Discover VDI in Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V
Network Administration - Initially virtualization tools were used to overcome issues such as server crashes, low server utilization, data center traffic, power problems, and reduce IT costs.
Over the past few years, the Virtual Desktop Infrustructure (VDI) is an area of interest, since many new virtualisation tools have been tested and implemented to address the management and provisioning issues for desktops. end user. In addition, VDI is a measure to reduce IT operation costs.
VDI allows an organization to deploy virtual computers on the server in the data center and provide direct connections to users to another virtual computer through multiple workstations distributed from simple terminals to laptop or physical desktop. As a result, virtual computers are executed on data center servers, while user interfaces are displayed on workstations using remote desktop client applications. A VDI is not a separate tool, it also includes a hardware system, virtualization software and management tools to provide a comprehensive tool for deploying, configuring and managing desktops. Virtualization.
Microsoft VDI
Microsoft VDI shares many components with the systems used to deploy the server's virtualization architecture. Basically, the Microsoft VDI tool is developed on a server virtualization and management platform that adds a number of components to help manage virtual desktops. Microsoft, in collaboration with Citrix and many other partners, has provided a set of components that allow users to deploy both Static Virtual Desktop tools and Dynamic Virtual Desktops.
Static Virtual Desktop
A Static Virtual Desktop will directly replace a physical desktop in a stable virtual machine for a specific user. This user will connect directly to the virtual machine using a remote virtual machine connection application. A Static Virtual Desktop can include a guest operating system and some installed applications, or it can take advantage of the Terminal Server, application virtualization capabilities and data transfer applications for quarantine and partitioning. Launch of the application.
Dynamic Virtual Desktop
A Dynamic Virtual Desktop is often provided and combined from a single master image, and it uses Terminal Server, virtual application and data transfer application as well as specific user settings to transfer a virtual virtual desktop. These are unstable to a user. User data storage areas can be stabilized by storing in a virtual hard disk that will be connected when the virtual machine is launched and disconnected when turned off.
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V is a virtualization class in the Microsoft VDI tool. With Hypervisor platform technology, Hyper-V supports separate and concurrent security partitions in which users can run separate virtual machines. Based on compatibility with Windows Server 2008, Hyper-V provides the ability to move virtual machines between Hyper-V servers using integrated switch clustering to minimize downtime. This feature is like Quick Migration. With Quick Migration, virtual machines are transferred to the archived state before being moved and restarted on another Hyper-V Cluster node. This feature is only useful when a Hyper-V server requires regular maintenance or users need to rebalance the Hyper-V virtual machine load. Cluster transition support also provides the ability to restart the virtual machine on a new Hyper-V cluster node in the generated situation, such as a hardware failure. Because Hyper-V can support many devices, including: SAN, NAS, DAS and iSCSI, users can choose the optimal configuration to support large and small VDI deployments. As client connections to virtual machines, Hyper-V will provide access via remote desktop protocol (RDP).
Centralized Desktop in Windows Vista Enterprise
Centralized Desktop in Windows Vista Enterprise (VECD) includes existing license options for deploying Windows virtual computers in a VDI environment. VECD defines license forms for virtual computers that are accessed via regular or thin client computers (a network device capable of independent data processing but must rely on the server for programs and storage). data and administration). Licenses are allocated on a base device. A normal desktop license needs to be periodically verified in addition to Windows Software Assurance, while a thin client license is just a periodic confirmation of Windows Software Assurance. In any case, users can also install countless copies of the Windows Vista Enterprise operating system or previous operating systems, and users can simultaneously access up to 4 operating systems from one device. licensed. These licenses will apply to both Static Virtual Desktop and Dynamic Virtual Desktop structures. Because licensing options are often very complex, we need to verify VECD licensing options based on VDI structure plans.
