Realizing 3G network
In fact, what are the benefits of 3G technology for users? Which technologies do mobile phone service providers (called Telco for short) use, at what speed?
Four operators of mobile phone services (Vinaphone, MobiFone, Viettel and EVN Telecom joint venture - Hanoi Telecom) have officially received 3G licenses (the band 1900MHz-2200MHz follows IMT-2000 standard). After more than a month from the date of licensing (August 13), there are still many questions being asked. What are the benefits of this technology? Which technologies do mobile phone service providers (called Telco for short) use, at what speed?
3G benefits
 3G (third-generation) is a third-generation communication technology that allows to transmit both voice and data (file download, email, instant messaging, images .), giving users services High value-added. Some typical examples are:
3G (third-generation) is a third-generation communication technology that allows to transmit both voice and data (file download, email, instant messaging, images .), giving users services High value-added. Some typical examples are:
Video phones: With 3G, two dialogue partners can see each other through the mobile phone screen.
Information and news: You can access any website to view the hot news and events of the day with your mobile phone, a laptop with 3G network support. With the Internet, you can view weather forecasts, daily news, stock market, share information with friends and relatives . anytime, anywhere.
Email: Leaving the office but forgetting to send an important email, you can quickly complete the task with your mobile phone only. You can also use your phone instead of a modem to connect to a laptop or PDA to draft or get attached documents.
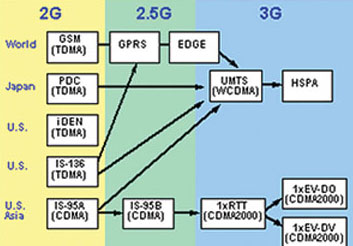
Figure 1 : The evolution of mobile communication technology in countries.
Game : The game was present in mobile phones very early with genres from simple to complex. As a developed technology, games are becoming more interactive, attractive and indispensable for entertainment needs. 3G network allows downloading games anytime, anywhere.
Movies : The speed and quality of 3G networks really contribute to improving the quality of movies when watching on mobile devices. You can watch game / movie trailers, download ringtones, wallpapers .
Sports : With high quality audio and video of 3G network, you can watch outstanding events, favorite matches and of course can see the latest scores.
Music : You can download songs, music videos, even edit your own ringtones.
Above are the common benefits of 3G network technology, but for each network infrastructure will have its own strengths. In addition, for each network technology (GSM, CDMA) and available infrastructure, each Telco will have its own choice of technologies (HSPA, HSPA +, CDMA20001xEV-DO, WCDMA .) for upgrading. 3G. The following are the technologies that are highly appreciated by experts for the current network infrastructure of Telco.
HSPA for GSM networks
Developed by 3GPP, HSPA (High-Speed Packet Access) is a wireless transmission technology for GSM mobile communication devices (Global System for Mobile communications - Mobile Information System). global dynamic). HSPA supports a maximum speed of 14.4Mbps (Release 5 –R5) for downlink (HSDPA- High-Speed Downlink Packet Access) and 5.8Mbps (R6) for uplink (HSUPA - High-Speed Uplink Packet Access). This technology helps increase network capacity and reduce latency for interactive services. On average, users can download data at a rate 20 times faster than the GPRS connection offered by Telco. In the near future, HSPA will be upgraded to R8 at 42Mbps for downlink (downlink) and 12Mbps for uplink (uplink).
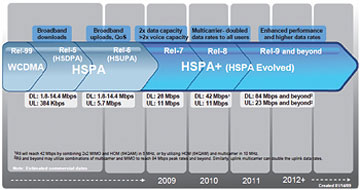
Figure 2 : Roadmap for HSPA and HSPA + technologies
HSDPA is considered 3.5G mobile network technology with the advantage of downlink speed: download speed from 1.8Mbps to 14.4Mbps. Although it is possible to transmit any form of data, the primary goal of HSDPA is video and music data.
HSDPA is developed based on WCDMA technology but uses other data conversion and encryption methods. It creates a data transmission channel within WCDMA called HS-DSCH (High Speed Downlink Shared Channel), also known as high-speed downlink sharing channel. This transmission channel works completely differently than conventional channels and allows for a speedy download. This means that data will be transmitted directly from the source to the phone, and the reverse process (transferring data from the phone to the source) is virtually impossible.
