How to save command line output to file on Windows, Mac and Linux
You can do this using output redirection on the command line. Learn how to send command output to a text file on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
Redirect command line output to a file
There are two operators you can use to redirect command output to file: >> and > . It is important that you understand the difference between these two operators to avoid unintended data loss.
The > icon creates a new file or overwrites the old file if it already exists. The >> operator also creates a new file if it does not exist but it will not overwrite the existing file. If the file already exists, it will add the text to the end of the file.
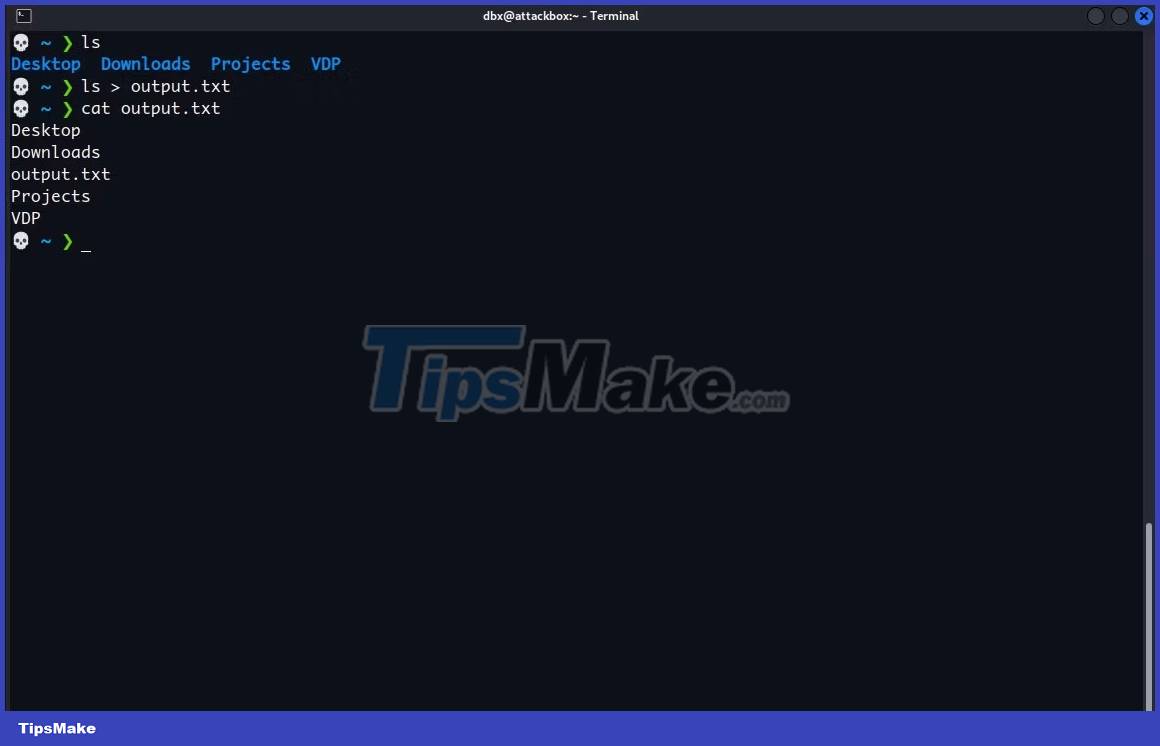
To redirect the output of a command to a file, enter the command, then specify the > or >> operator , and finally provide the path to the file you want to redirect the output to. For example, here's how you can save the output from the ls command, which lists the contents of a directory:
ls > /path/to/fileReplace /path/to/file with the full path to the file you want to use. The command will run silently, storing the output in the file you specify.
To view the contents of a file in the terminal, you can use the cat command. Again, replace /path/to/file with the full path to the file you want to view.
cat /path/to/fileYou should see the output from the command in your new file:
The > operator replaces the content of an existing file. If you want to save the results from multiple commands into a single file, use the >> operator instead. This will add to the file, so you won't lose any previous output you saved.