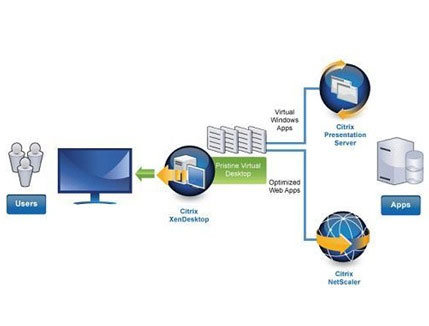
Citrix XenDesktop
If you want to deploy a Dynamic Virtual Desktop tool, Citrix, partner of Microsoft, has provided XenDesktop to manage the deployment process in the enterprise. XenDesktop works with Hyper-V and includes a number of components that act as a continuation mechanism to transfer the necessary virtual desktop to the user. It should be noted that the Desktop Delivery Controller (DDC) is XenDesktop's connectivity relay that identifies users and combines that user's virtual machines. After the user has been identified, XenDesktop can transfer this operating system to a virtualized host environment, bringing this user's profile to the operating system and providing user applications through an application transfer tool. Platform policy compatibility such as Microsoft Application Virtualization or Windows Terminal Services.

Microsoft Application Virtualization 4.5

Terminal Services RemoteApp in Microsoft Windows Server 2008
Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2008
Microsoft System Center Data Protection Manager 2007 SP1

Microsoft VDI in Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V
Over the past few years, the Virtual Desktop Infrustructure (VDI) is an area of interest, since many new virtualisation tools have been tested and implemented to address the management and provisioning issues for desktops. end user. In addition, VDI is a measure to reduce IT operation costs.
VDI allows an organization to deploy virtual computers on the server in the data center and provide direct connections to users to another virtual computer through multiple workstations distributed from simple terminals to laptop or physical desktop. As a result, virtual computers are executed on data center servers, while user interfaces are displayed on workstations using remote desktop client applications. A VDI is not a separate tool, it also includes a hardware system, virtualization software and management tools to provide a comprehensive tool for deploying, configuring and managing desktops. Virtualization.
Microsoft VDI
Microsoft VDI shares many components with the systems used to deploy the server's virtualization architecture. Basically, the Microsoft VDI tool is developed on a server virtualization and management platform that adds a number of components to help manage virtual desktops. Microsoft, in collaboration with Citrix and many other partners, has provided a set of components that allow users to deploy both Static Virtual Desktop tools and Dynamic Virtual Desktops.
Static Virtual Desktop
A Static Virtual Desktop will directly replace a physical desktop in a stable virtual machine for a specific user. This user will connect directly to the virtual machine using a remote virtual machine connection application. A Static Virtual Desktop can include a guest operating system and some installed applications, or it can take advantage of the Terminal Server, application virtualization capabilities and data transfer applications for quarantine and partitioning. Launch of the application.
Dynamic Virtual Desktop
A Dynamic Virtual Desktop is often provided and combined from a single master image, and it uses Terminal Server, virtual application and data transfer application as well as specific user settings to transfer a virtual virtual desktop. These are unstable to a user. User data storage areas can be stabilized by storing in a virtual hard disk that will be connected when the virtual machine is launched and disconnected when turned off.
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V is a virtualization class in the Microsoft VDI tool. With Hypervisor platform technology, Hyper-V supports separate and concurrent security partitions in which users can run separate virtual machines. Based on compatibility with Windows Server 2008, Hyper-V provides the ability to move virtual machines between Hyper-V servers using integrated switch clustering to minimize downtime. This feature is like Quick Migration. With Quick Migration, virtual machines are transferred to the archived state before being moved and restarted on another Hyper-V Cluster node. This feature is only useful when a Hyper-V server requires regular maintenance or users need to rebalance the Hyper-V virtual machine load. Cluster transition support also provides the ability to restart the virtual machine on a new Hyper-V cluster node in the generated situation, such as a hardware failure. Because Hyper-V can support many devices, including: SAN, NAS, DAS and iSCSI, users can choose the optimal configuration to support large and small VDI deployments. As client connections to virtual machines, Hyper-V will provide access via remote desktop protocol (RDP).