HSUPA (Nokia name set) or EUL - Enhanced Uplink (launched by 3GPP) is a mobile network technology born after HSDPA and is considered as 3.75G technology or 4G. This is the dominant technology at uplink speed: from 1.4Mbps to 5.76Mbps. In contrast to HSDPA, HSUPA uses the E-DCH (Enhanced Dedicated Channel) uplink channel to follow HSDPA-like techniques. The primary goal of HSUPA is to improve the upload speed for mobile devices and reduce latency in game applications, email, chat . HSUPA is the post-HSDPA development technology to satisfy interactive needs. Real-time with applications that require high speed and reliability.
With this outstanding feature, HSPA is becoming a much-developed technology of Telco. According to the announcements of four operators, all three Telco Vinaphone, MobiFone and Viettel choose HSDPA technology of WCDMA platform to transfer to 3G network with the maximum starting speed from 7.2Mbps (MobiFone, Viettel) to 14.4Mbps (Vinaphone).
To be able to use the value-added services of HSPA technology, users must have terminals (cell phones, laptops, laptops, PDAs, routers .) that support the same technology. Currently, there are many devices that have built-in HSPA technology, otherwise, you can still equip an USB modem or an external HSPA card.
3G mobile standards: IMT-2000 of ITU
In the mid-1980s, the IMT-2000 (International Mobile Telecommunications) concept was launched by ITU (International Telecommunications Union) 3G mobile communication system. After more than 10 years of development, in 2000, ITU introduced a unique standard for future mobile networks called IMT-2000. Frequency spectrum from 400MHz to 3GHz is suitable for 3G telecommunications systems.
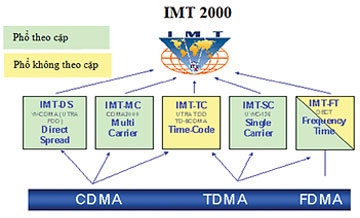
The IMT-2000 provides technical infrastructure for added services and single-standard applications for mobile communication networks. It is expected that this platform provides services from fixed, mobile, voice, data, Internet to multimedia services. More importantly, it provides a global roaming service, allowing users to move to any country using a single phone number. IMT-2000 supports higher transmission speeds: minimum speed of 2Mbps for office users or walkers; 348Kbps when moving on the car. Meanwhile, the 2G telecommunications system only has speeds from 9.6Kbps to 28.8Kbps.
IMT-2000 has the following key features:
1. Flexibility
With a large number of mergers and acquisitions in the mobile phone industry and the ability to bring services to foreign markets, operators do not want to support other interfaces and technologies. This will undoubtedly hinder the development of 3G worldwide. IMT-2000 supports this problem, by providing a highly flexible system, capable of supporting a wide range of advanced services and applications. IMT-2000 incorporates five techniques (IMT-DS, IMT-MC, TMT-TC, IMT-SC, IMT-FT) for wave communication based on three different access technologies (FDMA - Multi-access access by frequency, TDMA - Multi-time split access and CDMA - Multi-access division by code).
Worldwide incremental service and application development on unique standards with 5 techniques and 3 technologies.
2. Economy
The consolidation between 3G industries is an important step in determining the number of users and operators.
3. Compatibility
The services on IMT-2000 are compatible with existing systems. For example, the GSM standard 2G network will continue to exist for a while and compatibility with these systems must be ensured efficiently and seamlessly through transition steps.
4. Modular design
IMT-2000's strategy is to have an easy scalability to develop new users, coverage, and services with the lowest initial investment.
HSPA + technology
HSPA + (HSPA plus) or HSPA Evolution (HSPA improved) is the next generation of HSPA launched by 3GPP after R6 (HSUPA technology). HSPA + is considered 3.5G technology. This means that HSPA + will be backward compatible with HSPA. Therefore, Telco has HSPA infrastructure available, upgrading to HSPA + will be very easy, cost-effective (due to the availability of existing stations), the speed is quite high.

Figure 3 : HSPA + is capable of serving all IP services *: Multicasting is a one-to-many way of transferring data.This is an effective way to transmit text, audio, and video to a group of people online.
