Use Journalctl to read the system log on Linux
For years, system log and kernel log have been processed by a utility called syslogd. Most Linux-based operating systems have switched to systemd, which comes with a different daemon log called journald. To interact with these logs, use the journalctl utility.
How to use Journalctl on Linux
- Authorize users to read the system log
- Check the continuity of the journal
- Select whether to boot entry journal
- Navigate and search through System Journal
- Filter log entries by priority
- Filter log entries according to the path to handle executable files or Systemd unit
Authorize users to read the system log
Only users of 'adm' or 'systemd-journal' can read the systemd logs. Distributions like Ubuntu have allowed users to add to the adm group.
Open a terminal emulator and type the following command:
groups 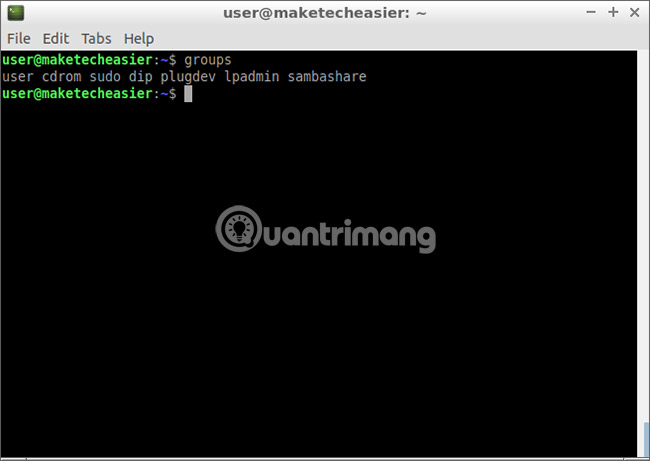
If you see 'adm' or 'systemd-journal' in the output, you can skip the remaining steps in this section. If not, add yourself to the 'adm' group .
sudo adduser $USER adm You will have to restart the login session in order for these changes to take effect (logging out and logging in). If you can't do it for a variety of reasons, use this command to log in to the new group without restarting the graphics session:
newgrp adm Do not close the terminal window. You are now in the adm group, at the current terminal session, but not in the graphics session. If you open a new terminal at this time, you won't be able to log in to the adm group anymore.
Check log continuity
Systemd log records can be recorded continuously or intermittently. On Ubuntu and other distributions, by default, they will continue. On Debian 9, logs are not recorded continuously, meaning they are only stored in memory (not the drive) and disappear when the user shuts down or restarts. Please enter the following command:
journalctl --list-boots 
If there are multiple entries here, then you don't have to do anything else. That means the logs are saved on the drive (continuous). If you only get a single entry, the log is not recorded continuously. Please change it to be recorded continuously.
sudo sed -i '/Storage/ cStorage=persistent' /etc/systemd/journald.conf Choose to view the boot entry log
Normally, you will want to see the log for the current boot time. Sometimes you want to see information about the previous boot, such as after a system problem occurs. But this doesn't happen very often.
To view the log for the current boot time:
journalctl -b 0 
For the previous boot, use '-1' instead of '0', or give two previous booting '-2', etc.
journalctl -b -1 Navigate and search through System Journal
After you open the log with journalctl, you can navigate through the text with the arrow keys and the PAGE UP or PAGE DOWN keys . Other useful keys are:
- > to go to the end of the output.
- < to go to the beginning of the output.
- / to search for a text string. After you press the slash key, enter the desired string, then press Enter. This string is case sensitive, so 'network' will be different from 'Network'. Search starts from the current viewing position downward. To search upwards, use the?
- n find the next match in the current search operation. N finds previous matches.
- q exit journalctl utility.

Filter log entries by priority
Sometimes you just want to search for errors, ignore notes and status messages. Each log entry has a different priority: emergency, alert, critical, error, warning, notice, info (emergency, important notifications, important, errors, warnings, notifications, information). They are listed in order of importance. Emergency status (emergency) is reserved for the worst cases (the system will no longer work). The Info messages are just informational text, reporting the status of the normal operating programs.
To display only the error message from the current boot, enter:
journalctl -b 0 -p err 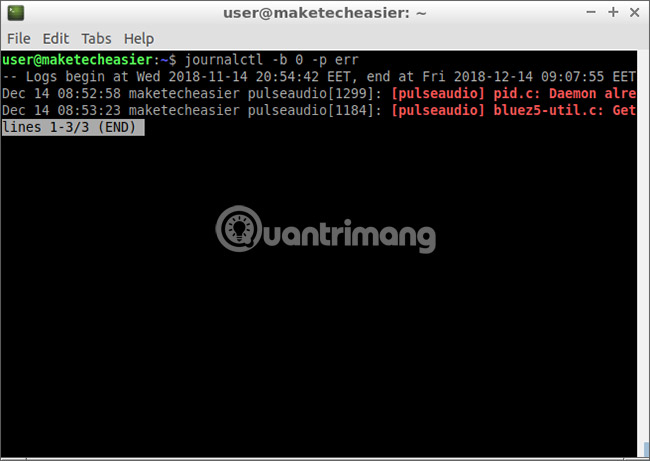
If you want to see errors from all booting times, just delete the parameter '-b':
journalctl -p err These are the codes you can pass to the parameter of '-p':
- alert
- crit
- debug
- emerg
- err
- info
- notice
- cảnh báo
Filter log entries according to the path to handle executable files or Systemd unit
Some processes are started and managed by units called systemd. To see all records related to cron service unit, enter:
journalctl -u cron.service You can view available units with the command:
systemctl list-dependencies 
You can navigate the list with the up and down arrow keys. Press q to exit.
If you want to use the path to the executable file (binary file) of the program, simply pass its full path as an argument.
journalctl /usr/sbin/cron Don't forget, you can also filter by the current boot item to remove unnecessary notifications.
journalctl -b 0 /usr/sbin/cron Journalctl aims to help you easily find what you are looking for. Hope you will feel the information above useful. Good luck!
See more:
- System log in Unix / Linux
- Basic file system in Unix / Linux
- Manage the Event Log with the command line