How to use Terminal on a Mac
Open Terminal on Mac
Of course, the first step would have to be to open Terminal. There are several options for doing that, but the easiest is to press Command + Space to open Spotlight , then search for "Terminal". The first result is exactly what you are looking for. Double-click to open.

When the Terminal window opens, you can resize it by dragging one of the corners to expand it. You can also change the look of the application by going to Terminal> Preferences or pressing Command + comma ',' . In the Profiles dialog box , you can change the look of the command prompt windows to suit your style or needs.

Once the Terminal window has the desired interface, you can start using it to execute commands on the computer.
Basic Terminal Commands
You can do a lot of cool (and useful) things with Terminal. For example, if you really want to, you can use the Terminal command to get your Mac to talk to you. But before you get started, you must know how to write Terminal commands.
Each Terminal command has 3 parts.
- Command part : These are the actual characters that you will enter into the Terminal window to execute the command. Be very careful when using Terminal commands, as some commands can delete files or cause other damage to the system, causing the computer to stop working.
- Arguments : This indicates which resource the command should work on. For example, should a cp, or copy command, be copied from one window or another?
- An output modification option : This is an indicator of where the results of a particular command should appear.
For example, if you wanted to move a file, you'd use the mv command. The argument for that command will be the location of the file you want to move. And the output will be where you want the file moved. So the command to move a file from your desktop to your Documents file might look like this:
mv ~/Desktop/TerminalTestFile.rtf ~/DocumentsRules for using Terminal commands
Now that you have a basic understanding of how to write and use Terminal commands, there are a few rules to understand.
- When using the terminal, you must always enter a command and then press Enter or Return on your keyboard.
- You can't use the mouse to interact with a Terminal window other than using the three close, expand, and hide buttons in the upper left corner of the window.
- To interrupt a command is running, type Control + C .
- To exit the terminal without using the mouse, type Command + Q .
Commands automatically execute in the last used location on your computer. If you want to specify a different location for the command to execute, you will need to use the cd command and the directory path to specify where you want the command to execute.
If you have never used a terminal before, you may be confused executing a command and nothing happens in the Terminal window. Don't worry, in some cases it is very likely.
For example, when you type cd ~, you will be taken back to your Home Directory. In the Terminal window, the cursor will move to the next line with no indication of what happened. But rest assured, you are now back in your Home Directory.
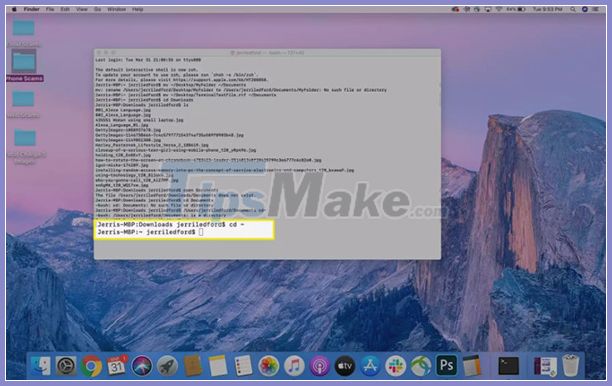
Use the Terminal command on the Mac
With the basics, you can start using Terminal commands to navigate faster and more efficiently while you are using your computer. Here are a few Terminal commands you can try, but there are dozens of Mac Terminal commands that you can use to suit almost any of your needs.
Most of the basic Terminal commands involve navigating files or folders on your computer. For example, you can use the ls command to see a list of all the files in the current directory. So if you're in Documents and type ls, you'll see a list of all the files or folders in Documents.
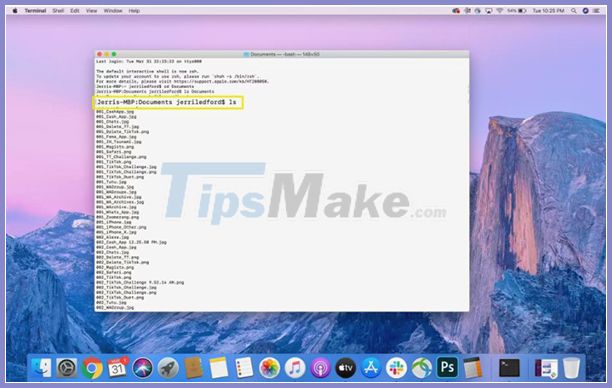
You can modify (or change the output) of the ls command by adding an operator. For example, ls -C sorts the files in the requested list by size.
Here are some basic commands that you can learn:
- open : Open the file you specified using the directory path.
- rm : Delete file
- cp : Copy
- mkdir : Create a large directory
- ditto : Make copies of files in directories.
- caffeinate : Keep your PC from going to Sleep while Terminal is open
- clear : Clear the Terminal screen
- pwd : Returns the path to the home directory
- . : Take you to the root directory
- man
: Takes you to the manual page of that command so you can read about the command, its function, and how to use it - Say : The Mac will say whatever you want
- history : View the history of Terminal commands
- history -c : Clear the Terminal command history