What is GRUB bootloader?
This article will show you what a bootloader is and its role in a Linux system. In particular, this guide will focus on Grand Unified Bootloader (GRUB), a powerful and highly versatile bootloader program. But before looking at GRUB in detail, it's important to understand the boot process in Linux.
Linux boot process
The boot process on Linux is a series of activities that take place from the time you press the power button on your PC until the login screen appears.
There are 4 main stages in the operating system boot process and they happen in the following order:
1. BIOS: Short for Basic Input/Output System and is mainly responsible for loading the bootloader. When the computer boots up, it runs a Power On Self Test (POST) to make sure that core hardware like memory and hard drives are working properly. The BIOS then checks the Master Boot Record (MBR) of the main hard drive, which is the part on the hard drive where the bootloader is located.
2. Bootloader: Loads the kernel into RAM with a set of kernel parameters.
3. Kernel: The main function of the kernel is to initialize devices and memory. Then it loads the init process.
4. Init: Responsible for starting and stopping essential services on the system.
Note : BIOS is not a Linux-only process, it is a process that occurs regardless of your operating system.
What is Grand Unified Bootloader?
GRUB is primarily responsible for providing you with an options menu from which you can select the operating system or environment you want to boot into. In addition, GRUB is responsible for loading the Linux kernel.
This is what the GRUB menu option looks like. If you have installed multiple operating systems, they will be listed here.
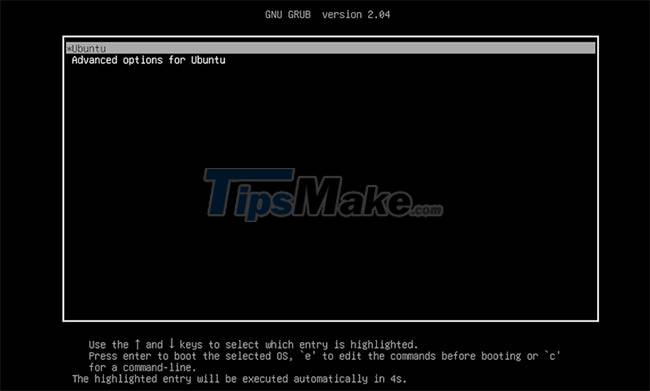
Note : GRUB is not only limited to booting into the Linux operating system, you can also use it to boot into other operating systems like Windows.
There are two major versions of GRUB available at the time of this writing.
1. GRUB Legacy : This is the first version of GRUB and was first developed in 1995.
2. GRUB 2 : This is the latest version of GRUB used by many mainstream Linux distributions such as Manjaro, Ubuntu, Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). GRUB 2 gives you better tools and configuration options than its predecessor.
In addition to GRUB, Linux distributions also use other bootloaders such as Linux Loader (LILO), coreboot, and SYSLINUX.
The role of GRUB
When you select the operating system to boot, GRUB will load the selected kernel. GRUB uses kernel parameters to know where it is and what other important parameters to use.
- initrd: Used to specify the initial RAM drive.
- BOOT_IMAGE: The location of the Linux kernel image.
- root: Specifies the location of the root file system. Used by the kernel to find init, from which to load important services.
- ro: Responsible for mounting the file system in read-only mode.
- quite: Hides some system-specific messages when the PC is booting.
- splash: Used to display the splash screen when your system is booting.
Once in the GRUB options menu, you can edit kernel parameters by pressing the E key on your keyboard.
Configuring GRUB Bootloader
GRUB 2 gives you a lot of flexibility and power when it comes to configuring the bootloader.
The /boot/grub directory contains a file named grub.cfg , which is the main configuration file for GRUB. However, you should not edit the grub.cfg file directly, you should edit the /etc/default/grub file instead.
When you make changes to the /etc/default/grub file , you should make sure to run the command below so that the changes are automatically written to the grub.cfg file .
sudo update-grubYou can learn more about GRUB and some of its configuration options by running the following command:
info -f grub