Centralized Desktop in Windows Vista Enterprise
Centralized Desktop in Windows Vista Enterprise (VECD) includes existing license options for deploying Windows virtual computers in a VDI environment. VECD defines license forms for virtual computers that are accessed via regular or thin client computers (a network device capable of independent data processing but must rely on the server for programs and storage). data and administration). Licenses are allocated on a base device. A normal desktop license needs to be periodically verified in addition to Windows Software Assurance, while a thin client license is just a periodic confirmation of Windows Software Assurance. In any case, users can also install countless copies of the Windows Vista Enterprise operating system or previous operating systems, and users can simultaneously access up to 4 operating systems from one device. licensed. These licenses will apply to both Static Virtual Desktop and Dynamic Virtual Desktop structures. Because licensing options are often very complex, we need to verify VECD licensing options based on VDI structure plans.
Citrix XenDesktop
If you want to deploy a Dynamic Virtual Desktop tool, Citrix, partner of Microsoft, has provided XenDesktop to manage the deployment process in the enterprise. XenDesktop works with Hyper-V and includes a number of components that act as a continuation mechanism to transfer the necessary virtual desktop to the user. It should be noted that the Desktop Delivery Controller (DDC) is XenDesktop's connectivity relay that identifies users and combines that user's virtual machines. After the user has been identified, XenDesktop can transfer this operating system to a virtualized host environment, bringing this user's profile to the operating system and providing user applications through an application transfer tool. Platform policy compatibility such as Microsoft Application Virtualization or Windows Terminal Services.
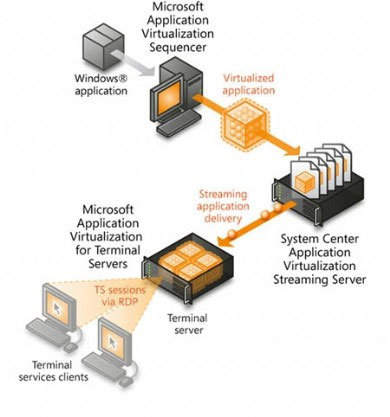
Microsoft Application Virtualization 4.5
Microsoft Application Virtualization 4.5 (App-V) provides a number of server platform components for central storage and application management capabilities, and when needed, delivers applications to virtual machines. With App-V's server components, App-V requires a workstation platform component to create a separate environment on the virtual machine in which an application operates independently, eliminating problems. about system stability caused by conflicting registr or file versions. App-V also has the ability to only send the necessary code to start an application on the virtual machine, providing the necessary parts based on the actual needs of the user. App-V can preserve application references in file platform caching on virtual machines to speed up subsequent application launches, a feature that is quite useful during Static Virtual Desktop deployment. In a pure dynamic environment, user and application references are reused whenever the Dynamic Virtual Desktop is combined and transferred to the end user.
Terminal Services RemoteApp in Microsoft Windows Server 2008
Terminal Services RemoteApp in Microsoft Windows Server 2008 can also be integrated into a VDI tool to provide access to applications for virtual machine users without having to operate or operate them on a virtual machine. In addition, the RemoteApp provides a tool for users who need to operate some applications that are incompatible with the operating system of the virtual machine. With RemoteApp, the application will be installed and operated remotely on Windows Terminal Services. Users can launch a RemoteApp platform application by clicking on the application's icon in the virtual machine or on the Start menu. This icon is linked to an MSI or RDP package that contains instructions and parameters to start an RDP session to the Terminal Server and run this application. Once the connection has been established, the application will operate in a resizable window on the virtual machine along with local applications. Related file extensions to RemoteApp will automatically launch the application, just like when the user launches the application locally.
Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2008
Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2008 (VMM) is a management tool that provides users with a console to manage physical servers using Hyper-V and virtual machines and they operate. VMM can provide virtual machines and use Intelligent Placement to determine the most suitable Hyper-V server to deploy them based on a number of properties, including the Hyper-V server load capability. Intelligent Placement is based on the compatibility between VMM and System Center Operations Manager (SCOM), which is the executable data source taken from Hyper-V servers. VMM also provides an integrated feature to perform the physical-to-virtual migration of a disk image, the ability to manage and store virtual machine libraries, and the ability to support users of the policy platform of virtual machine.
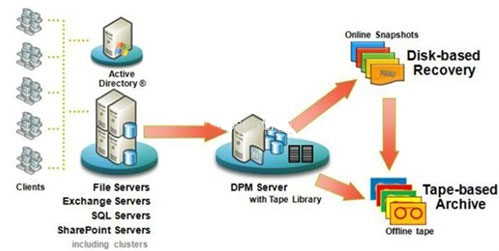
Microsoft System Center Data Protection Manager 2007 SP1
Microsoft System Center Data Protection Manager 2007 SP1 (DPM) is a management tool that allows users to support backup Volume Shadow Copy Services (VSS) of operating virtual machine operating systems as long as they are aware of VSS. For desktop operating systems that are not VSS aware, DPM will allow bakup virtual machines offline by turning off or saving the state of the virtual machines, then bakup the group of files that make up a virtual machine.
Microsoft VDI in Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V
In the upcoming Microsoft VDI in Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V, the Microsoft VDI tool integrates three main features: Live Migration, Cluster Shared Volumes and Remote Desktop Connection Broker. Live Migration supports the process of moving virtual machines between Hyper-V transition node clusters without causing service interruption.
Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) allows multiple cluster nodes to forward simultaneous access to a Unit Number (LUN) Logical on a shared storage system while providing an empty file area suitable for all cluster nodes. With CSV, the process of managing and storing multiple virtual machine or virtual drive (VDI) files is much simpler, and eliminates the drive letter limit that users may encounter in Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V. A VHD is a file format used by Hyper-V to summarize the virtual machine's operating system and application data.
In Windows Server 2008 R2, Terminal Services has been renamed to Remote Desktop Services. Remote Desktop Connection Broker takes care of Session Broker functionality in Windows Server 2008 to help provide connectivity to remote desktops based on normal connection sessions and extend it to provide connectivity for Static and Dynamic Virtual Desktop. Although this feature is only for small and medium virtual machine deployments, it can be used as a platform to develop into a larger-scale enterprise tool.
Conclude
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure represents a combination of hardware, virtualization software and management tools that provide a comprehensive tool to provide, configure and manage virtual machines. Another VDI tool is a Terminal Services tool in that it provides each user with a separate, secure application operating system and stack instead of a separate session performed on a separate operating system. Whether users need to deploy a Static or Dynamic Virtual Desktop structure, the components of Microsoft VDI include Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V, VECD, System Center VMM 2008, System Center DPM 2007 SP1, Windows Server 2008 Terminal Services, Microsoft Application Virtualization 4.5, and Citrix XenDesktop.
Conclude
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure represents a combination of hardware, virtualization software and management tools that provide a comprehensive tool to provide, configure and manage virtual machines. Another VDI tool is a Terminal Services tool in that it provides each user with a separate, secure application operating system and stack instead of a separate session performed on a separate operating system. Whether users need to deploy a Static or Dynamic Virtual Desktop structure, the components of Microsoft VDI include Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V, VECD, System Center VMM 2008, System Center DPM 2007 SP1, Windows Server 2008 Terminal Services, Microsoft Application Virtualization 4.5, and Citrix XenDesktop.
Share by
Samuel Daniel
Update 25 May 2019
You should read it
- ★ How to open a file or an application on a virtual Windows 10 Desktop?
- ★ Already able to test Windows 11 on Azure Virtual Desktop
- ★ Google officially introduces the virtual desktop feature on Chrome OS
- ★ How to use virtual desktop on Windows 11
- ★ Create virtual machines in Hyper-V on Windows Server 2008