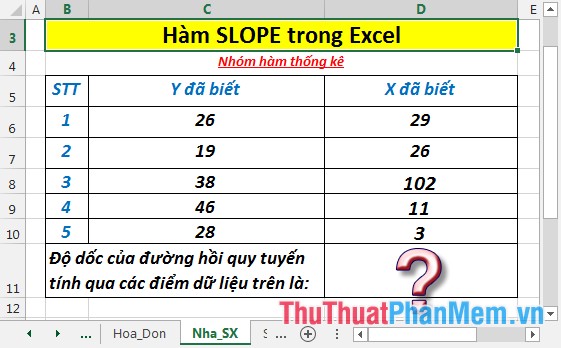
- In the cell to calculate enter the formula : = SLOPE (C6: C10, D6: D10)
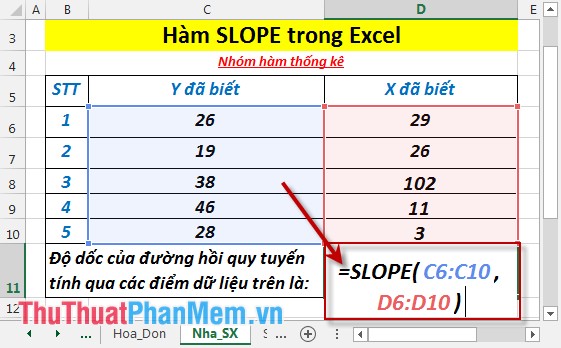
- Press Enter -> slope of the linear regression line through the above data points is:

Above are instructions and some specific examples when using SLOPE function in Excel.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ STEYX function - The function returns the standard error of the predicted value of y for each value of x in regression in Excel
- ★ TREND - The function returns values in a linear trend in Excel
- ★ AVEDEV function - The function returns the average absolute deviation of data points from their midpoint in Excel
- ★ PEARSON function - The function returns the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient in Excel
- ★ COVARIANCE.P function - The function returns the covariance of a set, the product of the average of degrees of instruction for each pair of data points in Excel