Learn about the mechanism of NAT (Network Address Translation) (Part 1)
Modern Internet connection today must use NAT (Network Address Translation) technology. NAT (Network Address Translation) allows one or more local IP addresses to be mapped to one or more external IP addresses . To understand more about NAT as well as NAT's operation mechanism, please refer to the article below.
The Internet is more and more developed than our imagination. Although it is impossible to list the exact number, we can estimate the number of more than 100 million Hosts and more than 350 million people accessing the Internet daily. In fact, this rate doubles every year.
Modern Internet connection today must use NAT (Network Address Translation) technology. NAT allows one (or more) local IP addresses to be mapped to one (or more) external IP addresses .
IP address ( IP - Internet Protocol ) is a series of 32-bit (IPv4) or 128-bit (IPv6) numbers used to identify a network device on the network that helps them identify and communicate with each other. In a network model, each network device has only one IP address . It is understandable that the IP address is like the address where you live. Others can find you and send information to you via that address.
Along with the current Internet boom and the increasing demand for network systems, the IPv4 address space began to be limited. The solution is to redesign the IP address format, allowing more IP addresses (namely IPv6 ). However, this solution is still in the research and development stage and it takes many years to implement.
Therefore, the best solution is to use NAT (Network Address Translation) technology . NAT or Network AddressTranslation allows a device such as the Router to act as an intermediary between the Internet (or Public Network : public network) and Local (or Private : local network). This means that a computer only has a unique IP address .
What is NAT (Network Address Translation)?
Understandably, NAT is like a receptionist at a large office. If you want to meet someone in the company you have to go through and follow the receptionist's instructions. Or if you want to call and talk to someone but the person is not at the company or they are busy at the meeting, . you can leave a message for the receptionist then they will forward the message to the person You need to talk to inform. In another case you can talk to the receptionist and ask them to connect to the person you need to meet.
Or you can understand when someone wants to talk to you, but they only know the office phone number where you work. They will call your office and ask the receptionist to forward the call to you. Now the receptionist will conduct a check on the lookup table to find out your name and other extended information. And then they will forward the call to you on your extension.
What does NAT (Network Address Translation) do?
Network Address Translation ( NAT ) is like a router , forwarding packets between different network layers on a large network. NAT translates or changes one or both addresses inside a packet when the packet goes through a Router , or some other device. Usually NAT usually changes the address is usually the private address ( Private IP ) of a network connection to a public address (IP Public).
NAT can also be considered a basic firewall. NAT maintains a table of information about each packet sent. When a computer on the network connects to a website on the Internet header of the source IP address that is replaced by a pre-configured public address on the NAT server , after a packet returns to NAT based on the record table it has save to packets, change the destination IP address to the PC 's address in the network and forward it. Through that mechanism, network administrators can filter packets sent to or sent from an IP address and allow or prevent access to a specific port.
More reference: General introduction about NAT
NAT (Network Address Translation) was developed by Cisco . NAT includes some basic types below:
Static NAT (static NAT)
Static NAT (static NAT) is a NAT method that has a double. A Private IP address will be mapped with a Public IP address.
Static NAT is used when the device needs to be accessed from outside the network.
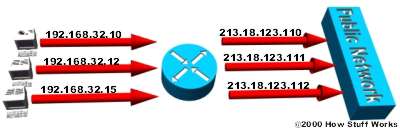
In Static NAT , the IP address of the computer is 192.168.32.10. It is always compiled by the Router to the IP address 213.18.123.110.
Dynamic NAT (dynamic NAT)
A Private IP address will be mapped with a Public IP address in the Public IP address group .
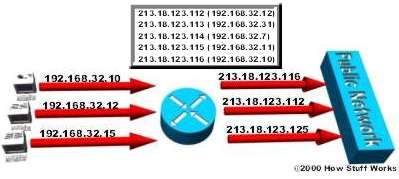
In Dynamic NAT , the computer with the IP address 192.168.32.10 is always compiled by the Router to the first address 213.18.123.100 in the IP address range from 213.18.123.100 to 213.18.123.150.
See also: Trick to change dynamic NAT configuration
Overloading NAT
NAT Overloading is a dynamic NAT form (Dynamic Overload) . Many Private IP addresses will be mapped with a Public IP address through different Ports .
Just like PAT (Port Address Translation) , a NAT or Port address will have many different NAT levels.

In Overloading NAT , each computer on the local network (Private Network) is compiled by the Router to the same IP address 213.18.123.100 but on different communication ports.
Overlapping NAT
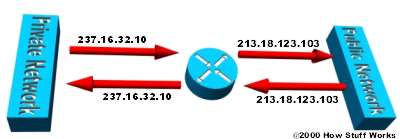
When the IP address in the local network is IP Public being used on another network, the Router must maintain a table looking for these addresses to prevent and replace with a single Public IP .
It is important to note that the NAT router must compile the "internal" address into a single public IP address as well as compile the "external" address into a single Private IP address . You can use static NAT or use a combination of dynamic DNS and NAT.
The local network is usually LAN (Local Are Network) , or Stub Domain. A Domain Stub is a LAN using an internal IP address .
Most Network Traffic (which is stable, uninterrupted network traffic) in Stub Domain is local, so the internal network never gets exposed to the outside.
A Stub Domain can include both Public IP and Private IP addresses . Any computer using Private IP addresses must use NAT (Network Address Translation) to exchange information with other computers.
In the next section, Network Administrator will introduce you to configure NAT.