HSPA + R7 is currently commercialized earlier this year, and HSPA + R8 will be officially launched next year. The highlight of this technology compared to HSPA is the use of 2x2 MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology with 2 transmitting antennas and 2 receiving antennas, using 16QAM modulation method (HSPA using QPSK) for uplink and 64QAM ( instead of 16QAM as HSPA) for downlink, it is much faster than HSPA. HSPA + R7 has 28Mbps downlink speed (twice as high as HSPA and more than double that of WCDMA), 11Mbps uplink; HSPA + R8 has downlink speeds of up to 42Mbps and 11Mbps uplink. In the future, HSPA + R9 may have uplink speeds of up to 84Mbps and uplink up to 23Mbps or higher.(See pictures 2 and 3)
GPRS and EDGE
GPRS (General Package Radio Service - general packet radio service) is a value-added service of GSM network. GPRS uses packet switching technology to access external data networks (such as LAN, Internet .) using IP (Internet Protocol) protocol with high speed. This is considered generation network technology 2.5 (2.5G) - a step forward from GSM to 3G. The traditional data service of GSM network only has a maximum speed of 9.6Kbps, while GPRS R98 and R99 have a maximum speed of up to 171.2Kbps (theoretically), nearly 20 times higher than Data service of GSM network. According to R97, GPRS has a speed of 40Kbps (downlink) and 14Kbps (uplink). With this relatively high speed, GSM network subscribers can access additional value-added services such as WAP, MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service - multimedia messaging service), web browsing, video watching, music listening . GPRS allows 8 subscribers to use a radio channel and a subscriber can use 8 radio channels simultaneously. This technology uses modulation method for GMSK.
EDGE (Enhanced Data GSM Environment) is a technology that speeds up data transmission in GSM networks. EDGE is not a 3G network but it is only at 2.75G. EDGE, sometimes called EGPRS, is an upgraded GPRS technology that allows data transfer at speeds of up to 384Kbps for fixed or slow-moving users and 144Kbps for high-speed users. . According to R98, EDGE has a downlink rate of 1.3Mbps and uplink of 653Kbps. This technology is the premise for mobile information service providers when switching to 3G using HSPA technology - a GSM transition of 2.5G to 3G. During the transition period when switching to 3G, Telco has applied EDGE technology to enhance the transmission speed for its value-added services.
EDGE is also a value-added service of GSM networks but has higher speeds, lower latency than GPRS. EDGE supports EGPRS (Enhanced General Packet Radio Service) packet switching and ESCD (Enhanced Circuit Switched Data) circuit switching. With a high data transfer rate, EDGE allows providers to deploy advanced mobile services such as downloading videos, music clips, multimedia messages, Internet access, email . EDGE using methods New modulation, coding and transmission mechanism to achieve maximum data transfer rate (3 times the maximum speed of GPRS). While GPRS uses GMSK modulation, EDGE uses an additional 8-PSK modulation. Therefore, to implement EDGE, mobile information service providers also need to prepare appropriate upgrade / replacement solutions.
CDMA20001xEVDO for CDMA network
Originally, 1xEV-DO was an acronym for ' 1x Evolution-Data Only ' (1x Improvements - Data-exclusive). After that, because the negative meaning can be given when the market of the word ' Only ' is introduced, the ' DO ' part in the name 1xEV-DO has been changed to 'Data Optimized'. Therefore, 1xEV-DO stands for '1x Evolution-Data Optimized' (1x Improvements - Data Optimization), to make a better impression of the ability to optimize data transfer when marketed. This is the standard for wireless broadband data transmission for wireless devices, allowing speeds up to 2.4Mbps (downlink) on CDMA networks (Code Division Multiple Access - multiple accesses divided by code). This technology is standardized by the 3GPP2 agreement as part of the CDMA2000 set of standards. The main objective of CDMA20001xEV-DO is to allow users to implement high-speed applications, 2-way interactions (downlink and uplink) in real time such as sending / receiving emails, photos, videos, and music content. great…
WCDMA
WCDMA followers claim that CDMA technology outperforms GSM technology. CDMA is 3G technology. To go to 3G, GSM also has to rely on CDMA (exactly Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) - Multi-access technology divided by broadband code. In spread spectrum engineering, instead of using GSM or FDMA or TDMA methods, WCDMA uses DS-CDMA (Direct Spread CDMA) direct spread method to get higher speed and support more users than 2G network. .
