How to delete the user and the machine name in the command prompt on Terminal
For Linux users (or Macs) using Terminal, you will see that the default prompt will have the format [username @ hostname ~] $. For example, on a Dell laptop, bash prompt will display [damien @ damien-dell ~] $, in which 'damien' is the author's username and 'damien-dell' is the server name. Please note that this is only the default setting and you can freely change, as well as show everything you want or even delete the information completely.
The following steps will show you how to do that.
1. In File manager, press Ctrl + H to display hidden files.
2. Open the '.bashrc' file in the text editor.
3. Find the line starting with PS1 =. The complete line must look like the following:
PS1='[u@h W]$ ' Where u represents the user name, h is the host name and W is the location in the file structure.

4. To delete the username and server name from the prompt, simply delete the u @ h section, ie the above line will look like this:
PS1='[W]$ ' 
5. For those who love pure minimalism, you can delete everything and leave only a prompt:
PS1='$ ' 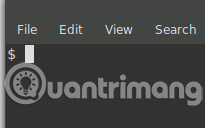
6. When you have finished editing, save the file.
Now restart your terminal and the changes will be reflected immediately. If you cannot restart the terminal because a session is running, enter the source ~ / .bashrc instead.
Very simple, right? Hope you are succesful.
See more:
- How to customize Terminal on Mac
- How to run 2 or more Terminal commands at the same time on Linux
- Ubuntu Bash tutorial on Windows 10
You should read it
- ★ Windows Terminal will soon become the default terminal emulator in Windows 11
- ★ Notable changes in Windows Terminal ver 0.11
- ★ Set up Windows Terminal to always open with Command Prompt on Windows 11
- ★ How to customize Windows Terminal application
- ★ Windows Terminal is about to have a retro version with a 'classic' interface.