How to execute Linux commands in the background
Fortunately, you can run Linux commands in the background by following some simple methods. The rest of this article illustrates some of these methods.
1. Add the ampersand after the command
The easiest way to run a Linux command in the background is to add the & symbol after the command. For example, if you start the gedit editor from your Terminal, you cannot use the shell until the editor is closed. However, when you add a symbol & in your command, you can use the shell immediately.
gedit &2. Use bg to send running commands to the background
Sometimes you run a command and realize that it takes even longer to complete. You can easily send these commands to the background by pressing Ctrl + Z and then using the bg command. Ctrl + Z stops the running process and bg brings it to the background.
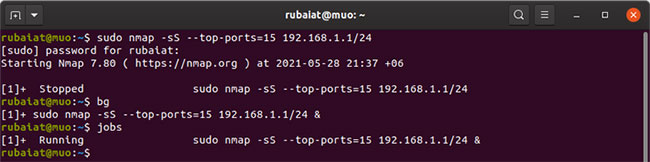
You can see a list of all the jobs running in the background by typing the jobs into Terminal. Use the fg command to return to the running task.
3. Send commands to the background with nohup
The nohup command in Linux allows admins to run Terminal commands that are immune to HUP or Hang Up signals. You can run Linux commands in the background using nohup.
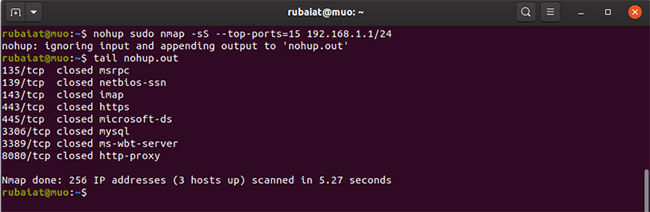
The example below runs an Nmap port scan in the background.
nohup sudo nmap -sS --top-ports=15 192.168.1.1/24A major benefit of nohup is that your commands will run even if you exit the shell. Furthermore, it generates log files that record the execution process. Look for nohup.out in the current directory or inside $HOME.
4. Run commands in the background using system redirection
You can also run commands in the background on Linux using the system redirection feature. For example, if you run the ping command below, the shell will run it in the background and immediately return a Terminal prompt:
ping -c5 8.8.8.8 >output.log 2>&1 &Here, the output of the ping command is redirected to the output.log file . You can replace it with /dev/null if you want to get rid of the results. 2>&1 tells bash to redirect any errors to the same file. Finally & signals bash to run this command in the background.

5. Set a Linux command to run in the background using the disown . command
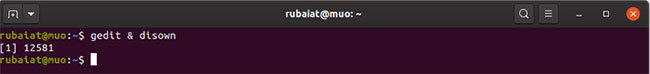
The disown command in Linux makes it easy to run commands in the background. First, you need to dispatch the task in the background using the & operator . Then type disown to detach it from the shell:
gedit & disownA major advantage of disown is that, like nohup, the system will not stop the task when you close the shell or log out.
6. Run Linux commands in the background using Tmux
Tmux is a powerful multiplexer (multiplexer or MUX) that allows to run multiple Terminal sessions in a single window. Learning Tmux is a great option for those who are new to the tool. Tmux makes it easy to run commands in the background on Linux.
tmux new -d 'ping -c 10 8.8.8.8 > output.log' 
When you run the tmux command above, it will do the ping in a separate shell and keep it in the background. You can execute any Linux command in the background using this method.