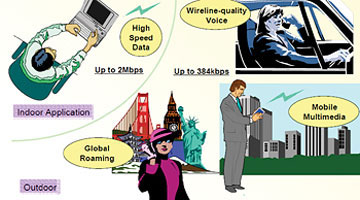
The advantage of this technology is to support many different speed levels: 144Kbps when moving fast, 384Kbps when walking (outdoor) and the highest is 2Mbps when not moving (indoors). With high speed, WCDMA is capable of supporting broadband services such as high-speed Internet access, watching movies, listening to music at the same level as the wired connection. WCDMA is in the 1920MHz -1980MHz range, 2110MHz - 2170MHz . This technology is currently being deployed on GSM networks available in the US and some other regions.
1x technology mainly uses CDM algorithm (Code Division Multiplexing) while EV-DO uses TDM technology (Time Division Multiplexing). When deployed with an existing mobile network, CDMA20001xEV-DO requires a separate 1.25MHz bandwidth. Note that CDMA20001xEV-DO has many versions. In particular, CDMA20001xEV-DO Rev.A (data and voice), which was developed from the first version CDMA20001xEV-DO Rev.0 (data only), has been implemented in Japan and South Korea. Rev.A shows how to set up high-speed packet data transfer in both up and down directions. Rev.B is improved by combining multiple 1.25MHz channels on Rev. A speed up, reduce latency. Download / upload speed of CDMA20001xEV-DO Rev.0 is 2.4576Mbps / 157Kbps, Rev.A is 3.1Mbps / 1.8Mbps and Rev.B is 9.3Mbps / 5.4Mbps, much faster than public GPRS and EDGE technology on GSM network.
The next step of CDMA20001xEV-DO technology is CDMA20001xEV-DV technology (1x Evolution Data and Voce). CDMA20001X EV-DV includes subsequent versions of CDMA20001XEV-DO: Rev.C and Rev.D. Download / upload speeds of CDMA20001xEV-DV Rev.C are 2.4576Mbps / 307Kbps and Rev.D are 3.1Mbps / 1.8Mbps (like Rev.A).
Based on this high-speed platform, top speed 2.4Mbps (Rev.0), suppliers can create a lot of services for customers, such as mobile applications in cars, trucks, taxis. , commercial services, advertising, performances, conferences, replying letters . and Rev.A's radio communication technology help reduce latency and have higher speeds than Rev.0 for translation VoIP service and phone with picture on the same carrier channel.
Currently, S-Fone is providing services based on CDMA20001xEVDO technology (download speed is 2.4Mbps, uploading 380Kbps) this attractive: VOD / MOD (watching movies, television / listening to music directly on electricity mobile phones) and Mobile Internet (mobile Internet - connect to the Internet for computers using S-Fone network phones). To use this service, you must be a S-Fone subscriber along with a mobile phone or USB modem supporting CDMA20001xEVDO technology (refer to B0810_77).
Being licensed for 3G deployment, does not mean that Telco can only use 3G technologies. Based on their own infrastructure, financial capacity and business strategy, operators can choose 3G technology; 3.5G even 3.75G or 4G.
The basic difference between CDMA & GSM *
GSM (Global System for Mobile communications) and CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access - Multi-access code division) are two advanced mobile communication systems widely applied across world. In particular, GSM networks account for more than 74% of the worldwide network. GSM is Europe's digital information system, using TDMA (Multi-temporal division access) method with time slot structure to create flexibility in voice, data and control information. . GSM digitizes and compresses data, then transfers to the transmission channel by two different user data streams, each occupying a separate time slot. The bandwidth initially divided into 200kHz wave channels and then channeled based on the time slot. Users of wave channels take turns sequentially, so there is only one user on a channel and can only be used in very short periods.
Meanwhile, CDMA uses a multiple-access method, divided by code, ie all subscribers of the CDMA network talk on the same broadband band and are distinguished by random code. Each subscriber will be coded with different random codes, then mixed and broadcast on the same frequency band and only recovered at the subscriber device (mobile phone) with random code corresponding.
Technology
GSM
The number of GSM networks is the majority, so it is easy for users to roam (roaming) when moving from one country to another. GSM is superior to CDMA because it uses SIM card, flexibility, security and high security. Users can remove the SIM card on this phone and install it in another device easily. Users have more freedom in selecting terminals.
CDMA
With high frequency reuse frequency reuse and energy control, CDMA allows the management of the number of subscribers to be 5-20 times higher than GSM. Improved call quality: CDMA provides clearer and clearer sound quality than other technology-based mobile systems. High security. Less battery life, longer talk time and smaller device size. Provides a variety of high-speed data transfer and addition services. The coverage radius of the base station is larger than GSM.