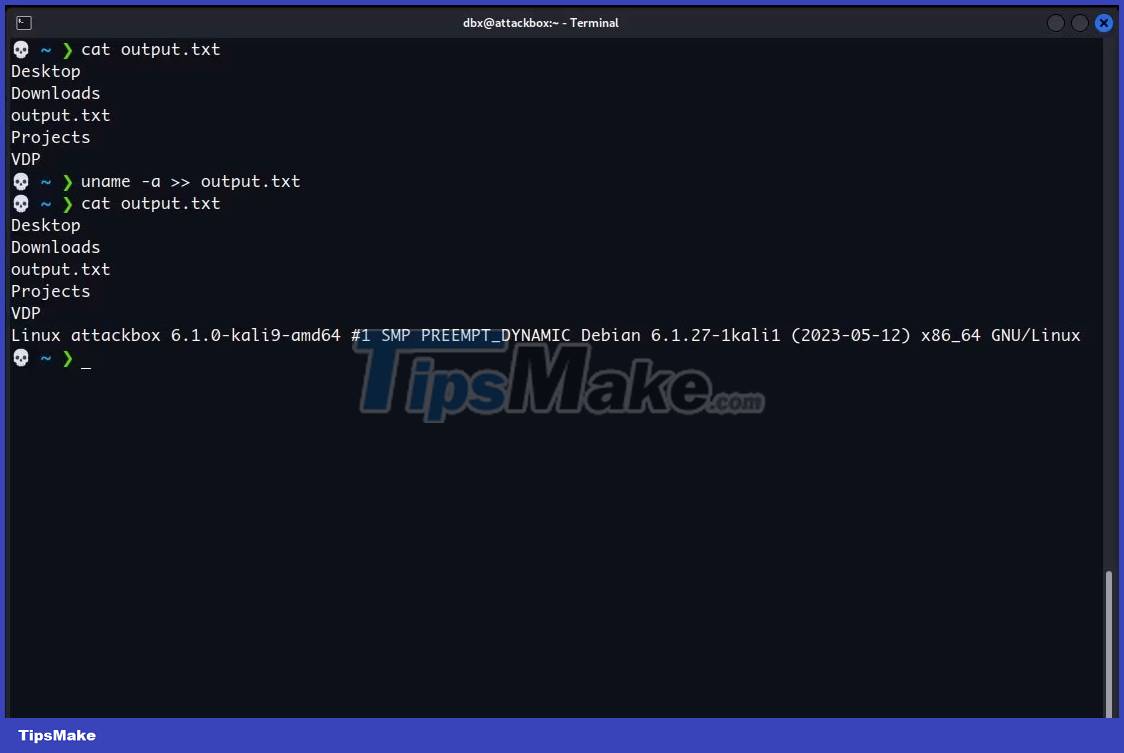
For example, try adding system information to the end of the file you just created. Just run uname -a on Linux/Mac - or the ver command if you're on Windows - and add the >> operator along with the path to the file:
uname -a >> /path/to/fileRepeat this process as many times as you need to continue adding command output to the end of the file.
Export output to screen and redirect it to a file
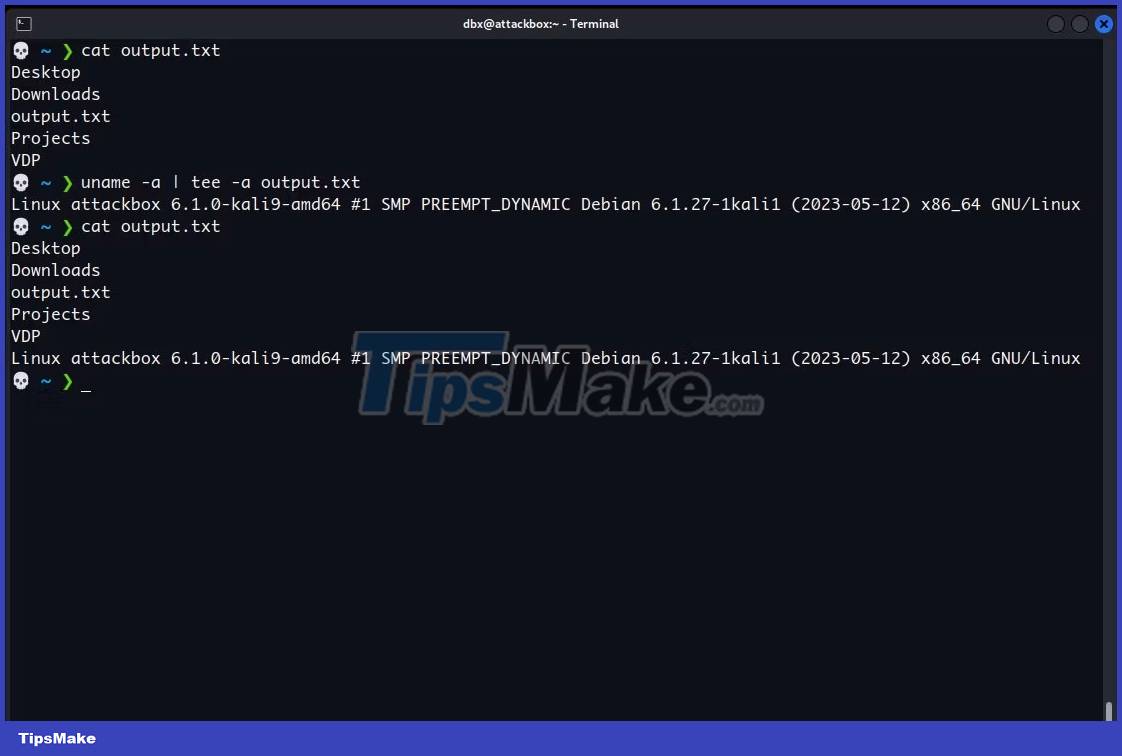
The > and >> operators do not display the output of the command on the screen, they just send it to a file. If you want to send output to a file and view it on the screen, use the tee command.
To use the tee command, send output from another command to that command using the pipe operator, a vertical bar (|). For example, here's how you can send the output of the ls command to tee using a pipe:
ls | tee /path/to/output.txtThe tee command then sends that output to both the screen and the file you specify. This operation will overwrite the file or create a new file if it does not exist, just like the > operator .
To use the tee command to print the result to the screen and append it to the end of the file, add the -a flag before the file path, for example:
uname -a | tee -a /path/to/output.txtYou will see the command output on the screen and you can use cat to verify that tee also added it to the file: