Technical Network Address Translation (NAT)
TipsMake.com - Most people who own a modern Internet connection today must use NAT (Network Address Translation) technology. NAT has been an integral part of deploying a wide area IP network because the IPv4 address space has begun to shrink. Basically, NAT allows one (or more) local IP addresses to be mapped to one (or more) external IP addresses. This allows the use of a private IP address range based on RFC 1918 on local networks while using only one or a few public IP addresses.
The article will cover the basic concepts of NAT, types of NAT and how this technology works.
NAT
There are three different types of NAT: dynamic NAT, static NAT, and NAT overload (NAT overloaded).
With static NAT, an internal IP address specified will be mapped to a specified IP address other than the domain, as shown below.
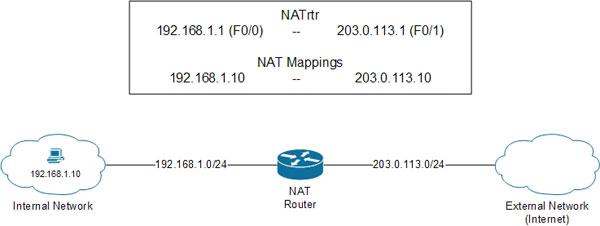
In the image above, an internal network PC needs to communicate to another computer on the external network, in this case the Internet. But the RFC 1918 address is not capable of routing on the public Internet, so it cannot be used as a source or destination address. To handle this problem, NAT can be statically configured to connect the internal address 192.168.1.10 to the external address 203.0.113.10. Thus, for external networks, the incoming traffic will be from address 203.0.113.10 instead of 192.168.1.10. In this situation, NAT will treat the IP address 192.168.1.10 as the local address and the address mapped 203.0.113.10 as the internal address.
With dynamic NAT, the internal IP address is automatically matched to a set of external IP addresses. The mapping process is still between an internal address and an external address but occurs automatically.

In the above figure, the two PCs in the local network need to communicate to the machine on the external network, in this case the Internet. The NAT is dynamically configured to map internal addresses of 192.168.1.25 and 192.168.1.50 to IP addresses in the set of configured NAT addresses. In the figure, the machine has 192.168.1.50 address mapped to address 203.0.113.10 and the device has 192.168.1.25 address mapped to address 203.0.113.11. This means that the device with 192.168.1.50 address will be initialized first.
With NAT overloading (also called PAT port address compilation), mapping one as dynamic NAT and static NAT is not used. Instead of an external address assigned to only one internal IP address, it can now be assigned to all local machines based on the port number. Only when the number of available ports used by the external IP address is exhausted, can a second external IP address be used with the same method.
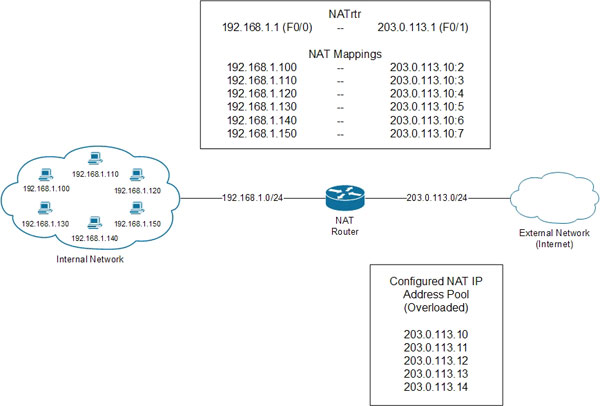
In the image above, there are six different machines accessing the external network. Overload NAT is configured with a collection of addresses in the range 203.0.113.10 to 203.0.113.14. Assuming that traffic passes through the NAT router sequentially, each type of traffic will be mapped to an external IP address (in this case the first IP address in range-203.0.113.10) and the specified port number. .
For each example, the NAT router configured to use the same IP address 192.168.1.1 on the Fast Ethernet interface 0/0 marked as internal NAT interface and 203.0.113.1 on the FastEthernet interface 0/1, is typed. The sign is an external NAT interface.
Conclude
There are many more complex methods for deploying NAT but the purpose of the article is to introduce NAT and how it works in simple examples. Hopefully the article has helped you better understand NAT and how it is used online.